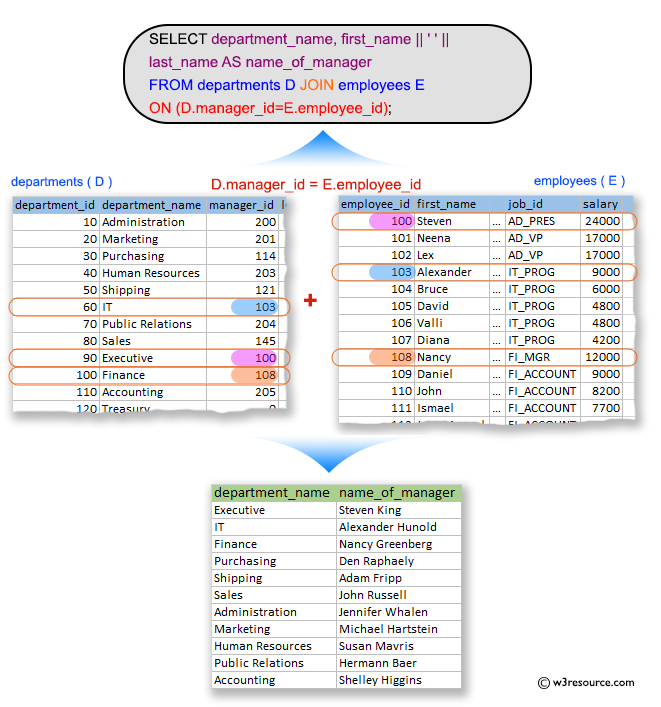
SQL Exercise: Department name and the full name of the manager
18. From the following tables, write a SQL query to find the department name and the full name (first and last name) of the manager.
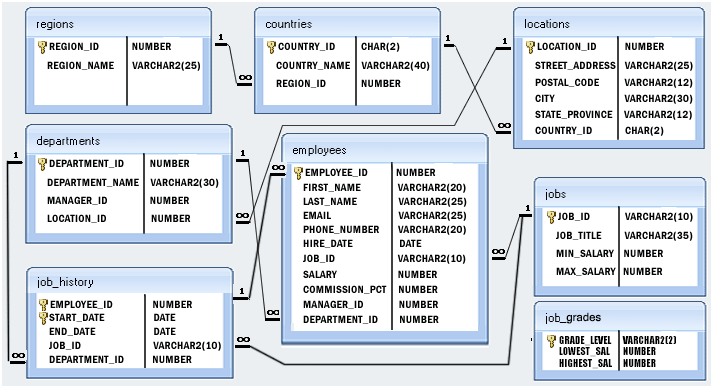
Sample table: departments
+---------------+----------------------+------------+-------------+ | DEPARTMENT_ID | DEPARTMENT_NAME | MANAGER_ID | LOCATION_ID | +---------------+----------------------+------------+-------------+ | 10 | Administration | 200 | 1700 | | 20 | Marketing | 201 | 1800 | | 30 | Purchasing | 114 | 1700 | | 40 | Human Resources | 203 | 2400 | | 50 | Shipping | 121 | 1500 | | 60 | IT | 103 | 1400 | | 70 | Public Relations | 204 | 2700 | | 80 | Sales | 145 | 2500 | | 90 | Executive | 100 | 1700 | | 100 | Finance | 108 | 1700 | ...... | 270 | Payroll | 0 | 1700 | +---------------+----------------------+------------+-------------+
Sample table: employees
+-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | EMPLOYEE_ID | FIRST_NAME | LAST_NAME | EMAIL | PHONE_NUMBER | HIRE_DATE | JOB_ID | SALARY | COMMISSION_PCT | MANAGER_ID | DEPARTMENT_ID | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | 100 | Steven | King | SKING | 515.123.4567 | 2003-06-17 | AD_PRES | 24000.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 90 | | 101 | Neena | Kochhar | NKOCHHAR | 515.123.4568 | 2005-09-21 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 102 | Lex | De Haan | LDEHAAN | 515.123.4569 | 2001-01-13 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 103 | Alexander | Hunold | AHUNOLD | 590.423.4567 | 2006-01-03 | IT_PROG | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 102 | 60 | | 104 | Bruce | Ernst | BERNST | 590.423.4568 | 2007-05-21 | IT_PROG | 6000.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 105 | David | Austin | DAUSTIN | 590.423.4569 | 2005-06-25 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 106 | Valli | Pataballa | VPATABAL | 590.423.4560 | 2006-02-05 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 107 | Diana | Lorentz | DLORENTZ | 590.423.5567 | 2007-02-07 | IT_PROG | 4200.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 108 | Nancy | Greenberg | NGREENBE | 515.124.4569 | 2002-08-17 | FI_MGR | 12008.00 | 0.00 | 101 | 100 | | 109 | Daniel | Faviet | DFAVIET | 515.124.4169 | 2002-08-16 | FI_ACCOUNT | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 108 | 100 | ...... | 206 | William | Gietz | WGIETZ | 515.123.8181 | 2002-06-07 | AC_ACCOUNT | 8300.00 | 0.00 | 205 | 110 | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+
Sample Solution:
-- Selecting specific columns (department_name, first_name || ' ' || last_name AS name_of_manager) from the 'departments' table, aliased as 'D', and the 'employees' table, aliased as 'E'
SELECT department_name, first_name || ' ' || last_name AS name_of_manager
-- Performing an INNER JOIN between the 'departments' table (aliased as 'D') and the 'employees' table (aliased as 'E') based on the condition that 'D.manager_id' is equal to 'E.employee_id'
FROM departments D
JOIN employees E
ON (D.manager_id = E.employee_id);
Sample Output:
department_name name_of_manager Executive Steven King IT Alexander Hunold Finance Nancy Greenberg Purchasing Den Raphaely Shipping Adam Fripp Sales John Russell Administration Jennifer Whalen Marketing Michael Hartstein Human Resources Susan Mavris Public Relations Hermann Baer Accounting Shelley Higgins
Code Explanation:
The above query in SQL that selects the department name and the name of the manager of each department from the 'departments' table and 'employees' table, respectively, where the manager_id in the 'departments' table matches the employee_id in the 'employees' table. The "||" operator is used to concatenate the first name, a space, and the last name of the manager.
The JOIN clause joins the departments table (aliased as D) and the employees table (aliased as E) on the condition that the manager_id in the departments table matches the employee_id in the employees table. This ensures that we only get the name of the manager for each department.
Visual Presentation:
Alternative Solutions:
Using INNER JOIN with Aliases:
SELECT d.department_name, CONCAT(e.first_name, ' ', e.last_name) AS name_of_manager
FROM departments d
JOIN employees e ON d.manager_id = e.employee_id;
Explanation:
This query uses INNER JOINs with aliases (d for 'departments', e for 'employees'). It combines the two tables based on matching keys ("manager_id" and "employee_id") and selects the department name and the name of the manager.
Using INNER JOIN with Explicit Column Names:
SELECT departments.department_name, CONCAT(employees.first_name, ' ', employees.last_name) AS name_of_manager
FROM departments
JOIN employees ON departments.manager_id = employees.employee_id;
Explanation:
This query uses INNER JOINs but explicitly specifies column names. It performs INNER JOINs based on matching keys and selects the department name and the name of the manager.
Go to:
PREV : Display country, city, and the departments.
NEXT : Display the job title and average salary of employees.
Practice Online
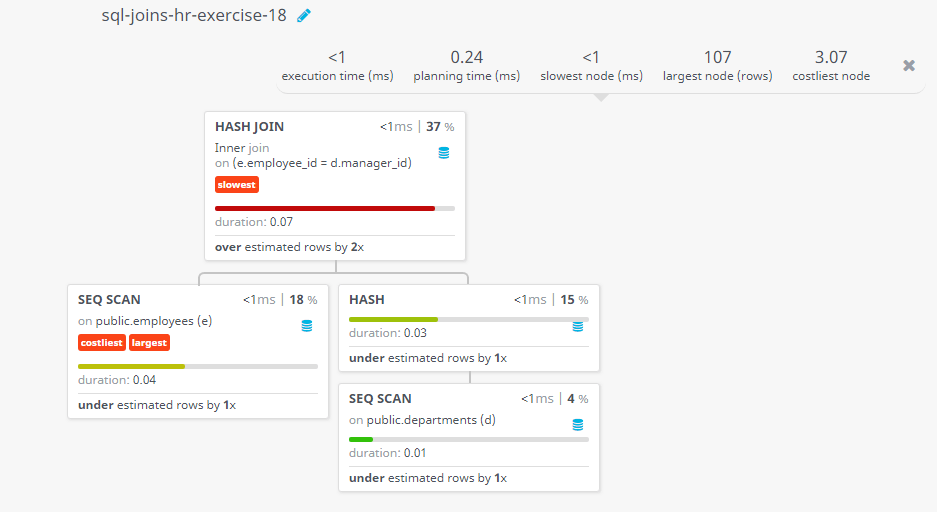
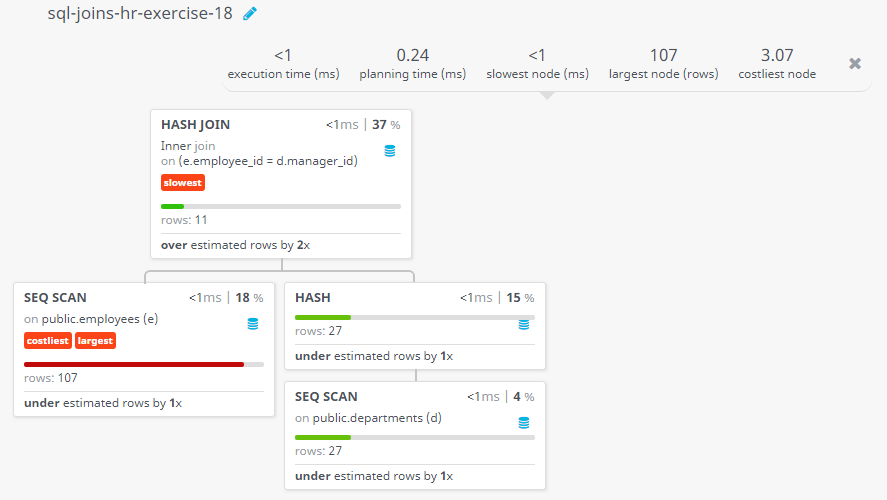
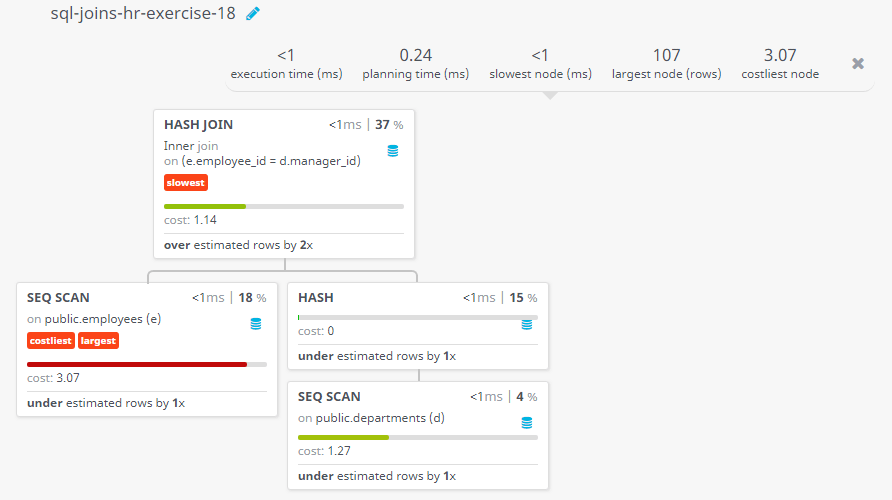
Query Visualization:
Duration:
Rows:
Cost:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.