Preventing duplicate values using PL/SQL triggers
PL/SQL Trigger: Exercise-5 with Solution
Write a code in PL/SQL to create a trigger that checks for duplicate values in a specific column and raises an exception if found.
Sample Solution:
PL/SQL Code:
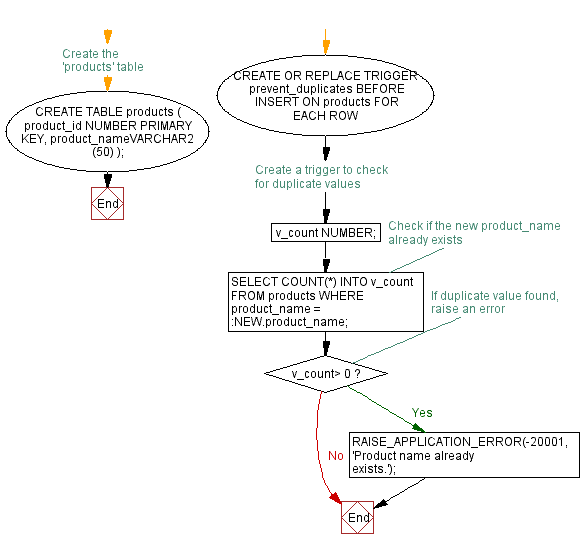
-- Create the 'products' table
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
product_nameVARCHAR2(50)
);
-- Create a trigger to check for duplicate values
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER prevent_duplicates
BEFORE INSERT ON products
FOR EACH ROW
DECLARE
v_count NUMBER;
BEGIN
-- Check if the new product_name already exists
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO v_count FROM products WHERE product_name = :NEW.product_name;
-- If duplicate value found, raise an error
IF v_count> 0 THEN
RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(-20001, 'Product name already exists.');
END IF;
END;
/
Let's see how trigger can be used:
PL/SQL Code:
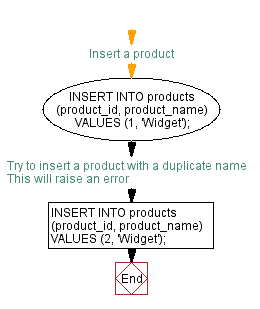
-- Insert a product
INSERT INTO products (product_id, product_name) VALUES (1, 'Widget');
-- Try to insert a product with a duplicate name
INSERT INTO products (product_id, product_name) VALUES (2, 'Widget'); -- This will raise an error
Output:
1 row(s) inserted. ORA-00933: SQL command not properly ended
Flowchart:
Explanation:
The said code in PL/SQL that demonstrates the use of a PL/SQL trigger to maintain data integrity by preventing the insertion of duplicate values into a specific column.
A table 'products' is with columns 'product_id' and 'product_name' is involve with this trigger.
A trigger named 'prevent_duplicates' is created using the BEFORE INSERT event that fires before an insertion operation.
Inside the trigger, a local variable v_count is used to store the count of existing rows in the 'products' table where the 'product_name' matches the new value being inserted.
A SELECT statement is that counts the matching rows.
When an attempt is made to insert a new product the trigger fires due to the BEFORE INSERT event and checks for duplicate values, the trigger raises an application error with the code -20001 and a message indicating that the product name already exists, and preventing the insertion of the duplicate value.
Go to:
PREV :Enforcing referential integrity in PL/SQL trigger.
NEXT : Restricting total order amount using PL/SQL Triggers.
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
