Java: Checks if two stacks are equal
20. Check if two stacks are equal.
Write a Java program that implements a stack and checks if two stacks are equal.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
import java.util.Scanner;
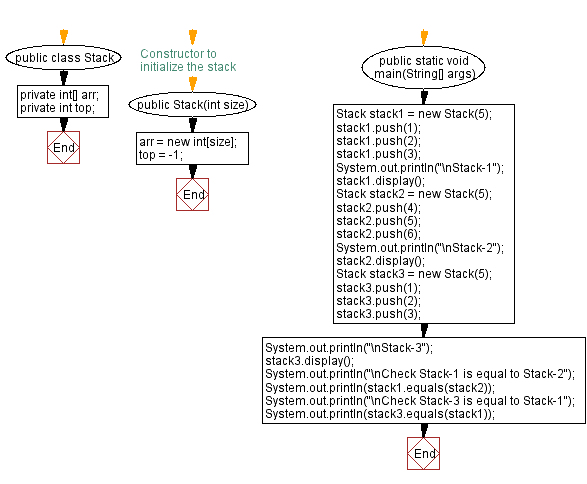
public class Stack {
private int[] arr;
private int top;
// Constructor to initialize the stack
public Stack(int size) {
arr = new int[size];
top = -1;
}
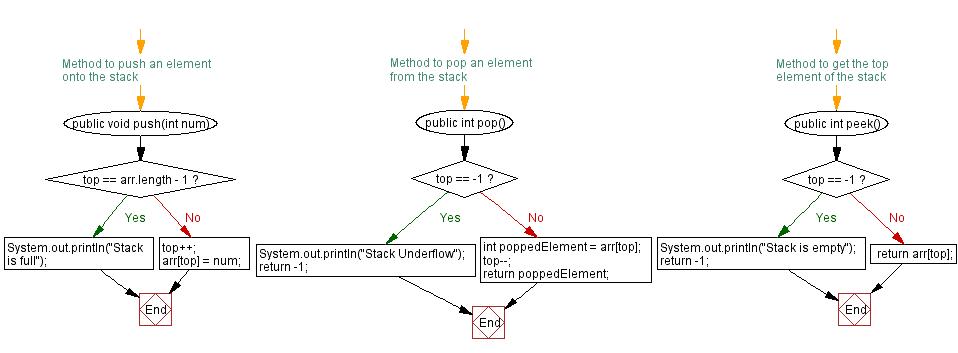
// Method to push an element onto the stack
public void push(int num) {
if (top == arr.length - 1) {
System.out.println("Stack is full");
} else {
top++;
arr[top] = num;
}
}
// Method to pop an element from the stack
public int pop() {
if (top == -1) {
System.out.println("Stack Underflow");
return -1;
} else {
int poppedElement = arr[top];
top--;
return poppedElement;
}
}
// Method to get the top element of the stack
public int peek() {
if (top == -1) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return -1;
} else {
return arr[top];
}
}
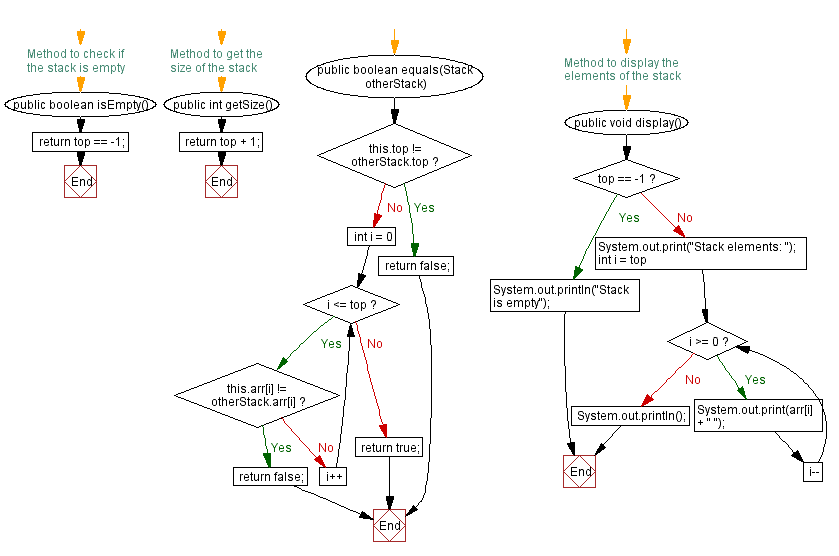
// Method to check if the stack is empty
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
// Method to get the size of the stack
public int getSize() {
return top + 1;
}
public boolean equals(Stack otherStack) {
if (this.top != otherStack.top) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++) {
if (this.arr[i] != otherStack.arr[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Method to display the elements of the stack
public void display() {
if (top == -1) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
} else {
System.out.print("Stack elements: ");
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack stack1 = new Stack(5);
stack1.push(1);
stack1.push(2);
stack1.push(3);
System.out.println("\nStack-1");
stack1.display();
Stack stack2 = new Stack(5);
stack2.push(4);
stack2.push(5);
stack2.push(6);
System.out.println("\nStack-2");
stack2.display();
Stack stack3 = new Stack(5);
stack3.push(1);
stack3.push(2);
stack3.push(3);
System.out.println("\nStack-3");
stack3.display();
System.out.println("\nCheck Stack-1 is equal to Stack-2");
System.out.println(stack1.equals(stack2));
System.out.println("\nCheck Stack-3 is equal to Stack-1");
System.out.println(stack3.equals(stack1));
}
}
Sample Output:
Stack-1 Stack elements: 3 2 1 Stack-2 Stack elements: 6 5 4 Stack-3 Stack elements: 3 2 1 Check Stack-1 is equal to Stack-2 false Check Stack-3 is equal to Stack-1 true
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to compare two stacks element-by-element for equality using an iterative approach.
- Write a Java program to check if two stacks are equal in content and order by converting them to arrays.
- Write a Java program to implement a recursive method that compares two stacks for equality without modifying them.
- Write a Java program to use Java streams to compare two stacks by zipping their elements and checking for mismatches.
Go to:
PREV : Check if one stack is a subset of another stack.
NEXT : Find common elements between two stacks.
Live Demo:
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
