Python GUI Program: Creating a tabbed interface with Tkinter
Write a Python GUI program to create a Notebook (tabbed interface) with three tabs, each containing different content using tkinter module.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
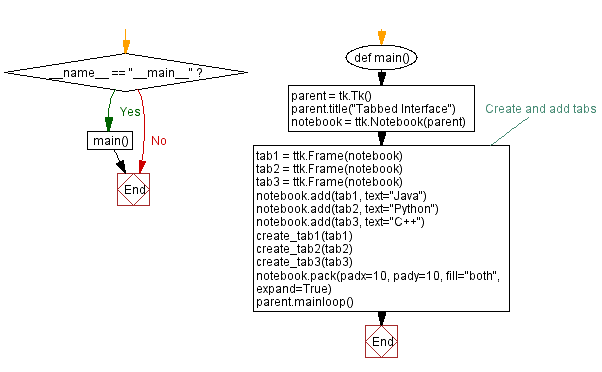
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
def create_tab1(tab):
label = ttk.Label(tab, text="Java Exercises")
label.pack(padx=20, pady=20)
def create_tab2(tab):
label = ttk.Label(tab, text="Python Exercises")
label.pack(padx=20, pady=20)
def create_tab3(tab):
label = ttk.Label(tab, text="C++ Exercises")
label.pack(padx=20, pady=20)
def main():
parent = tk.Tk()
parent.title("Tabbed Interface")
notebook = ttk.Notebook(parent)
# Create and add tabs
tab1 = ttk.Frame(notebook)
tab2 = ttk.Frame(notebook)
tab3 = ttk.Frame(notebook)
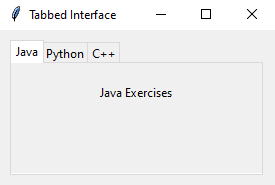
notebook.add(tab1, text="Java")
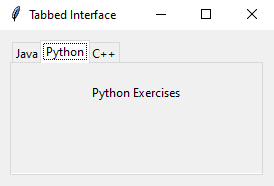
notebook.add(tab2, text="Python")
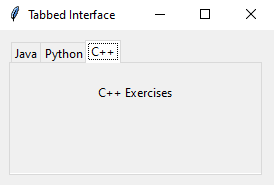
notebook.add(tab3, text="C++")
create_tab1(tab1)
create_tab2(tab2)
create_tab3(tab3)
notebook.pack(padx=10, pady=10, fill="both", expand=True)
parent.mainloop()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- First we create three functions (create_tab1(), create_tab2(), and create_tab3()) that create content for each tab.
- Next we create a tk.Tk() instance as the main window and a ttk.Notebook to hold the tabs.
- Three tabs (tab1, tab2, and tab3) are created as ttk.Frame widgets and added to the notebook using the add method.
- Each tab's content is created using the functions defined earlier.
- The notebook is packed into the main window, and the main event loop is started with parent.mainloop().
Sample Output:
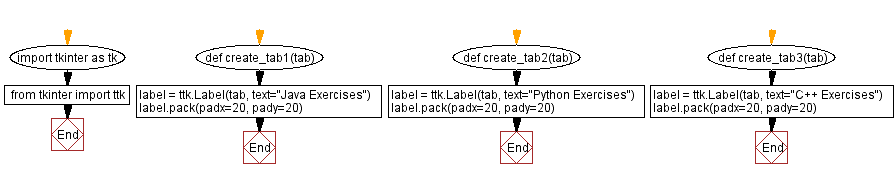
Flowchart:
Go to:
Previous: Create a Listbox bar widgets using tkinter module.
Next: Building a Hierarchical list widget.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.