PL/SQL Fundamentals Exercises: PL/SQL Variable Declarations
PL/SQL Fundamentals: Exercise-7 with Solution
Write PL/SQL blocks to show the declaration of variables.
The following PL/SQL block shows how to declare variables with scalar data type.
PL/SQL Code:
DECLARE
item_number NUMBER(5); -- SQL data type
item_name VARCHAR2(20); -- SQL data type
stock_yn BOOLEAN; -- PL/SQL-only data type
item_rate NUMBER(8,2); -- SQL data type
item_description VARCHAR2(40); -- SQL data type
BEGIN
NULL;
END;
/
Declaration of constant with scalar data type.
PL/SQL Code:
DECLARE
maximum_deposit CONSTANT REAL := 25000.00; -- SQL data type
min_no_of_days CONSTANT INTEGER := 75; -- SQL data type
nominee_yn CONSTANT BOOLEAN := FALSE; -- PL/SQL-only data type
BEGIN
NULL;
END;
/
Declaration of variable with initial value
PL/SQL Code:
DECLARE
worked_no_of_days INTEGER := 15;
employee_no INTEGER := 0;
pi CONSTANT REAL := 3.14159;
radius REAL := 10;
area REAL := (pi * radius**2);
BEGIN
NULL;
END;
/
Initialize NULL by default to variable.
PL/SQL Code:
DECLARE
ctr INTEGER; -- initial value is NULL by default
BEGIN
ctr := ctr + 1; -- NULL + 1 is still NULL
IF ctr IS NULL THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('The counter ctr is NULL.');
END IF;
END;
/
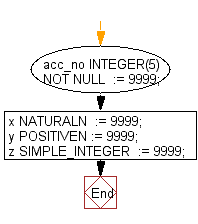
Declaration of variable with NOT NULL Constraint
PL/SQL Code:
DECLARE
acc_no INTEGER(5) NOT NULL := 9999;
x NATURALN := 9999;
y POSITIVEN := 9999;
z SIMPLE_INTEGER := 9999;
BEGIN
NULL;
END;
/
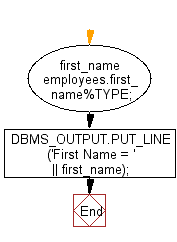
Declaration of variable as same column type
In the following example the variable first_name inherits the data type and size of the column employees.first_name, which has a NOT NULL constraint and this declaration does not need an initial value.
PL/SQL Code:
DECLARE
first_name employees.first_name%TYPE;
BEGIN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('First Name = ' || first_name);
END;
/
Sample Output:
First Name = Statement processed. 0.07 seconds
Flowchart:
Declaration of variables with scalar data type
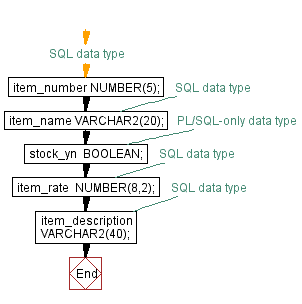
Declaration of constant with scalar data type
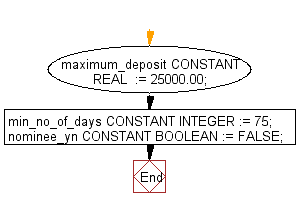
Declaration of variable with initial value
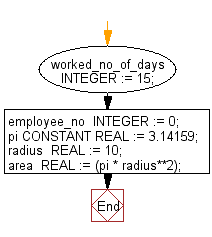
Initialize NULL by default to variable.
Declaration of variable with NOT NULL Constraint
Declaration of variable as same column type
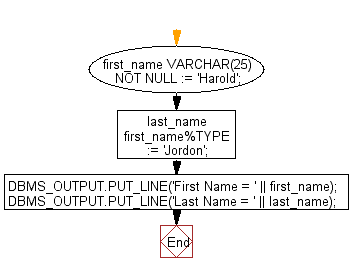
Declaration of variable as same type of another variable
In the following example the variable last_name inherits the data type, size, and NOT NULL constraint of the variable first_name. Because last_name does not inherit the initial value of first_name and its declaration needs an initial value (which cannot exceed 25 characters).
PL/SQL Code:
DECLARE
first_name VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL := 'Harold';
last_name first_name%TYPE := 'Jordon';
BEGIN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('First Name = ' || first_name);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Last Name = ' || last_name);
END;
/
Sample Output:
First Name = Harold Last Name = Jordon Statement processed. 0.00 seconds
Flowchart:
Declaration of variable as same type of another variable
Go to:
PREV : Write a PL/SQL block to show single and multiline comments.
NEXT : Write PL/SQL blocks to show the scope and visibility of local and global identifiers.
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
