JavaScript Exercises: Insert a new node at any position of a Doubly Linked List
JavaScript Data Structures: Exercise-5 with Solution
Insert a new node at any position in a DLL
Write a JavaScript program to insert a new node at any position of a Doubly Linked List.
Sample Solution:
JavaScript Code:
// Define a class for creating nodes of a doubly linked list
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value; // Store the value of the node
this.next = null; // Pointer to the next node in the list, initially set to null
this.previous = null; // Pointer to the previous node in the list, initially set to null
}
}
// Define a class for creating a doubly linked list
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor(value) {
// Initialize the head node with the given value and no next or previous node
this.head = {
value: value, // Store the value of the head node
next: null, // Pointer to the next node in the list, initially set to null
previous: null // Pointer to the previous node in the list, initially set to null
};
this.length = 0; // Initialize the length of the list to 0
this.tail = this.head; // Set the tail node to the head node initially
}
// Method to add a new node at the end of the list
add(newNode) {
// Check if the head is null, indicating an empty list
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = newNode; // Set the head to the new node
this.tail = newNode; // Set the tail to the new node
} else {
newNode.previous = this.tail; // Set the previous pointer of the new node to the current tail
this.tail.next = newNode; // Set the next pointer of the current tail to the new node
this.tail = newNode; // Update the tail to the new node
}
this.length++; // Increment the length of the list
}
// Method to insert a new node at a specified position in the list
insertAt(position, data) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) {
return false; // Return false if the position is invalid
}
var newNode = { // Create a new node with the given data
value: data,
next: null,
previous: null
};
if (this.length === 0) { // If the list is empty, set the head and tail to the new node
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
} else if (position === 0) { // If inserting at the beginning, update the head
newNode.next = this.head;
this.head.previous = newNode;
this.head = newNode;
} else if (position === this.length) { // If inserting at the end, update the tail
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.previous = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
} else { // Otherwise, find the position and insert the new node
var current = this.head;
var index = 0;
while (index < position) {
current = current.next;
index++;
}
newNode.next = current;
newNode.previous = current.previous;
current.previous.next = newNode;
current.previous = newNode;
}
this.length++; // Increment the length of the list
return true; // Return true to indicate successful insertion
}
// Method to print the values of the nodes in the list
printList() {
let current = this.head; // Start from the head of the list
let result = []; // Array to store the values of the nodes
while (current !== null) { // Iterate through the list until reaching the end
result.push(current.value); // Push the value of the current node to the array
current = current.next; // Move to the next node
}
console.log(result.join(' ')); // Log the values of the nodes separated by space
return this; // Return the DoublyLinkedList object for chaining
}
}
// Create a new instance of the DoublyLinkedList class
let numList = new DoublyLinkedList();
// Add nodes to the list
numList.add(new Node(2));
numList.add(new Node(3));
numList.add(new Node(4));
numList.add(new Node(5));
numList.add(new Node(6));
numList.add(new Node(7));
// Display the original doubly linked list
console.log("Original Doubly Linked List:");
numList.printList();
// Insert a new node at the 0th position with value 12
console.log("Insert at 0 position and value = 12");
numList.insertAt(0, 12);
numList.printList();
// Insert another new node at the 6th position with value 14
console.log("Insert at 6th position and value = 14");
numList.insertAt(6, 12);
numList.printList();
// Insert another new node at the 4th position with value 16
console.log("Insert at 4th position and value = 16");
numList.insertAt(4, 15);
Output:
Original Doubly Linked Lists: 2 3 4 5 6 7 Insert at 0 position and value = 12 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 Insert at 6th position and value = 14 12 2 3 4 5 12 6 7 Insert at 4th position and value = 16
Flowchart:
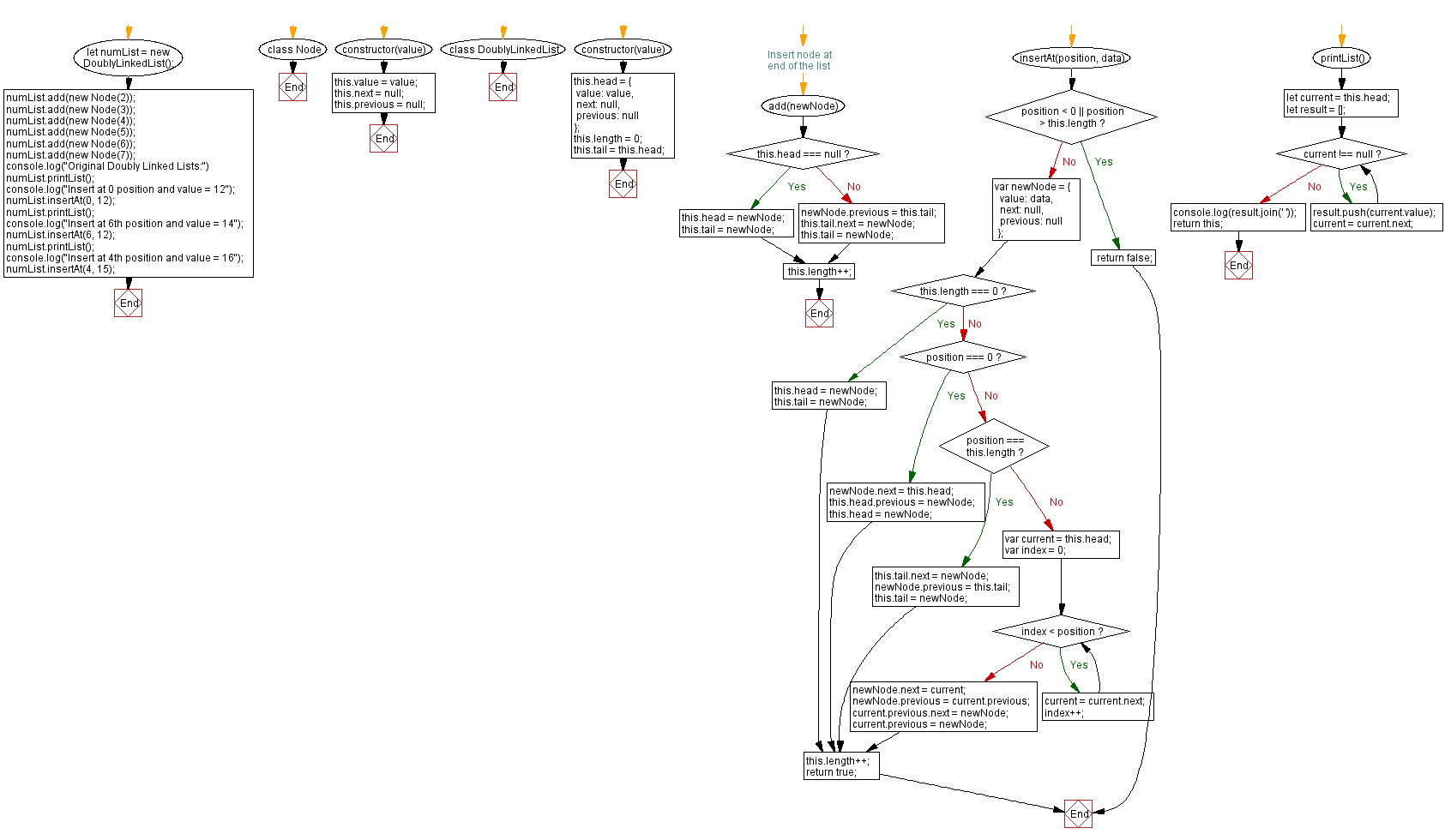
Live Demo:
See the Pen javascript-doubly-linked-list-exercise-5 by w3resource (@w3resource) on CodePen.
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a JavaScript function that inserts a new node at a specified index in a doubly linked list and updates the adjacent pointers.
- Write a JavaScript function that handles insertion in a DLL at various positions and verifies pointer consistency.
- Write a JavaScript function that inserts a node in a sorted DLL while maintaining sorted order.
- Write a JavaScript function that recursively inserts a node at the nth position in a doubly linked list.
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
Linked List Previous: Head and Tail of a Doubly Linked Lists.
Linked List Next: Insert a new node at the beginning of a Doubly Linked List.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
