NumPy: Collapse a 3-D array into one dimension array
Collapse 3D Array to 1D
Write a NumPy program to collapse a 3-D array into a one-dimensional array.
Pictorial Presentation:
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Importing the NumPy library with an alias 'np'
import numpy as np
# Creating a 3x3 identity matrix using np.eye
x = np.eye(3)
# Printing the original 3x3 identity matrix
print("3-D array:")
print(x)
# Raveling the 3x3 matrix in Fortran (column-major) order to create a one-dimensional array
f = np.ravel(x, order='F')
# Printing the resulting one-dimensional array after raveling
print("One dimension array:")
print(f)
Sample Output:
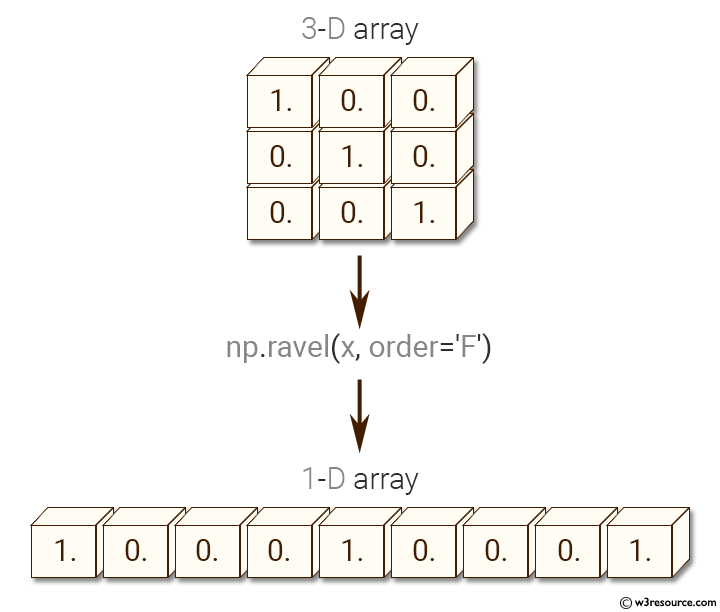
3-D array: [[ 1. 0. 0.] [ 0. 1. 0.] [ 0. 0. 1.]] One dimension array: [ 1. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 1.]
Explanation:
In the above code -
x = np.eye(3): This part creates a 3x3 identity matrix using the np.eye() function. In an identity matrix, the diagonal elements are 1, and the off-diagonal elements are 0.
f = np.ravel(x, order='F'): The np.ravel() function is used to flatten the input matrix x into a one-dimensional array. The order parameter is set to 'F' (Fortran order), which specifies that the elements should be flattened column-wise (i.e., going down columns first, then moving to the next column).
print(f) prints the resulting one-dimensional NumPy array f, which contains the flattened elements of the identity matrix x in Fortran order.
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Flatten a 3D array into a 1D array using np.reshape with -1 and verify the total number of elements.
- Write a function that collapses any multi-dimensional array into a one-dimensional array while preserving order.
- Compare the outputs of np.flatten and np.ravel for a non-contiguous 3D array to understand their differences.
- Test the flattening process on a large 3D array and measure the time efficiency of the operation.
Go to:
PREV : Create 2D Array with Specific Values
NEXT : Find 4th Element of Array
Python-Numpy Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
