A Comprehensive Guide to Numpy.diff for Array Operations
Understanding np.diff: Compute Differences Between Array Elements
np.diff is a NumPy function used to calculate the n-th order discrete differences between consecutive elements of an array. It is often applied in numerical analysis, data processing, and signal processing to analyze changes or trends in data.
Syntax:
numpy.diff(a, n=1, axis=-1, prepend=<no value>, append=<no value>)
Parameters:
1. a (array_like): Input array.
2. n (int, optional): Number of times to perform the differencing. Default is 1.
3. axis (int, optional): Axis along which differences are calculated. Default is -1 (last axis).
4. prepend (array_like, optional): Values to prepend to the array.
5. append (array_like, optional): Values to append to the array.
Returns:
An array of the same shape as a (except along the specified axis) with discrete differences.
Examples and Code:
Example 1: Basic First-Order Difference
Code:
import numpy as np
# Define an input array
array = [10, 15, 25, 30]
# Compute the first-order differences
result = np.diff(array)
# Print the result
print("First-order differences:", result)
Output:
First-order differences: [ 5 10 5]
Explanation:
The differences are computed as [15-10, 25-15, 30-25].
Example 2: Higher-Order Differences
Code:
import numpy as np
# Define an input array
array = [10, 15, 25, 30]
# Compute second-order differences
result = np.diff(array, n=2)
# Print the result
print("Second-order differences:", result)
Output:
Second-order differences: [ 5 -5]
Explanation:
The second-order differences are computed as the differences of the first-order differences: [10-5, 5-10].
Example 3: Differences Along a Specific Axis
Code:
import numpy as np
# Define a 2D array
array = np.array([[1, 2, 4], [7, 11, 18]])
# Compute differences along the rows (axis=1)
result = np.diff(array, axis=1)
# Print the result
print("Differences along rows:", result)
Output:
Differences along rows: [[1 2]
[4 7]]
Explanation:
Differences are calculated along each row:
- Row 1: [2-1, 4-2]
- Row 2: [11-7, 18-11]
Example 4: Using Prepend and Append
Code:
import numpy as np
# Define an input array
array = [5, 10, 15]
# Compute differences with prepended and appended values
result = np.diff(array, prepend=0, append=20)
# Print the result
print("Differences with prepend and append:", result)
Output:
Differences with prepend and append: [ 5 5 5 5]
Explanation:
The array is extended as [0, 5, 10, 15, 20], and differences are calculated:
- Differences: [5-0, 10-5, 15-10, 20-15].
Example 5: Analyzing Trends in Data
Code:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define a simple dataset
data = [1, 2, 4, 7, 11, 16]
# Compute first-order differences
differences = np.diff(data)
# Plot the data and differences
plt.plot(data, label="Original Data")
plt.plot(range(1, len(data)), differences, label="Differences", linestyle="--")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Output:
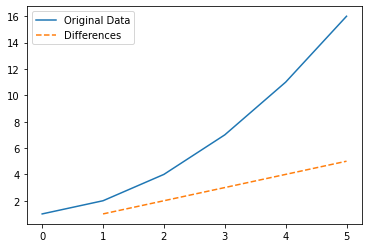
Explanation:
This example highlights the changes between data points, useful for identifying trends or irregularities in datasets.
Key Notes:
1. Higher Orders: Setting n greater than 1 computes the differences iteratively.
2. Multi-Dimensional Arrays: Use the axis parameter to control along which dimension differences are calculated.
3. Data Extension: Use prepend and append to avoid losing elements at the array boundaries.
Additional Tips:
- Use np.diff in financial applications to calculate daily returns or changes.
- When working with time-series data, this function is helpful for detecting peaks or calculating velocity in motion data.
