Java: Print after removing duplicates from a given string
38. Remove Duplicate Characters
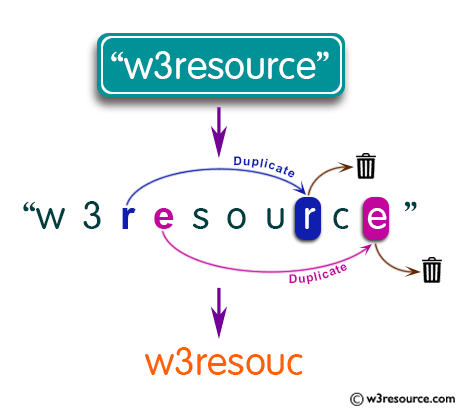
Write a Java program to print the result of removing duplicates from a given string.
Visual Presentation:
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Importing necessary Java utilities.
import java.util.*;
// Define a class named Main.
public class Main {
// Main method to execute the program.
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare and initialize a string variable.
String str1 = "w3resource";
// Print the original string.
System.out.println("The given string is: " + str1);
// Print the new string after removing duplicate characters.
System.out.println("After removing duplicates characters the new string is: " + removeDuplicateChars(str1));
}
// Method to remove duplicate characters from a string.
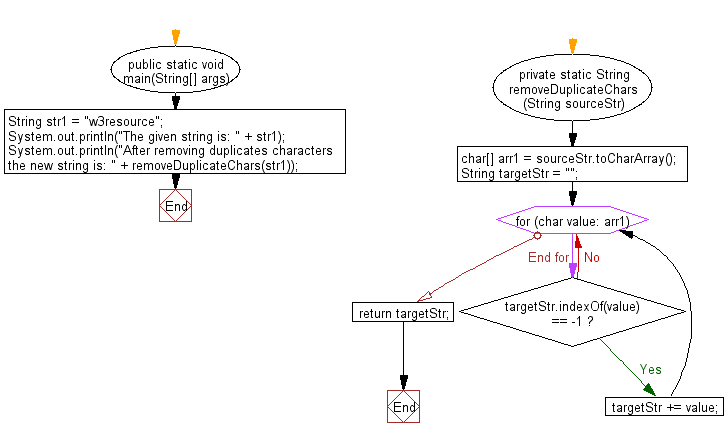
private static String removeDuplicateChars(String sourceStr) {
// Convert the input string to a character array.
char[] arr1 = sourceStr.toCharArray();
// Initialize an empty string to store the resulting string without duplicates.
String targetStr = "";
// Loop through each character in the character array.
for (char value: arr1) {
// Check if the character doesn't exist in the targetStr.
if (targetStr.indexOf(value) == -1) {
// If the character doesn't exist, add it to the targetStr.
targetStr += value;
}
}
// Return the resulting string without duplicates.
return targetStr;
}
}
Sample Output:
The given string is: w3resource After removing duplicates characters the new string is: w3resouc
Flowchart:
Remove duplicate characters from a given string.
Main.java Code:
//MIT License: https://bit.ly/35gZLa3
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
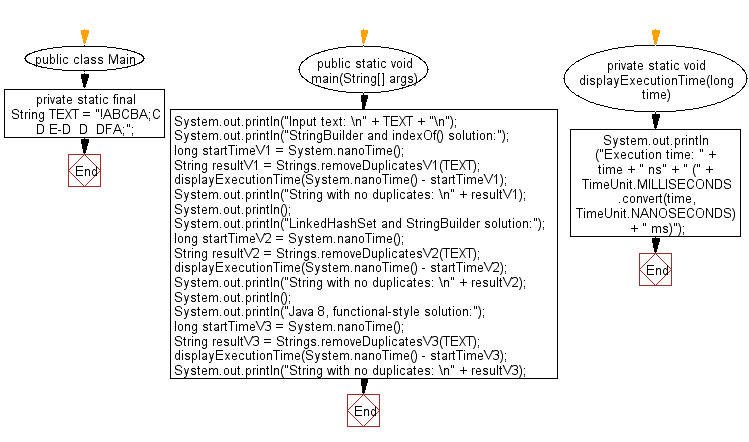
public class Main {
private static final String TEXT = "!ABCBA;C D E-D D DFA;";
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Input text: \n" + TEXT + "\n");
System.out.println("StringBuilder and indexOf() solution:");
long startTimeV1 = System.nanoTime();
String resultV1 = Strings.removeDuplicatesV1(TEXT);
displayExecutionTime(System.nanoTime() - startTimeV1);
System.out.println("String with no duplicates: \n" + resultV1);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("LinkedHashSet and StringBuilder solution:");
long startTimeV2 = System.nanoTime();
String resultV2 = Strings.removeDuplicatesV2(TEXT);
displayExecutionTime(System.nanoTime() - startTimeV2);
System.out.println("String with no duplicates: \n" + resultV2);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Java 8, functional-style solution:");
long startTimeV3 = System.nanoTime();
String resultV3 = Strings.removeDuplicatesV3(TEXT);
displayExecutionTime(System.nanoTime() - startTimeV3);
System.out.println("String with no duplicates: \n" + resultV3);
}
private static void displayExecutionTime(long time) {
System.out.println("Execution time: " + time + " ns" + " ("
+ TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(time, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS) + " ms)");
}
}
Strings.java Code:
//MIT License: https://bit.ly/35gZLa3
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
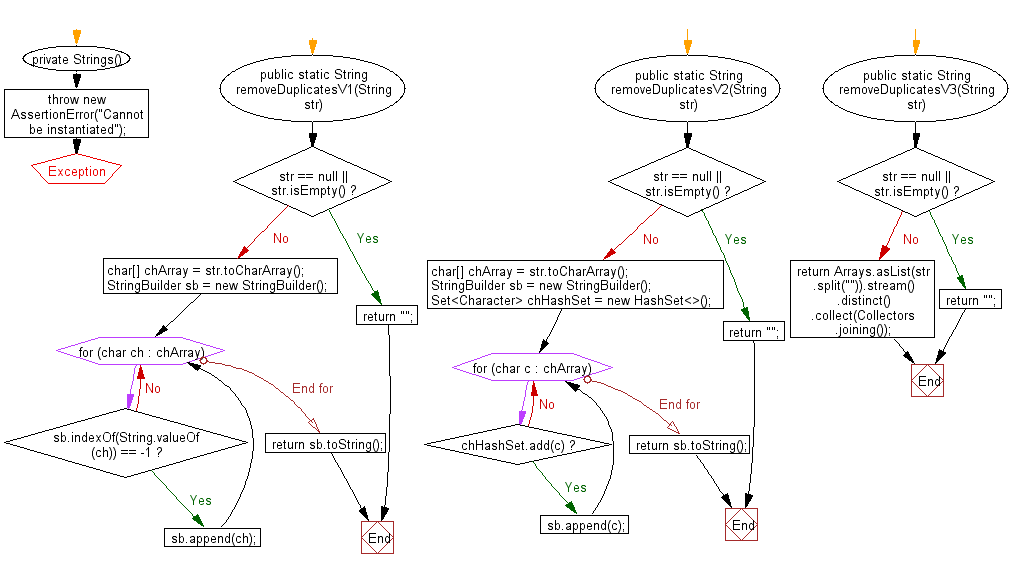
public final class Strings {
private Strings() {
throw new AssertionError("Cannot be instantiated");
}
public static String removeDuplicatesV1(String str) {
if (str == null || str.isEmpty()) {
// or throw IllegalArgumentException
return "";
}
char[] chArray = str.toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (char ch : chArray) {
if (sb.indexOf(String.valueOf(ch)) == -1) {
sb.append(ch);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static String removeDuplicatesV2(String str) {
if (str == null || str.isEmpty()) {
// or throw IllegalArgumentException
return "";
}
char[] chArray = str.toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Set<Character> chHashSet = new HashSet<>();
for (char c : chArray) {
if (chHashSet.add(c)) {
sb.append(c);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static String removeDuplicatesV3(String str) {
if (str == null || str.isEmpty()) {
// or throw IllegalArgumentException
return "";
}
return Arrays.asList(str.split("")).stream()
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.joining());
}
}
Sample Output:
Input text: !ABCBA;C D E-D D DFA; StringBuilder and indexOf() solution: Execution time: 760557 ns (0 ms) String with no duplicates: !ABC; DE-F LinkedHashSet and StringBuilder solution: Execution time: 705992 ns (0 ms) String with no duplicates: !ABC; DE-F Java 8, functional-style solution: Execution time: 84676685 ns (84 ms) String with no duplicates: !ABC; DE-F
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to remove all duplicate characters from a string while preserving the original order.
- Write a Java program to eliminate duplicate characters from a string and then reverse the resulting string.
- Write a Java program to remove duplicates from a string and count the number of characters removed.
- Write a Java program to filter out duplicate characters from a string and display only the unique ones in alphabetical order.
Go to:
PREV : Longest Substring Without Repeats.
NEXT : First Non-Repeating Character.
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
