Python Object-Oriented Programming: Shape class with area and perimeter calculation
4. Shape Class with Subclasses for Different Shapes
Write a Python program to create a class that represents a shape. Include methods to calculate its area and perimeter. Implement subclasses for different shapes like circle, triangle, and square.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Import the math module to access mathematical functions like pi
import math
# Define a base class called Shape to represent a generic shape with methods for calculating area and perimeter
class Shape:
# Placeholder method for calculating area (to be implemented in derived classes)
def calculate_area(self):
pass
# Placeholder method for calculating perimeter (to be implemented in derived classes)
def calculate_perimeter(self):
pass
# Define a derived class called Circle, which inherits from the Shape class
class Circle(Shape):
# Initialize the Circle object with a given radius
def __init__(self, radius):
self.radius = radius
# Calculate and return the area of the circle using the formula: π * r^2
def calculate_area(self):
return math.pi * self.radius**2
# Calculate and return the perimeter of the circle using the formula: 2π * r
def calculate_perimeter(self):
return 2 * math.pi * self.radius
# Define a derived class called Rectangle, which inherits from the Shape class
class Rectangle(Shape):
# Initialize the Rectangle object with given length and width
def __init__(self, length, width):
self.length = length
self.width = width
# Calculate and return the area of the rectangle using the formula: length * width
def calculate_area(self):
return self.length * self.width
# Calculate and return the perimeter of the rectangle using the formula: 2 * (length + width)
def calculate_perimeter(self):
return 2 * (self.length + self.width)
# Define a derived class called Triangle, which inherits from the Shape class
class Triangle(Shape):
# Initialize the Triangle object with a base, height, and three side lengths
def __init__(self, base, height, side1, side2, side3):
self.base = base
self.height = height
self.side1 = side1
self.side2 = side2
self.side3 = side3
# Calculate and return the area of the triangle using the formula: 0.5 * base * height
def calculate_area(self):
return 0.5 * self.base * self.height
# Calculate and return the perimeter of the triangle by adding the lengths of its three sides
def calculate_perimeter(self):
return self.side1 + self.side2 + self.side3
# Example usage
# Create a Circle object with a given radius and calculate its area and perimeter
r = 7
circle = Circle(r)
circle_area = circle.calculate_area()
circle_perimeter = circle.calculate_perimeter()
# Print the results for the Circle
print("Radius of the circle:", r)
print("Circle Area:", circle_area)
print("Circle Perimeter:", circle_perimeter)
# Create a Rectangle object with given length and width and calculate its area and perimeter
l = 5
w = 7
rectangle = Rectangle(l, w)
rectangle_area = rectangle.calculate_area()
rectangle_perimeter = rectangle.calculate_perimeter()
# Print the results for the Rectangle
print("\nRectangle: Length =", l, " Width =", w)
print("Rectangle Area:", rectangle_area)
print("Rectangle Perimeter:", rectangle_perimeter)
# Create a Triangle object with a base, height, and three side lengths, and calculate its area and perimeter
base = 5
height = 4
s1 = 4
s2 = 3
s3 = 5
# Print the results for the Triangle
print("\nTriangle: Base =", base, " Height =", height, " side1 =", s1, " side2 =", s2, " side3 =", s3)
triangle = Triangle(base, height, s1, s2, s3)
triangle_area = triangle.calculate_area()
triangle_perimeter = triangle.calculate_perimeter()
print("Triangle Area:", triangle_area)
print("Triangle Perimeter:", triangle_perimeter)
Sample Output:
Radius of the circle: 7 Circle Area: 153.93804002589985 Circle Perimeter: 43.982297150257104 Rectangle: Length = 5 Width = 7 Rectangle Area: 35 Rectangle Perimeter: 24 Triangle: Base = 5 Height = 4 side1 = 4 side2 = 3 side3 = 5 Triangle Area: 10.0 Triangle Perimeter: 12
Explanation:
In this above exercise,
- we define a base class called Shape that provides the blueprint for other shapes. It includes two methods, calculate_area and calculate_perimeter, which are overridden by subclasses.
- The Circle class is a subclass of Shape and includes logic designed to calculate the area and perimeter of a circle using the provided radius.
- Rectangles, another subclass of Shape, include length and width attributes that enable them to calculate their area and perimeter.
- The Triangle class is also a subclass of Shape and includes the necessary attributes (base, height, and side lengths) to calculate a triangle's area and perimeter.
- In the example usage section, we create instances of each subclass and call the calculate_area and calculate_perimeter methods to obtain the area and perimeter values. The results are then printed.
Flowchart:
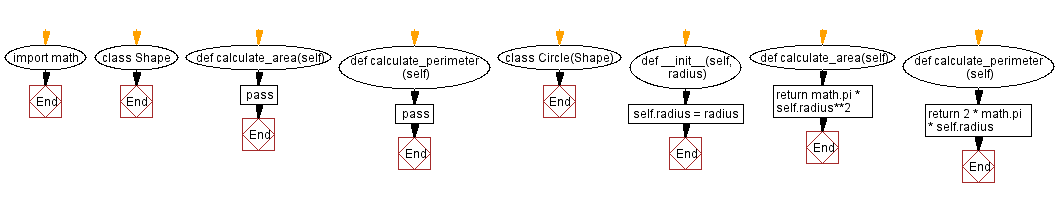
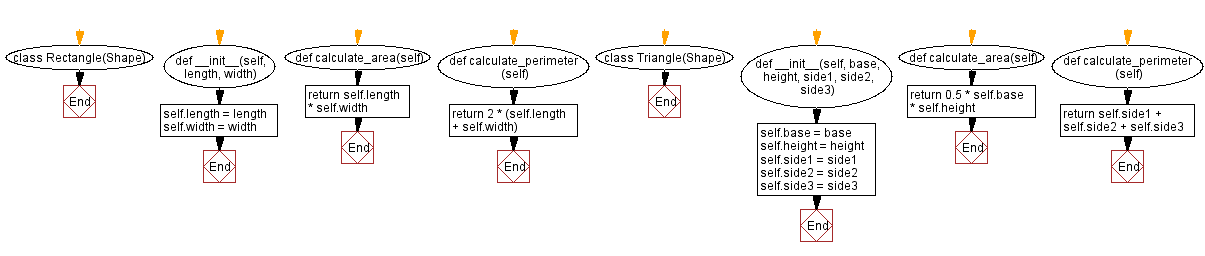
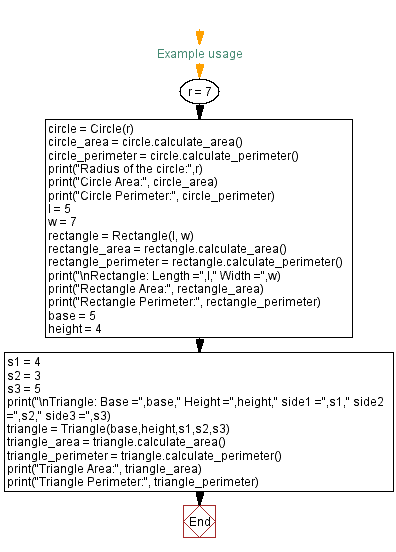
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python abstract base class Shape with abstract methods area() and perimeter(), and implement subclasses for Circle, Triangle, and Square.
- Write a Python class hierarchy for shapes that includes a method to scale dimensions and recalculate area and perimeter.
- Write a Python program that uses polymorphism to compute the total area of a mixed list of shapes.
- Write a Python class for each shape that overrides the __str__ method to return a formatted string of its dimensions and computed area and perimeter.
Go to:
Previous: Calculator class for basic arithmetic.
Next: Binary search tree class with insertion and search methods.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
