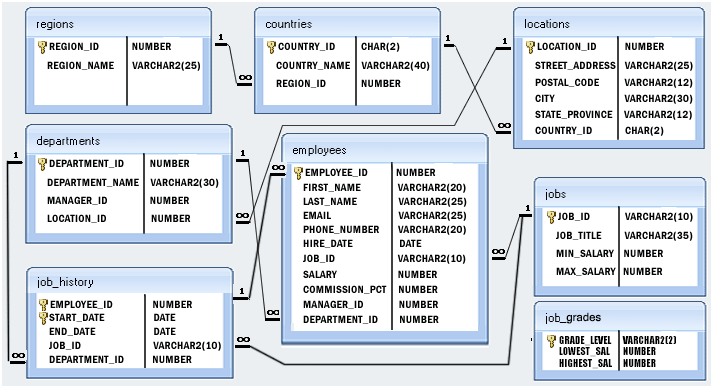
SQL Exercise: Find employees who did two or more jobs in the past
22. From the following table, write a SQL query to find those employees who worked more than two jobs in the past. Return employee id.
Sample table : job_history+-------------+------------+------------+------------+---------------+ | EMPLOYEE_ID | START_DATE | END_DATE | JOB_ID | DEPARTMENT_ID | +-------------+------------+------------+------------+---------------+ | 102 | 2001-01-13 | 2006-07-24 | IT_PROG | 60 | | 101 | 1997-09-21 | 2001-10-27 | AC_ACCOUNT | 110 | | 101 | 2001-10-28 | 2005-03-15 | AC_MGR | 110 | | 201 | 2004-02-17 | 2007-12-19 | MK_REP | 20 | | 114 | 2006-03-24 | 2007-12-31 | ST_CLERK | 50 | | 122 | 2007-01-01 | 2007-12-31 | ST_CLERK | 50 | | 200 | 1995-09-17 | 2001-06-17 | AD_ASST | 90 | | 176 | 2006-03-24 | 2006-12-31 | SA_REP | 80 | | 176 | 2007-01-01 | 2007-12-31 | SA_MAN | 80 | | 200 | 2002-07-01 | 2006-12-31 | AC_ACCOUNT | 90 | +-------------+------------+------------+------------+---------------+
Sample Solution:
-- Selecting 'employee_id' from the 'job_history' table
SELECT employee_id
-- Specifying the table to retrieve data from ('job_history')
FROM job_history
-- Grouping the results by 'employee_id'
GROUP BY employee_id
-- Filtering the grouped results based on the condition that the count of records for each employee is greater than or equal to 2
HAVING COUNT(*) >= 2;
Sample Output:
employee_id
-------------
101
176
200
(3 rows)
Code Explanation:
The said query in SQL that is selecting the "employee_id" from the 'job_history' table, grouping the results by the "employee_id" column, and only returning the groups that have a count of 2 or more records. In other words, it returns the "employee_id" values of employees who have changed jobs at least twice based on the records in the "job_history" table.
Relational Algebra Expression:
Relational Algebra Tree:
Go to:
PREV : Find employees who is working given departments.
NEXT : Difference between highest and lowest salary for a job.
Practice Online
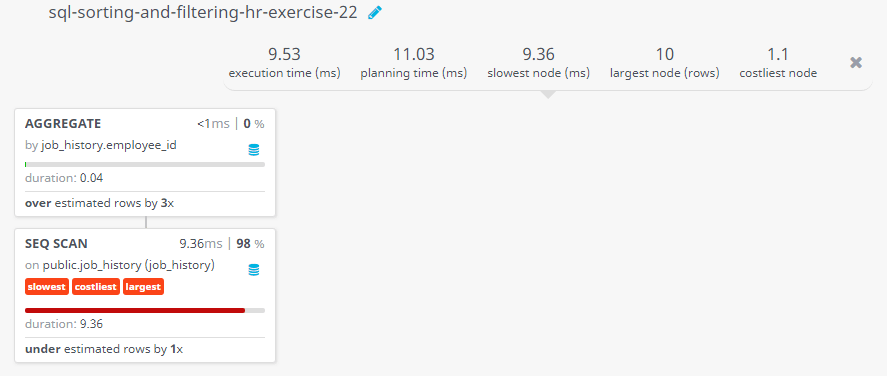
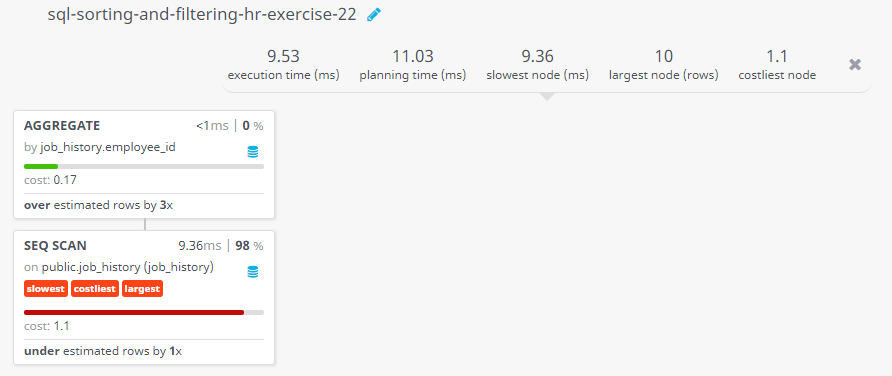
Query Visualization:
Duration:
Rows:
Cost:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.