PHP Exception Handling: Basic usage of try-catch blocks
1. Basic Try-Catch Usage
Write a PHP program that demonstrates the basic usage of try-catch blocks to handle exceptions.
Sample Solution:
PHP Code :
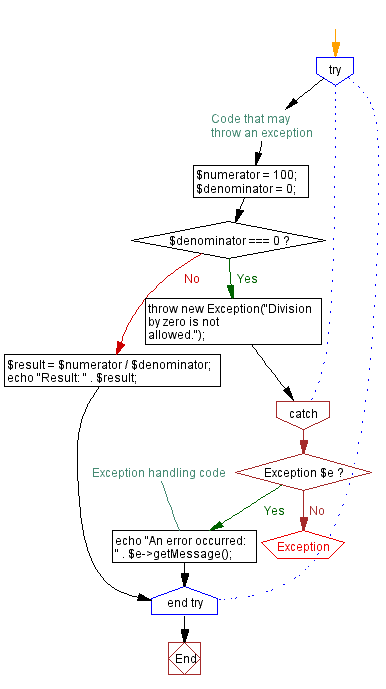
<?php
try {
// Code that may throw an exception
$numerator = 100;
$denominator = 0;
if ($denominator === 0) {
throw new Exception("Division by zero is not allowed.");
}
$result = $numerator / $denominator;
echo "Result: " . $result;
} catch (Exception $e)
{
// Exception handling code
echo "An error occurred: " . $e->getMessage();
}
?>
Sample Output:
An error occurred: Division by zero is not allowed.
Explanation:
In the above exercise, we have a division operation where the denominator is intentionally set to 0 to cause a division by zero exception. The code is wrapped inside a try block, and if an exception occurs within the try block, it is caught by the catch block. The catch block then handles the exception by displaying an error message using $e-<getMessage().
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a PHP script that triggers an exception inside a try block using a simple condition and catches it with a generic catch block.
- Write a PHP function that intentionally throws an exception when a specified condition is met and then catches it to print a custom error message.
- Write a PHP program that uses try-catch to handle multiple potential exceptions, including a manual throw when a value is out of range.
- Write a PHP script to simulate a scenario where a function call within a try block results in an exception, and then log the error message in the catch block.
Go to:
PREV : PHP Exception Handling Exercises Home
NEXT : Custom Exception Class.
PHP Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
