Java Recursive Method: Count occurrences of a specific element
Recursive Element Count in Array
Write a Java recursive method to count the number of occurrences of a specific element in an array.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
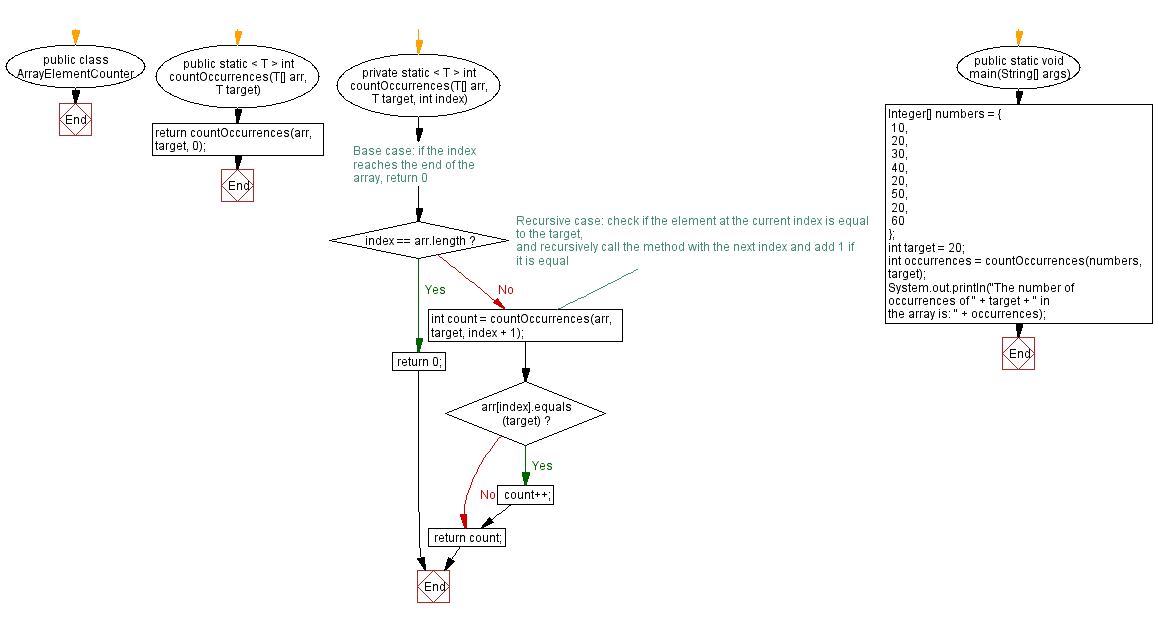
public class ArrayElementCounter {
public static < T > int countOccurrences(T[] arr, T target) {
return countOccurrences(arr, target, 0);
}
private static < T > int countOccurrences(T[] arr, T target, int index) {
// Base case: if the index reaches the end of the array, return 0
if (index == arr.length) {
return 0;
}
// Recursive case: check if the element at the current index is equal to the target,
// and recursively call the method with the next index and add 1 if it is equal
int count = countOccurrences(arr, target, index + 1);
if (arr[index].equals(target)) {
count++;
}
return count;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] numbers = {
10,
20,
30,
40,
20,
50,
20,
60
};
int target = 20;
int occurrences = countOccurrences(numbers, target);
System.out.println("The number of occurrences of " + target + " in the array is: " + occurrences);
}
}
Sample Output:
The number of occurrences of 20 in the array is: 3
Explanation:
In the above exercises -
First, we define a class "ArrayElementCounter" that includes a recursive method countOccurrences() to count the number of occurrences of a specific element target in an array arr.
The countOccurrences() method has two cases:
- Base case: If the index reaches the end of the array (index == arr.length), we return 0 as there are no more elements to check.
- Recursive case: For any index that is within the bounds of the array, we check if the element at that index is equal to the target. We then recursively call the method with the next index and add 1 to the count if the element is equal to the target. This process continues until we reach the end of the array.
In the main() method, we demonstrate the usage of the countOccurrences() method by counting the number of occurrences of the number 20 in the array {10, 20, 30, 40, 20, 50, 20, 60}and printing the result.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to recursively count the occurrences of a specified element in an array using a divide-and-conquer approach.
- Write a Java program to recursively count the number of even elements in an array.
- Write a Java program to recursively count the number of elements greater than a given threshold in an array.
- Write a Java program to recursively count the occurrences of a target string in an array of strings.
Java Code Editor:
Java Recursive Previous: Find the greatest common divisor.
Java Recursive Next: Sum of odd numbers in an array.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
