PostgreSQL JOINS: Make a join with three tables departments, employees and locations to display the department name, manager name, and city
9. Write a query to make a join with three tables departments, employees, and locations to display the department name, manager name, and city.
Sample Solution:
Code:
-- This SQL query retrieves department name, manager's first name, and city from the departments, employees, and locations tables.
SELECT w1.department_name, -- Selects the department_name column from the departments table
w2.first_name, -- Selects the first_name column from the employees table
w3.city -- Selects the city column from the locations table
FROM departments w1 -- Specifies the first table from which to retrieve data, aliasing it as 'w1'
JOIN employees w2 -- Joins the departments table with the employees table, specifying the second table and aliasing it as 'w2'
ON (w1.manager_id = w2.employee_id) -- Specifies the join condition based on the manager_id and employee_id columns
JOIN locations w3 USING (location_id); -- Joins the result with the locations table based on the location_id, using the USING keyword
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves department name, manager's first name, and city from the departments, employees, and locations tables.
- The SELECT statement selects the department name, manager's first name, and city columns.
- The FROM clause specifies the first table from which to retrieve data, which is the departments table, aliased as w1.
- A JOIN operation is performed between the departments table (w1) and the employees table (w2), specifying the second table and aliasing it as w2.
- The ON clause specifies the join condition where the manager_id from the departments table matches the employee_id from the employees table.
- Another JOIN operation is performed to join the result with the locations table (w3) based on the location_id, using the USING keyword to specify the column common to both tables.
- The result set will contain department name, manager's first name, and city for each department where a manager is assigned, retrieved from the departments, employees, and locations tables.
Sample table: employees
+-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | EMPLOYEE_ID | FIRST_NAME | LAST_NAME | EMAIL | PHONE_NUMBER | HIRE_DATE | JOB_ID | SALARY | COMMISSION_PCT | MANAGER_ID | DEPARTMENT_ID | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | 100 | Steven | King | SKING | 515.123.4567 | 1987-06-17 | AD_PRES | 24000.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 90 | | 101 | Neena | Kochhar | NKOCHHAR | 515.123.4568 | 1987-06-18 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 102 | Lex | De Haan | LDEHAAN | 515.123.4569 | 1987-06-19 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 103 | Alexander | Hunold | AHUNOLD | 590.423.4567 | 1987-06-20 | IT_PROG | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 102 | 60 | | 104 | Bruce | Ernst | BERNST | 590.423.4568 | 1987-06-21 | IT_PROG | 6000.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 105 | David | Austin | DAUSTIN | 590.423.4569 | 1987-06-22 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 106 | Valli | Pataballa | VPATABAL | 590.423.4560 | 1987-06-23 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 107 | Diana | Lorentz | DLORENTZ | 590.423.5567 | 1987-06-24 | IT_PROG | 4200.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 108 | Nancy | Greenberg | NGREENBE | 515.124.4569 | 1987-06-25 | FI_MGR | 12000.00 | 0.00 | 101 | 100 | .......... | 206 | William | Gietz | WGIETZ | 515.123.8181 | 1987-10-01 | AC_ACCOUNT | 8300.00 | 0.00 | 205 | 110 | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+
Sample table: departments
+---------------+----------------------+------------+-------------+ | DEPARTMENT_ID | DEPARTMENT_NAME | MANAGER_ID | LOCATION_ID | +---------------+----------------------+------------+-------------+ | 10 | Administration | 200 | 1700 | | 20 | Marketing | 201 | 1800 | | 30 | Purchasing | 114 | 1700 | | 40 | Human Resources | 203 | 2400 | | 50 | Shipping | 121 | 1500 | | 60 | IT | 103 | 1400 | | 70 | Public Relations | 204 | 2700 | | 80 | Sales | 145 | 2500 | | 90 | Executive | 100 | 1700 | ........ | 270 | Payroll | 0 | 1700 | +---------------+----------------------+------------+-------------+
Sample table: locations
location_id street_address postal_code city state_province country_id ----------- -------------------- ----------- ---------- -------------- ---------- 1000 1297 Via Cola di Rie 989 Roma IT 1100 93091 Calle della Te 10934 Venice IT 1200 2017 Shinjuku-ku 1689 Tokyo Tokyo Prefectu JP 1300 9450 Kamiya-cho 6823 Hiroshima JP 1400 2014 Jabberwocky Rd 26192 Southlake Texas US 1500 2011 Interiors Blvd 99236 South San California US 1600 2007 Zagora St 50090 South Brun New Jersey US 1700 2004 Charade Rd 98199 Seattle Washington US 1800 147 Spadina Ave M5V 2L7 Toronto Ontario CA ......... 3200 Mariano Escobedo 999 11932 Mexico Cit Distrito Feder MX
Output:
pg_exercises=# SELECT w1.department_name, w2.first_name, w3.city pg_exercises-# FROM departments w1 pg_exercises-# JOIN employees w2 pg_exercises-# ON (w1.manager_id = w2.employee_id) pg_exercises-# JOIN locations w3 USING (location_id); department_name | first_name | city ------------------+------------+--------------------- IT | Alexander | Southlake Purchasing | Den | Seattle Executive | Steven | Seattle Sales | John | OX9 9ZB Shipping | Adam | South San Francisco Finance | Nancy | Seattle Administration | Jennifer | Seattle Marketing | Michael | Toronto Human Resources | Susan | London Public Relations | Hermann | Munich Accounting | Shelley | Seattle (11 rows)
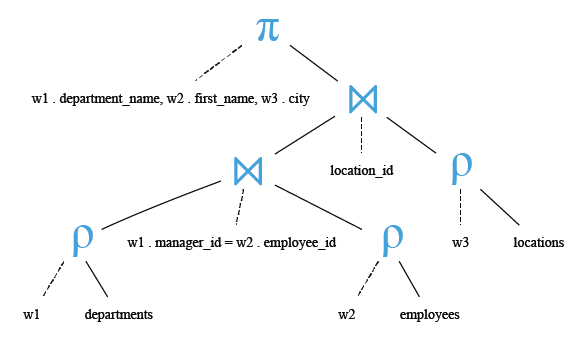
Relational Algebra Expression:
Relational Algebra Tree:
Go to:
PREV : Write a query to make a join with two tables employees and departments to display the department ID, department name and the first name of the manager.
NEXT : Write a query to make a join with two tables employees and jobs to display the job title and average salary of employees.
Practice Online
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?