PL/SQL Example: Handling COLLECTION_IS_NULL exception
PL/SQL Exception Handling: Exercise-10 with Solution
Handle the COLLECTION_IS_NULL exception when trying to access elements from a NULL collection.
Sample Solution:
Table: employees
employee_id integer first_name varchar(25) last_name varchar(25) email archar(25) phone_number varchar(15) hire_date date job_id varchar(25) salary integer commission_pct decimal(5,2) manager_id integer department_id integer
PL/SQL Code:
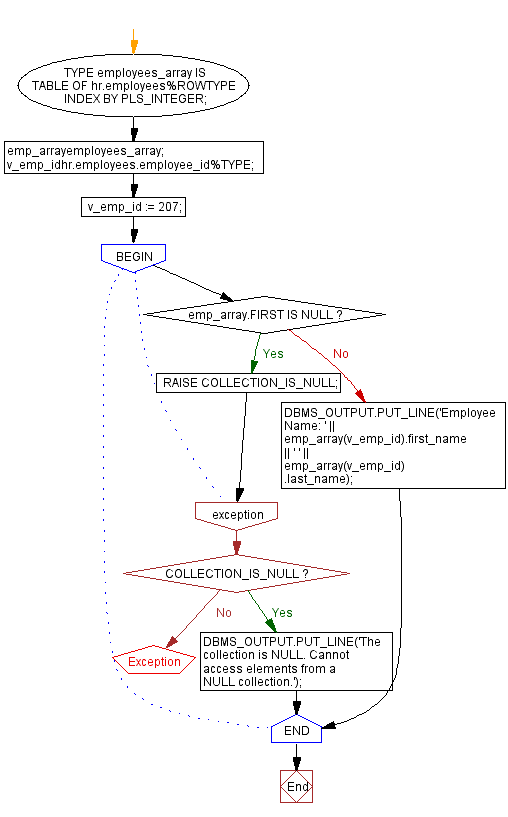
DECLARE
TYPE employees_array IS TABLE OF hr.employees%ROWTYPE INDEX BY PLS_INTEGER;
emp_arrayemployees_array;
v_emp_idhr.employees.employee_id%TYPE;
BEGIN
v_emp_id := 207;
BEGIN
IF emp_array.FIRST IS NULL THEN
RAISE COLLECTION_IS_NULL;
ELSE
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Employee Name: ' || emp_array(v_emp_id).first_name || ' ' || emp_array(v_emp_id).last_name);
END IF;
EXCEPTION
WHEN COLLECTION_IS_NULL THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('The collection is NULL. Cannot access elements from a NULL collection.');
END;
END;
/
Sample Output:
The collection is NULL. Cannot access elements from a NULL collection.
Explanation:
The said code in Oracle's PL/SQL that demonstrates the handling of the COLLECTION_IS_NULL exception when working with associative arrays in PL/SQL. It demonstrates the importance of checking if a collection is null before accessing its elements, helping to prevent runtime errors.
An array variable "employees_array" as a table of the 'employees' table's row type, indexed by PLS_INTEGER is declared.
An associative array called "emp_array" is declared using the "employees_array" type.
A variable, "v_emp_id," is declared to store an employee ID and initializes with the value 207.
It first checks whether the "emp_array" is empty or not. If it is null, the code raises the "COLLECTION_IS_NULL" exception and displays an appropriate error message using the DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE statement.
If it is not, it retrieves the first name and last name of the employee with the ID stored in "v_emp_id" from the "emp_array" and displays it using the DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE statement.
Flowchart:
Go to:
PREV : Handling INVALID_CURSOR Exception.
NEXT : Handling CASE_NOT_FOUND exception in PL/SQL with example code.
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
