SQL Exercises: Orders higher than any amount for a London customer
25. Find Orders with Amount Less Than the Max Order from London
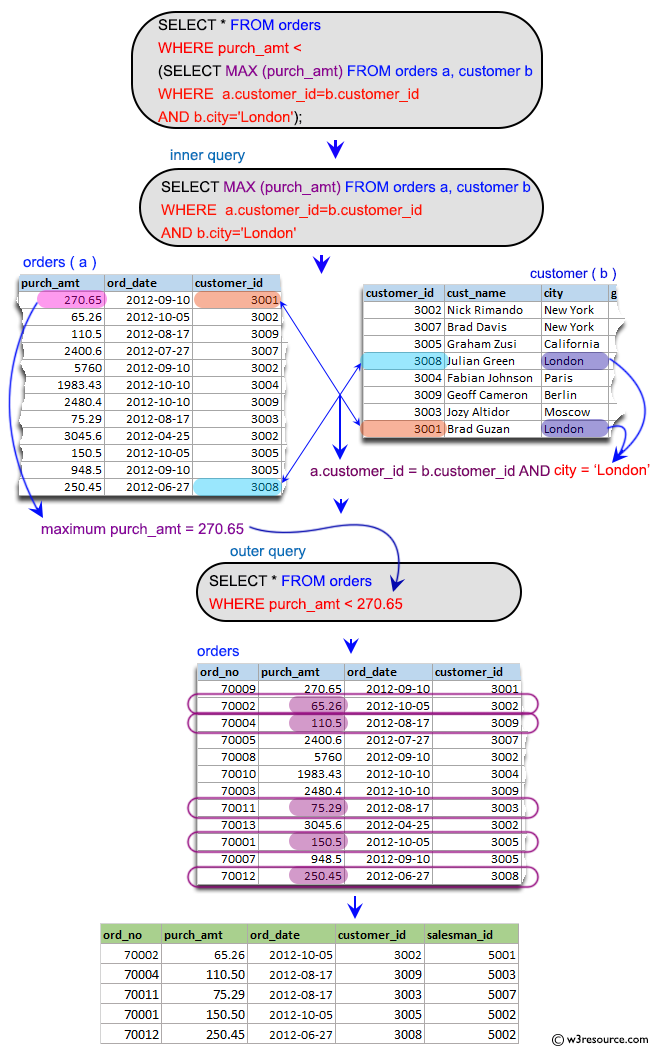
From the following tables write a SQL query to find those orders where every order amount is less than the maximum order amount of a customer who lives in London City. Return ord_no, purch_amt, ord_date, customer_id and salesman_id.
Sample table: Ordersord_no purch_amt ord_date customer_id salesman_id ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------- ----------- 70001 150.5 2012-10-05 3005 5002 70009 270.65 2012-09-10 3001 5005 70002 65.26 2012-10-05 3002 5001 70004 110.5 2012-08-17 3009 5003 70007 948.5 2012-09-10 3005 5002 70005 2400.6 2012-07-27 3007 5001 70008 5760 2012-09-10 3002 5001 70010 1983.43 2012-10-10 3004 5006 70003 2480.4 2012-10-10 3009 5003 70012 250.45 2012-06-27 3008 5002 70011 75.29 2012-08-17 3003 5007 70013 3045.6 2012-04-25 3002 5001Sample table : Customer
customer_id cust_name city grade salesman_id ----------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ----------- 3002 Nick Rimando New York 100 5001 3005 Graham Zusi California 200 5002 3001 Brad Guzan London 100 5005 3004 Fabian Johns Paris 300 5006 3007 Brad Davis New York 200 5001 3009 Geoff Camero Berlin 100 5003 3008 Julian Green London 300 5002 3003 Jozy Altidor Moncow 200 5007
Sample Solution:
-- Selecting all columns from the 'orders' table
SELECT *
-- Specifying the table to retrieve data from ('orders')
FROM orders
-- Filtering the results based on the condition that 'purch_amt' is less than the maximum 'purch_amt' value returned by a correlated subquery
WHERE purch_amt <
-- Correlated Subquery: Selecting the maximum 'purch_amt' value from the 'orders' table (aliased as 'a') where 'customer_id' matches the outer query's 'customer_id' and 'city' is 'London' in the 'customer' table (aliased as 'b')
(SELECT MAX(purch_amt)
FROM orders a, customer b
WHERE a.customer_id = b.customer_id
AND b.city = 'London');
Output of the Query:
ord_no purch_amt ord_date customer_id salesman_id 70002 65.26 2012-10-05 3002 5001 70004 110.50 2012-08-17 3009 5003 70011 75.29 2012-08-17 3003 5007 70001 150.50 2012-10-05 3005 5002 70012 250.45 2012-06-27 3008 5002
Explanation:
The above SQL query is selecting all columns (*) from the 'orders' table where the "purch_amt" value of the row is less than the maximum "purch_amt" value returned by the subquery.
The subquery is joining the 'orders' table (alias as 'a') with the 'customer' table (alias as 'b') on the "customer_id" column and then using the MAX function to select the highest "purch_amt" value from the 'orders' table for the rows where the "city" value of the 'customer' table is 'London'. The outer query will only return the rows from the "orders" table whose purch_amt is less than the maximum purch_amt of orders placed by the customer from London.
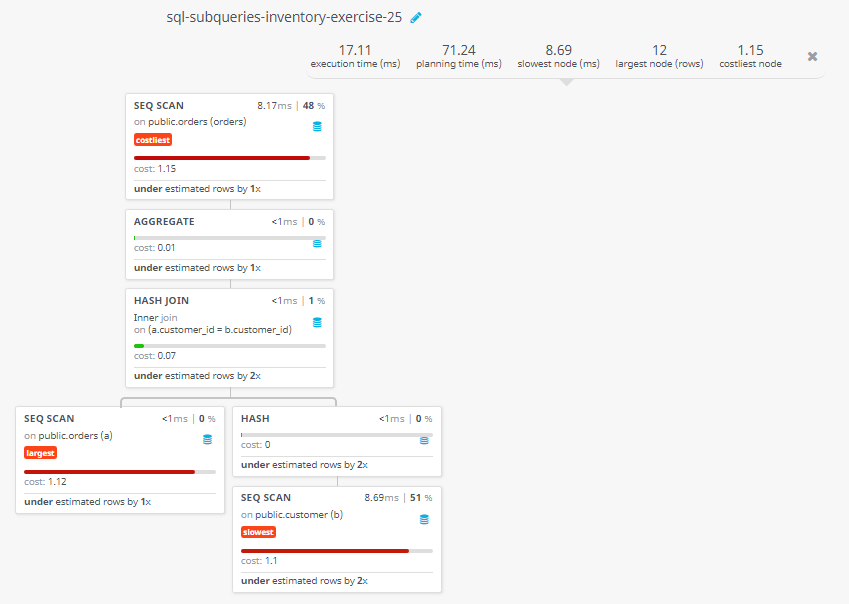
Visual Explanation:
Go to:
PREV : Find Orders with Amount Less Than Any Order from London.
NEXT : Find Customers with Higher Grades Than Those in New York.
Practice Online
Sample Database: inventory
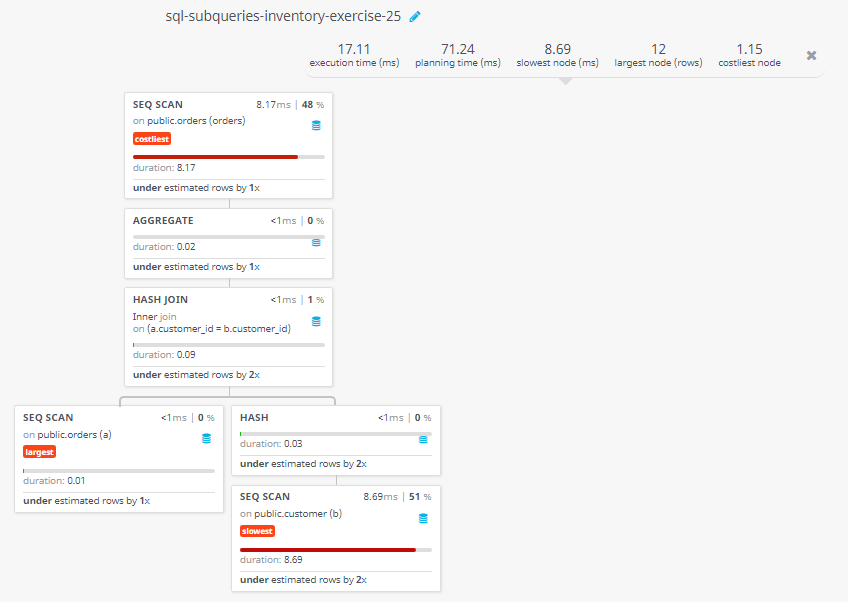
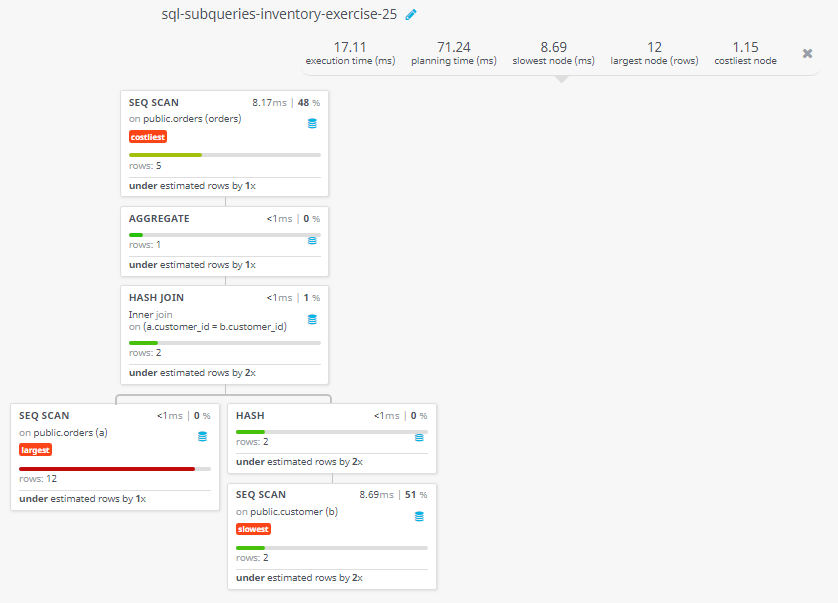
Query Visualization:
Duration:
Rows:
Cost:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.