PHP Exercises: Restore the original string by entering the compressed string with this rule
72. Compressed String Restoration
When character are consecutive in a string , it is possible to shorten the character string by replacing the character with a certain rule. For example, in the case of the character string YYYYY, if it is expressed as # 5 Y, it is compressed by one character.
Write a PHP program to restore the original string by entering the compressed string with this rule. However, the # character does not appear in the restored character string.
Note: The original sentences are uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, symbols, less than 100 letters, and consecutive letters are not more than 9 letters.
Input: Multiple character strings are given. One string is given per line
Sample Solution:
PHP Code:
<?php
// Input string containing "@" symbols with repetition information
$str = "@88 + 1 = 1@80";
// Initialize index for traversing the input string
$index = 0;
// Initialize an array to store the resulting characters
$result = array();
// Loop through each character in the input string
while ($index < strlen($str)) {
// Get the current character
$t = $str[$index++];
// Check if the current character is "@"
if ($t == "@") {
// Extract the length and character information for repetition
$len = $str[$index++];
$char = $str[$index++];
// Initialize an empty string to store repeated characters
$run = "";
// Repeat the character for the specified length
for ($i = 0; $i < $len; $i++) {
$run .= $char;
}
// Add the repeated characters to the result array
$result[] = $run;
} else {
// If the character is not "@", add it directly to the result array
$result[] = $t;
}
}
// Output the final result by concatenating the characters in the result array
echo implode("", $result);
?>
Explanation:
- Initialize Input and Variables:
- Defines the input string $str = "@88 + 1 = 1@80", which contains the "@" symbol to denote sections with repetition information.
- Initializes $index = 0 to traverse the string and $result = array() to store processed characters.
- Loop Through Each Character in $str:
- Uses a while loop to go through the string character by character until $index reaches the end.
- Check for "@" Symbol:
- If the character at $index is "@", it indicates the start of a repetition pattern.
- Extract Repetition Information:
- Reads the next two characters after "@":
- $len: Specifies the number of times to repeat the following character.
- $char: The character to be repeated.
- Create Repeated String:
- Uses a for loop to create a string ($run) with $char repeated $len times and adds it to $result.
- Handle Non-"@" Characters:
- If the character is not "@", it’s added directly to $result.
- Output the Result:
- Combines all elements in $result into a single string and displays it using echo implode("", $result);.
Sample Input:
@88 + 1 = 1@80
Sample Output:
88888888 + 1 = 100000000
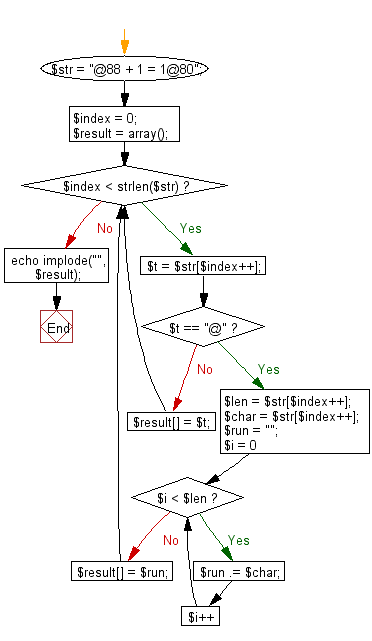
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a PHP script to expand a compressed string where a number preceded by '#' represents repeated characters.
- Write a PHP script to parse compressed tokens in a string and restore the original text using pattern matching.
- Write a PHP script to decompress a string containing multiple compressed segments separated by spaces.
- Write a PHP script to validate and restore an input string that uses a custom compression format with '#' symbols.
Go to:
PREV : Island Counting.
NEXT :
Convex Polygon Area Calculation.
PHP Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
