JavaScript Sorting Algorithm: Merge sort
JavaScript Sorting Algorithm: Exercise-2 with Solution
Merge Sort
Write a JavaScript program to sort a list of elements using Merge sort.
According to Wikipedia "Merge sort (also commonly spelled mergesort) is an O (n log n) comparison-based sorting algorithm. Most implementations produce a stable sort, which means that the implementation preserves the input order of equal elements in the sorted output."
Algorithm:
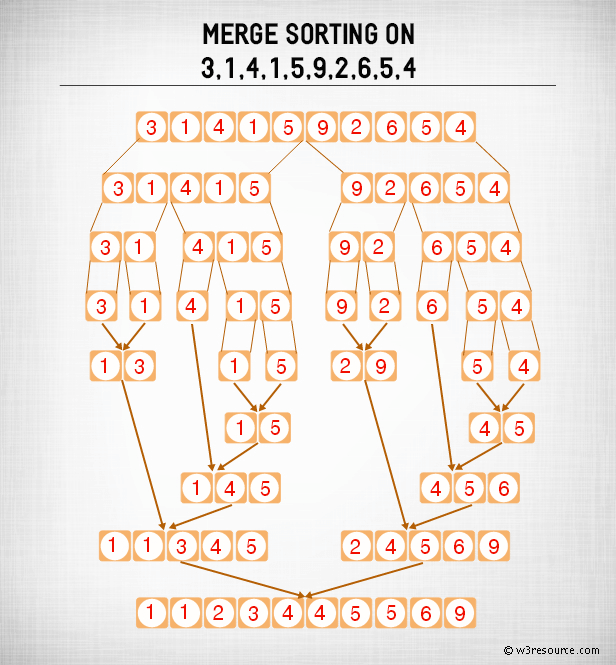
Conceptually, a merge sort works as follows :
- Divide the unsorted list into n sublists, each containing 1 element (a list of 1 element is considered sorted).
- Repeatedly merge sublists to produce new sorted sublists until there is only 1 sublist remaining. This will be the sorted list.
An example of merge sort:
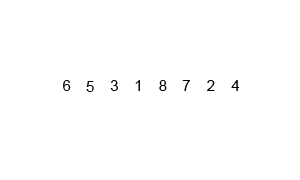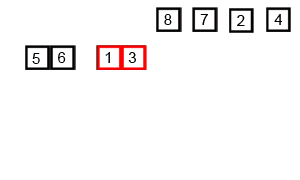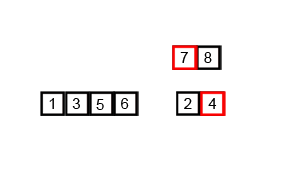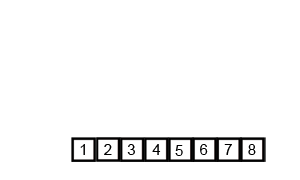
Merge Sort: Pictorial Presentation
Sample Solution-1:
JavaScript Code:
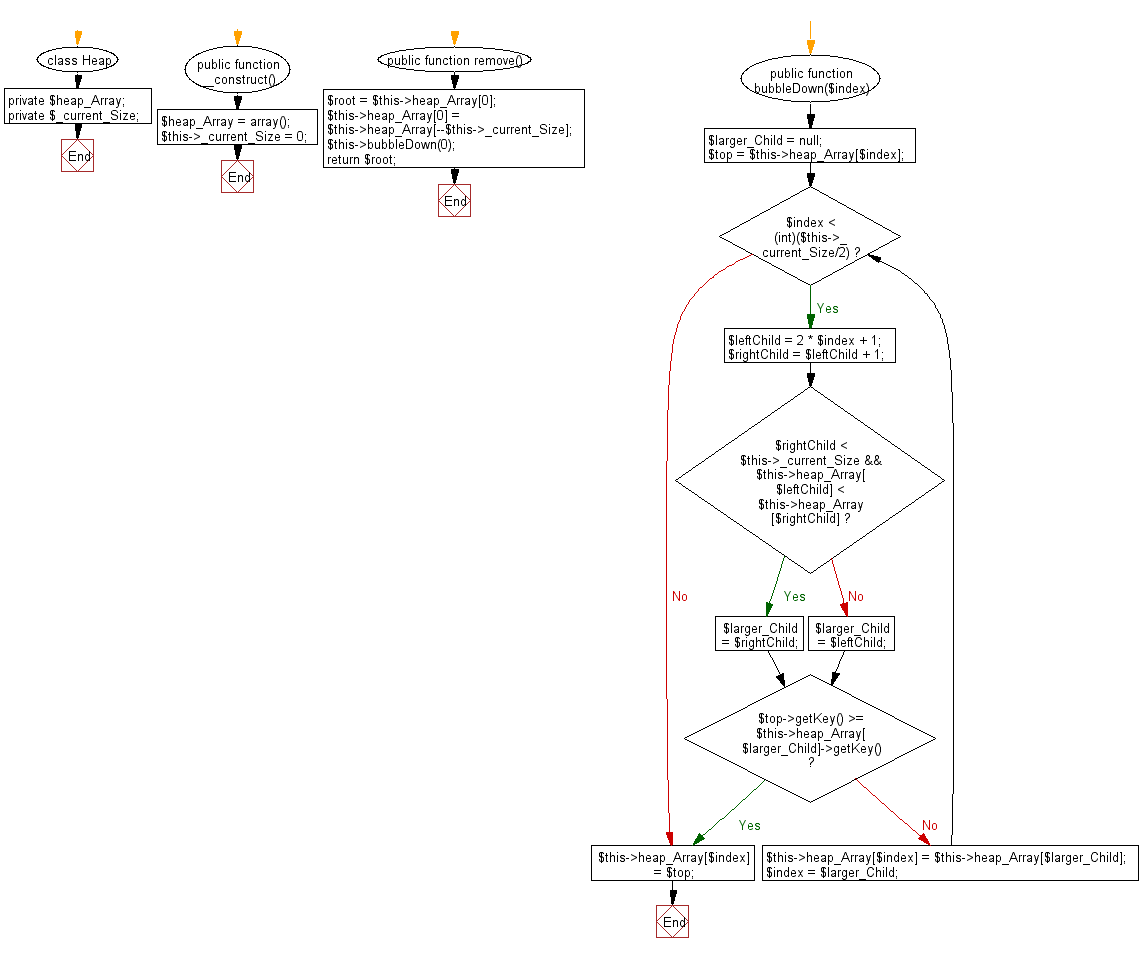
function merge_sort(left_part,right_part)
{
var i = 0;
var j = 0;
var results = [];
while (i < left_part.length || j < right_part.length) {
if (i === left_part.length) {
// j is the only index left_part
results.push(right_part[j]);
j++;
}
else if (j === right_part.length || left_part[i] <= right_part[j]) {
results.push(left_part[i]);
i++;
} else {
results.push(right_part[j]);
j++;
}
}
return results;
}
console.log(merge_sort([1,3,4], [3,7,9]));
Sample Output:
[1,3,3,4,7,9]
Flowchart:
Sample Solution-2:
- Use recursion.
- Use the spread operator (...) to clone the original array, arr.
- If the length of the array is less than 2, return the cloned array.
- Use Math.floor() to calculate the index of the pivot element.
- Use Array.prototype.reduce() and Array.prototype.push() to split the array into two subarrays (elements smaller or equal to the pivot and elements greater than it), destructuring the result into two arrays.
- Recursively call quickSort() on the created subarrays.
JavaScript Code:
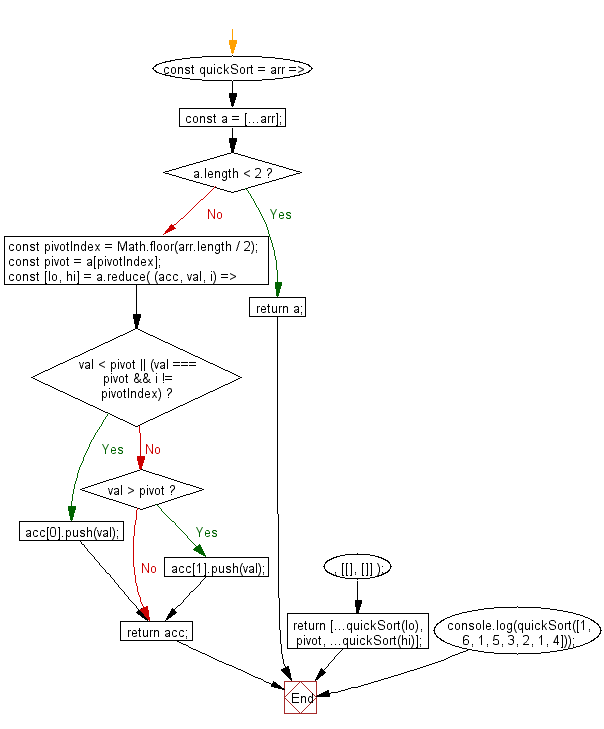
const quickSort = arr => {
const a = [...arr];
if (a.length < 2) return a;
const pivotIndex = Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
const pivot = a[pivotIndex];
const [lo, hi] = a.reduce(
(acc, val, i) => {
if (val < pivot || (val === pivot && i != pivotIndex)) {
acc[0].push(val);
} else if (val > pivot) {
acc[1].push(val);
}
return acc;
},
[[], []]
);
return [...quickSort(lo), pivot, ...quickSort(hi)];
};
console.log(quickSort([1, 6, 1, 5, 3, 2, 1, 4]));
Sample Output:
[1,1,1,2,3,4,5,6]
Flowchart:
Live Demo:
See the Pen searching-and-sorting-algorithm-exercise-2 by w3resource (@w3resource) on CodePen.
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a JavaScript function that implements merge sort recursively and returns the sorted array.
- Write a JavaScript function that logs the merging process at each recursive step during merge sort.
- Write a JavaScript function that applies merge sort on an array of strings and preserves case-insensitive order.
- Write a JavaScript function that adapts merge sort to work with a linked list structure.
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
Previous: Write a JavaScript program to sort a list of elements using Quick sort.
Next: Write a JavaScript program to sort a list of elements using Heap sort.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
