Tracking Deleted Rows with a PL/SQL Trigger
PL/SQL Trigger: Exercise-3 with Solution
Write a code in PL/SQL to implement a trigger that maintains a transaction history log whenever a row is deleted from a table.
Sample Solution:
PL/SQL Code:
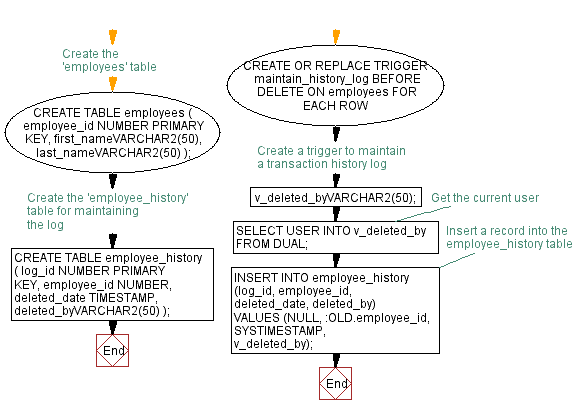
-- Create the 'employees' table
CREATE TABLE employees (
employee_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
first_nameVARCHAR2(50),
last_nameVARCHAR2(50)
);
-- Create the 'employee_history' table for maintaining the log
CREATE TABLE employee_history (
log_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
employee_id NUMBER,
deleted_date TIMESTAMP,
deleted_byVARCHAR2(50)
);
-- Create a trigger to maintain a transaction history log
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER maintain_history_log
BEFORE DELETE ON employees
FOR EACH ROW
DECLARE
v_deleted_byVARCHAR2(50);
BEGIN
-- Get the current user
SELECT USER INTO v_deleted_by FROM DUAL;
-- Insert a record into the employee_history table
INSERT INTO employee_history (log_id, employee_id, deleted_date, deleted_by)
VALUES (NULL, :OLD.employee_id, SYSTIMESTAMP, v_deleted_by);
END;
/
Let's see how the trigger functions:
PL/SQL Code:
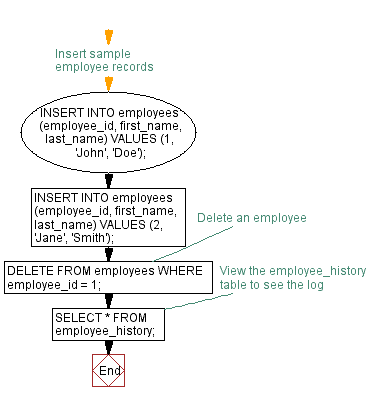
-- Insert sample employee records
INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name) VALUES (1, 'John', 'Doe');
INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name) VALUES (2, 'Jane', 'Smith');
-- Delete an employee
DELETE FROM employees WHERE employee_id = 1;
-- View the employee_history table to see the log
SELECT * FROM employee_history;
Output:
1 row(s) inserted.
1 row(s) inserted.
ORA-01400: cannot insert NULL into ("SQL_XWPLBLJQVQMCLONNGGTSSIRWZ"."EMPLOYEE_HISTORY"."LOG_ID") ORA-06512: at "SQL_XWPLBLJQVQMCLONNGGTSSIRWZ.MAINTAIN_HISTORY_LOG", line 8
ORA-06512: at "SYS.DBMS_SQL", line 1721
no data found
Flowchart:
Explanation:
The said code in PL/SQL that demonstrates how to use a PL/SQL trigger to maintain an audit trail by capturing deletion history for rows in a table.
Assume that the code executes with the table employees with columns employee_id, first_name, and last_name and another table employee_history that maintain the transaction history log. This table stores log_id, employee_id, deleted_date, and deleted_by columns to record the details of each deletion.
The trigger maintain_history_log is created using the BEFORE DELETE ON that fires before a row is deleted from the employees table.
The trigger inserts a record into the employee_history table, capturing the employee_id of the deleted row, the deletion timestamp using SYSTIMESTAMP, and the deleted_by user.
When deleting a record the trigger maintain_history_log is invoked before the deletion, logging the deletion in the employee_history table.
The contents of the employee_history table are queried using SELECT * FROM employee_history; to view the log entries.
Go to:
PREV :Restricting column updates during specific hours using PL/SQL triggers.
NEXT : Enforcing referential integrity in PL/SQL trigger.
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
