SQL Exercise: Jobs done by two or more for more than 300 days
24. From the following table, write a SQL query to find each job ids where two or more employees worked for more than 300 days. Return job id.
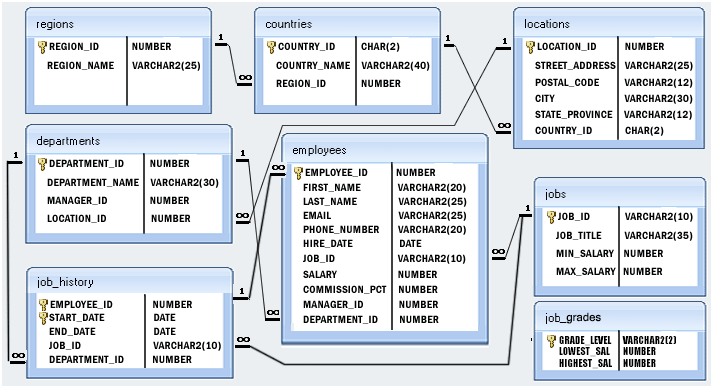
Sample table: job_history+-------------+------------+------------+------------+---------------+ | EMPLOYEE_ID | START_DATE | END_DATE | JOB_ID | DEPARTMENT_ID | +-------------+------------+------------+------------+---------------+ | 102 | 2001-01-13 | 2006-07-24 | IT_PROG | 60 | | 101 | 1997-09-21 | 2001-10-27 | AC_ACCOUNT | 110 | | 101 | 2001-10-28 | 2005-03-15 | AC_MGR | 110 | | 201 | 2004-02-17 | 2007-12-19 | MK_REP | 20 | | 114 | 2006-03-24 | 2007-12-31 | ST_CLERK | 50 | | 122 | 2007-01-01 | 2007-12-31 | ST_CLERK | 50 | | 200 | 1995-09-17 | 2001-06-17 | AD_ASST | 90 | | 176 | 2006-03-24 | 2006-12-31 | SA_REP | 80 | | 176 | 2007-01-01 | 2007-12-31 | SA_MAN | 80 | | 200 | 2002-07-01 | 2006-12-31 | AC_ACCOUNT | 90 | +-------------+------------+------------+------------+---------------+
Sample Solution:
-- Selecting 'job_id' from the 'job_history' table
SELECT job_id
-- Specifying the table to retrieve data from ('job_history')
FROM job_history
-- Filtering the results based on the condition that the difference between 'end_date' and 'start_date' is greater than 300
WHERE end_date - start_date > 300
-- Grouping the filtered results by 'job_id'
GROUP BY job_id
-- Filtering the grouped results based on the condition that the count of records for each 'job_id' is greater than or equal to 2
HAVING COUNT(*) >= 2;
Sample Output:
job_id ------------ AC_ACCOUNT ST_CLERK (2 rows)
Code Explanation:
The said query in SQL that retrieves job_id values from the 'job_history' table where the duration of a job (calculated as end_date - start_date) is greater than 300 days. The query then groups the results by job_id and returns only those groups that have at least two records (HAVING COUNT(*) >= 2).
The final result of this calculation will result in a list of the job_ids that have been held by at least two employees for more than 300 days.
Relational Algebra Expression:
Relational Algebra Tree:
Go to:
PREV : Difference between highest and lowest salary for a job.
NEXT : Country ID and number of cities in country has.
Practice Online
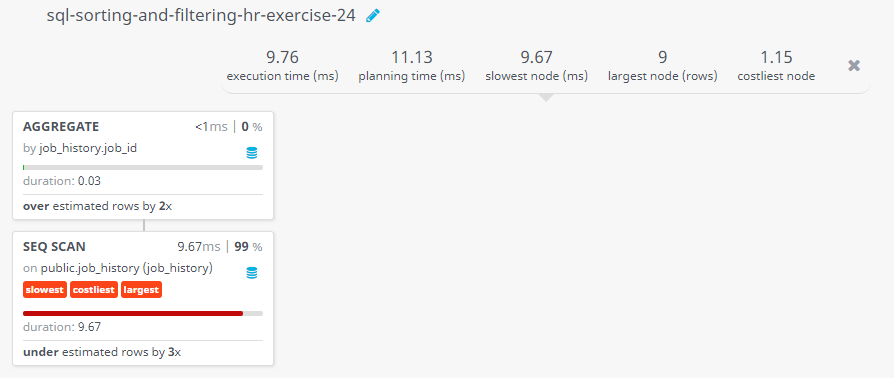
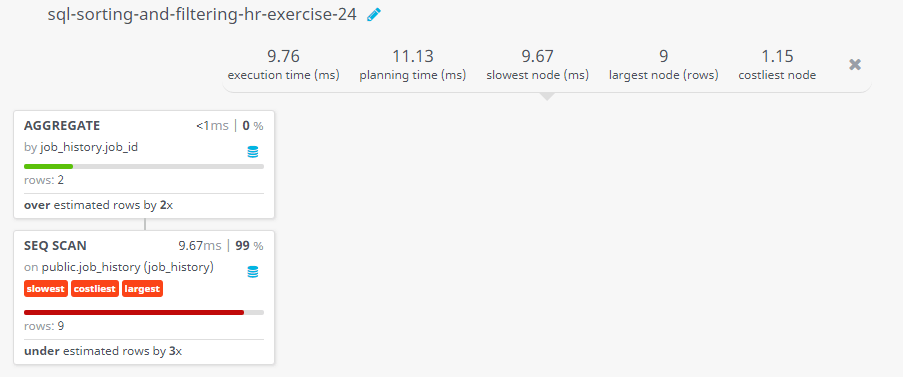
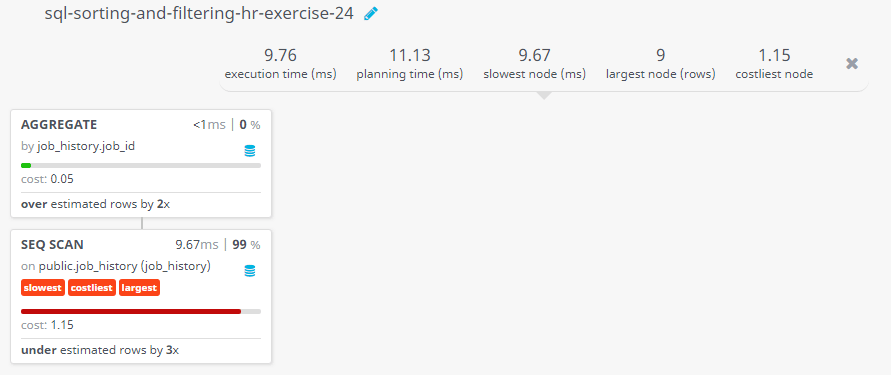
Query Visualization:
Duration:
Rows:
Cost:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.