PHP Searching and Sorting Algorithm: Patience sort
Write a PHP program to sort a list of elements using Patience sort.
Patience sorting is a sorting algorithm inspired by and named after, the card game patience. A variant of the algorithm efficiently computes the length of a longest increasing subsequence in a given array.
The algorithm's name derives from a simplified variant of the patience card game. This game begins with a shuffled deck of cards. These cards are dealt one by one into a sequence of piles on the table, according to the following rules.
- Initially, there are no piles. The first card dealt forms a new pile consisting of the single card.
- Each subsequent card is placed on the leftmost existing pile whose top card has a value greater than or equal the new card's value, or to the right of all of the existing piles, thus forming a new pile.
- When there are no more cards remaining to deal, the game ends.
This card game is turned into a two-phase sorting algorithm, as follows. Given an array of n elements from some totally ordered domain, consider this array as a collection of cards and simulate the patience sorting game. When the game is over, recover the sorted sequence by repeatedly picking off the minimum visible card; in order words, perform an p-way merge of the p piles, each of which is internally sorted.
Sample Solution :
PHP Code :
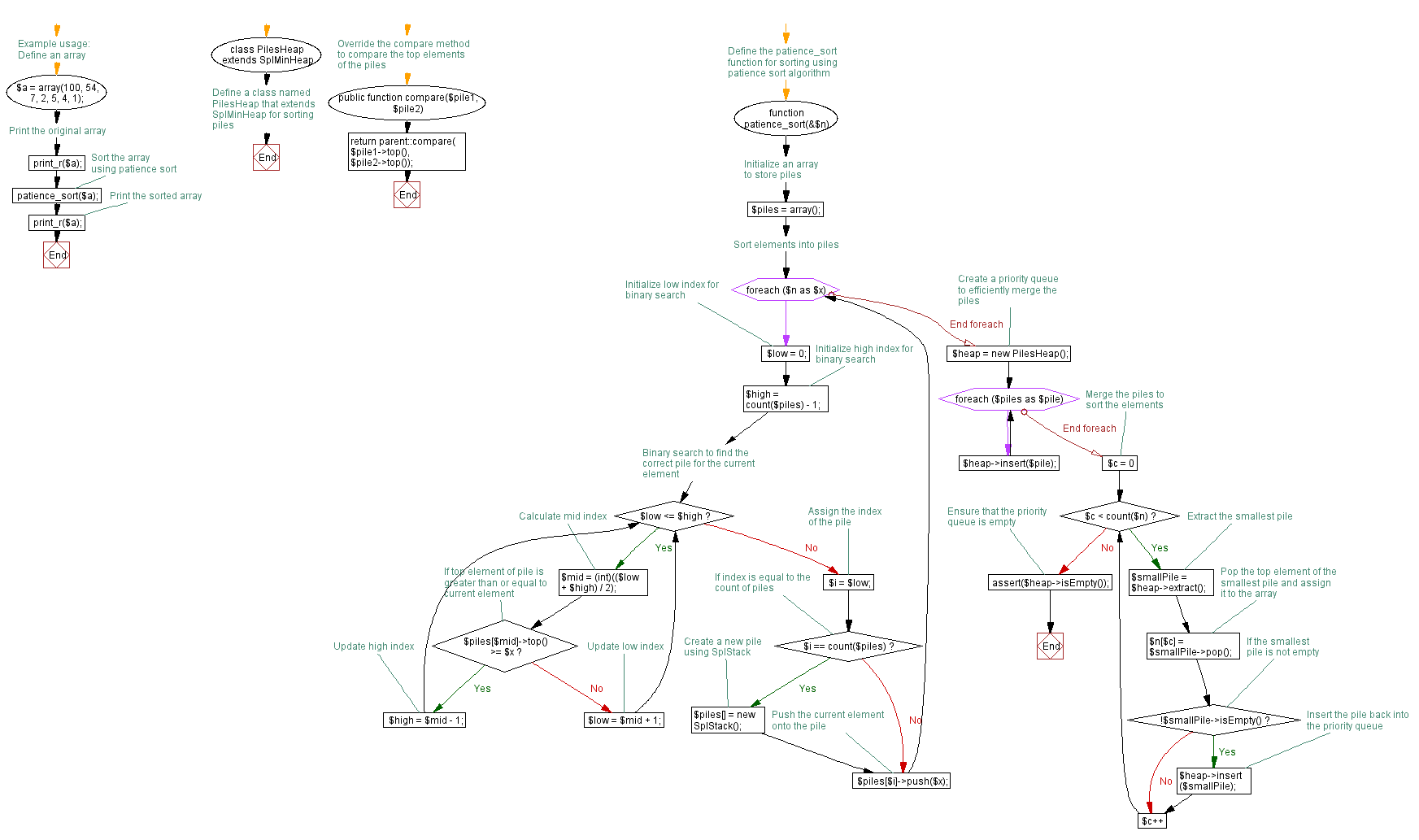
<?php
// Define a class named PilesHeap that extends SplMinHeap for sorting piles
class PilesHeap extends SplMinHeap {
// Override the compare method to compare the top elements of the piles
public function compare($pile1, $pile2) {
return parent::compare($pile1->top(), $pile2->top());
}
}
// Define the patience_sort function for sorting using patience sort algorithm
function patience_sort(&$n) {
$piles = array(); // Initialize an array to store piles
// Sort elements into piles
foreach ($n as $x) {
$low = 0; // Initialize low index for binary search
$high = count($piles) - 1; // Initialize high index for binary search
// Binary search to find the correct pile for the current element
while ($low <= $high) {
$mid = (int)(($low + $high) / 2); // Calculate mid index
if ($piles[$mid]->top() >= $x) // If top element of pile is greater than or equal to current element
$high = $mid - 1; // Update high index
else
$low = $mid + 1; // Update low index
}
$i = $low; // Assign the index of the pile
if ($i == count($piles)) // If index is equal to the count of piles
$piles[] = new SplStack(); // Create a new pile using SplStack
$piles[$i]->push($x); // Push the current element onto the pile
}
// Create a priority queue to efficiently merge the piles
$heap = new PilesHeap();
foreach ($piles as $pile)
$heap->insert($pile);
// Merge the piles to sort the elements
for ($c = 0; $c < count($n); $c++) {
$smallPile = $heap->extract(); // Extract the smallest pile
$n[$c] = $smallPile->pop(); // Pop the top element of the smallest pile and assign it to the array
if (!$smallPile->isEmpty()) // If the smallest pile is not empty
$heap->insert($smallPile); // Insert the pile back into the priority queue
}
assert($heap->isEmpty()); // Ensure that the priority queue is empty
}
// Example usage:
$a = array(100, 54, 7, 2, 5, 4, 1); // Define an array
print_r($a); // Print the original array
patience_sort($a); // Sort the array using patience sort
print_r($a); // Print the sorted array
?>
Output:
Array
(
[0] => 100
[1] => 54
[2] => 7
[3] => 2
[4] => 5
[5] => 4
[6] => 1
)
Array
(
[0] => 1
[1] => 2
[2] => 4
[3] => 5
[4] => 7
[5] => 54
[6] => 100
)
Explanation:
In the exercise above,
- PilesHeap Class: This class extends "SplMinHeap" and overrides the "compare()" method to compare the top elements of the piles. This class creates a min-heap based on the top elements of the piles.
- patience_sort Function: This function implements the patience sort algorithm. Here's how it works:
- It initializes an array called '$piles' to store piles.
- It iterates over each element in the input array '$n' and sorts them into piles using binary search to find the correct pile for each element.
- It creates a min-heap called '$heap' using the "PilesHeap" class to efficiently merge the piles.
- It iteratively extracts the smallest pile from the heap, pops the top element from it, and assigns it to the corresponding position in the input array '$n'.
- It reinserts the pile back into the heap if it's not empty.
- Finally, it ensures that the heap is empty using the "assert()" function.
- Finally, the "patience_sort()" function sorts an array '$a', prints the original array, sorts it using patience sort, and prints the sorted array.
Flowchart :
Go to:
PREV : Write a PHP program to sort a list of elements using Strand sort.
NEXT : Write a PHP program to sort a list of elements using Merge sort.
PHP Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
