SQL Exercise: Difference between highest and lowest salary for a job
23. From the following table, write a SQL query to count the number of employees, the sum of all salary, and difference between the highest salary and lowest salaries by each job id. Return job_id, count, sum, salary_difference.
Sample table: employees+-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | EMPLOYEE_ID | FIRST_NAME | LAST_NAME | EMAIL | PHONE_NUMBER | HIRE_DATE | JOB_ID | SALARY | COMMISSION_PCT | MANAGER_ID | DEPARTMENT_ID | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | 100 | Steven | King | SKING | 515.123.4567 | 2003-06-17 | AD_PRES | 24000.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 90 | | 101 | Neena | Kochhar | NKOCHHAR | 515.123.4568 | 2005-09-21 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 102 | Lex | De Haan | LDEHAAN | 515.123.4569 | 2001-01-13 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 103 | Alexander | Hunold | AHUNOLD | 590.423.4567 | 2006-01-03 | IT_PROG | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 102 | 60 | | 104 | Bruce | Ernst | BERNST | 590.423.4568 | 2007-05-21 | IT_PROG | 6000.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 105 | David | Austin | DAUSTIN | 590.423.4569 | 2005-06-25 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 106 | Valli | Pataballa | VPATABAL | 590.423.4560 | 2006-02-05 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 107 | Diana | Lorentz | DLORENTZ | 590.423.5567 | 2007-02-07 | IT_PROG | 4200.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 108 | Nancy | Greenberg | NGREENBE | 515.124.4569 | 2002-08-17 | FI_MGR | 12008.00 | 0.00 | 101 | 100 | | 109 | Daniel | Faviet | DFAVIET | 515.124.4169 | 2002-08-16 | FI_ACCOUNT | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 108 | 100 | ...... | 206 | William | Gietz | WGIETZ | 515.123.8181 | 2002-06-07 | AC_ACCOUNT | 8300.00 | 0.00 | 205 | 110 | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+
Sample Solution:
-- Selecting 'job_id', count of records, sum of 'salary', and the salary difference between maximum and minimum values
SELECT job_id, COUNT(*), SUM(salary), MAX(salary) - MIN(salary) AS salary_difference
-- Specifying the table to retrieve data from ('employees')
FROM employees
-- Grouping the results by 'job_id'
GROUP BY job_id;
Sample Output:
job_id | count | sum | salary_difference ------------+-------+-----------+------------------- AC_ACCOUNT | 1 | 8300.00 | 0.00 ST_MAN | 5 | 36400.00 | 2400.00 IT_PROG | 5 | 28800.00 | 4800.00 SA_MAN | 5 | 61000.00 | 3500.00 AD_PRES | 1 | 24000.00 | 0.00 AC_MGR | 1 | 12000.00 | 0.00 FI_MGR | 1 | 12000.00 | 0.00 AD_ASST | 1 | 4400.00 | 0.00 MK_MAN | 1 | 13000.00 | 0.00 PU_CLERK | 5 | 13900.00 | 600.00 HR_REP | 1 | 6500.00 | 0.00 PR_REP | 1 | 10000.00 | 0.00 FI_ACCOUNT | 5 | 39600.00 | 2100.00 SH_CLERK | 20 | 64300.00 | 1700.00 AD_VP | 2 | 34000.00 | 0.00 SA_REP | 30 | 250500.00 | 5400.00 ST_CLERK | 20 | 55700.00 | 1500.00 MK_REP | 1 | 6000.00 | 0.00 PU_MAN | 1 | 11000.00 | 0.00 (19 rows)
Code Explanation:
The said query in SQL that aggregates data from the 'employees' table, grouping by the "job_id" column. It returns the values mentioned below for each group of employees with the same job_id:
COUNT(*): the number of employees in the group
SUM(salary): the total salary of all employees in the group
salary_difference: the difference between the highest and lowest salary in the group, calculated as MAX(salary) - MIN(salary).
Relational Algebra Expression:
Relational Algebra Tree:
Go to:
PREV : Find employees who did two or more jobs in the past.
NEXT : Jobs done by two or more for more than 300 days.
Practice Online
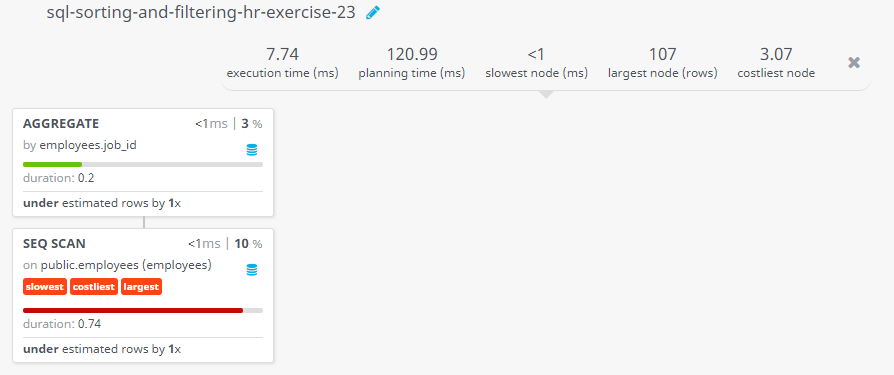
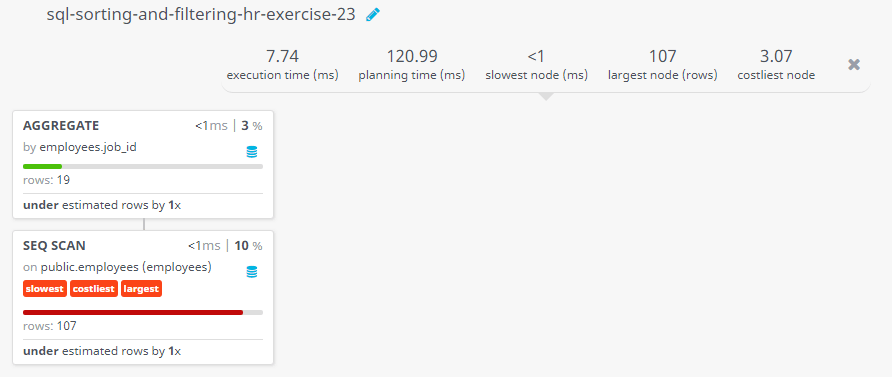
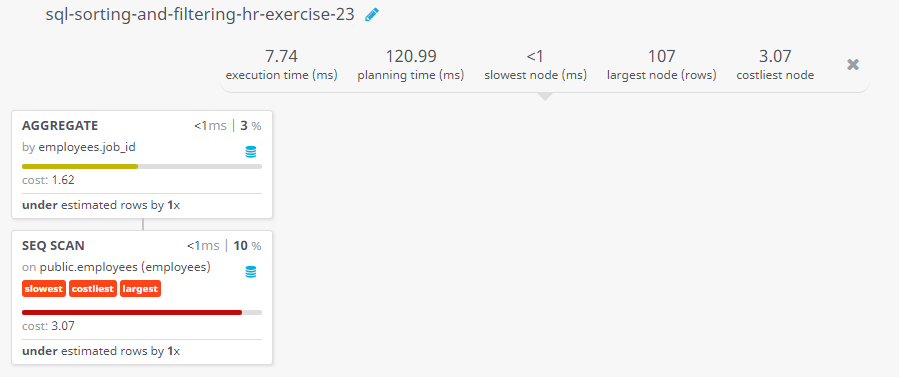
Query Visualization:
Duration:
Rows:
Cost:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.