Python: Geometric progression
Generate Range with Ratio
Write a Python program to initialize a list containing the numbers in the specified range where start and end are inclusive and the ratio between two terms is step. Return an error if step equals 1.
- Use range(), math.log() and math.floor() and a list comprehension to create a list of the appropriate length, applying the step for each element.
- Omit the second argument, start, to use a default value of 1.
- Omit the third argument, step, to use a default value of 2.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Import the 'floor' and 'log' functions from the 'math' module.
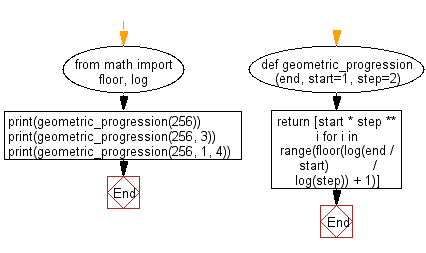
from math import floor, log
# Define a function 'geometric_progression' that calculates a geometric progression.
# It takes the ending value 'end' as a required parameter, and 'start' and 'step' as optional parameters with default values.
def geometric_progression(end, start=1, step=2):
# Calculate the number of terms in the geometric progression using logarithms and floor division.
num_terms = floor(log(end / start) / log(step) + 1)
# Use a list comprehension to generate the geometric progression.
progression = [start * step ** i for i in range(num_terms)]
# Return the list representing the geometric progression.
return progression
# Call the 'geometric_progression' function with different parameters and print the results.
print(geometric_progression(256))
print(geometric_progression(256, 3))
print(geometric_progression(256, 1, 4))
Sample Output:
[1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256] [3, 6, 12, 24, 48, 96, 192] [1, 4, 16, 64, 256]
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to generate a geometric progression list given a start, end, and a ratio, and validate that the ratio is not 1.
- Write a Python program to produce a list of numbers in a range where each term is the previous term multiplied by a specified ratio, with error handling for invalid ratios.
- Write a Python program to create a list representing a geometric series from a starting number up to a maximum value using a given multiplier.
- Write a Python program to generate a list of exponential values using a step ratio and then verify the integrity of the progression.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to check if a given function returns True for every element in a list.
Next: Write a Python program to that takes any number of iterable objects or objects with a length property and returns the longest one.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
