Java: School Management System
Write a Java program to create a class called "School" with attributes for students, teachers, and classes, and methods to add and remove students and teachers, and to create classes.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
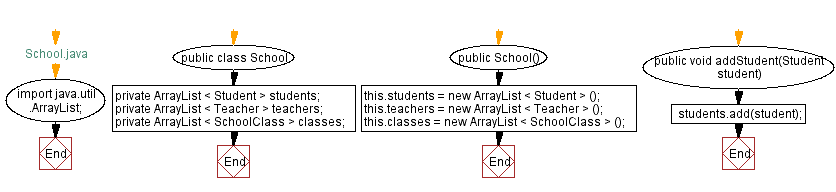
// School.java
// Import the ArrayList class from the java.util package
import java.util.ArrayList;
// Define the School class
public class School {
// Private field to store a list of Student objects
private ArrayList<Student> students;
// Private field to store a list of Teacher objects
private ArrayList<Teacher> teachers;
// Private field to store a list of SchoolClass objects
private ArrayList<SchoolClass> classes;
// Constructor to initialize the students, teachers, and classes fields
public School() {
// Create a new ArrayList to hold Student objects
this.students = new ArrayList<Student>();
// Create a new ArrayList to hold Teacher objects
this.teachers = new ArrayList<Teacher>();
// Create a new ArrayList to hold SchoolClass objects
this.classes = new ArrayList<SchoolClass>();
}
// Method to add a Student to the students list
public void addStudent(Student student) {
// Add the specified student to the students list
students.add(student);
}
// Method to remove a Student from the students list
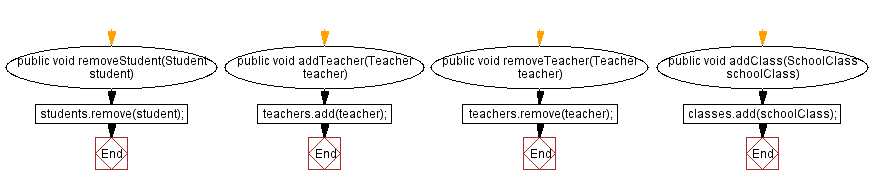
public void removeStudent(Student student) {
// Remove the specified student from the students list
students.remove(student);
}
// Method to add a Teacher to the teachers list
public void addTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
// Add the specified teacher to the teachers list
teachers.add(teacher);
}
// Method to remove a Teacher from the teachers list
public void removeTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
// Remove the specified teacher from the teachers list
teachers.remove(teacher);
}
// Method to add a SchoolClass to the classes list
public void addClass(SchoolClass schoolClass) {
// Add the specified school class to the classes list
classes.add(schoolClass);
}
// Method to remove a SchoolClass from the classes list
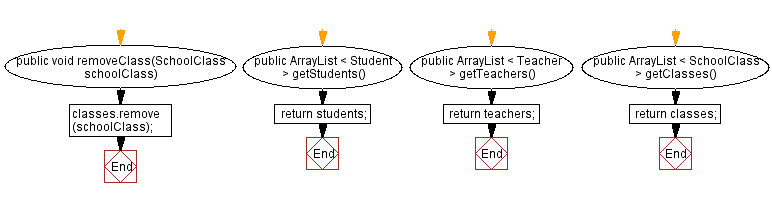
public void removeClass(SchoolClass schoolClass) {
// Remove the specified school class from the classes list
classes.remove(schoolClass);
}
// Method to get the list of students
public ArrayList<Student> getStudents() {
// Return the list of students
return students;
}
// Method to get the list of teachers
public ArrayList<Teacher> getTeachers() {
// Return the list of teachers
return teachers;
}
// Method to get the list of classes
public ArrayList<SchoolClass> getClasses() {
// Return the list of classes
return classes;
}
}
The above "School" class represents a school with students, teachers, and classes. It has three ArrayList attributes to store Student, Teacher, and SchoolClass objects. The constructor initializes these ArrayLists as empty lists. It has methods to add and remove students, teachers, and classes from their respective ArrayLists. It also has getter methods to access ArrayLists of students, teachers, and classes.
// Student.java
// Define the Student class
public class Student {
// Private field to store the name of the student
private String name;
// Private field to store the age of the student
private int age;
// Constructor to initialize the name and age of the student
public Student(String name, int age) {
// Assign the name parameter to the name field
this.name = name;
// Assign the age parameter to the age field
this.age = age;
}
// Getter method for the name field
public String getName() {
// Return the value of the name field
return name;
}
// Setter method for the name field
public void setName(String name) {
// Assign the name parameter to the name field
this.name = name;
}
// Getter method for the age field
public int getAge() {
// Return the value of the age field
return age;
}
// Setter method for the age field
public void setAge(int age) {
// Assign the age parameter to the age field
this.age = age;
}
}
The "Student" class represents a student with a name and an age. It has a constructor that takes two arguments, name and age, and initializes the corresponding attributes. It also has getter and setter methods to access and modify name and age attributes.
// Teacher.class
// Define the Teacher class
public class Teacher {
// Private field to store the name of the teacher
private String name;
// Private field to store the subject of the teacher
private String subject;
// Constructor to initialize the name and subject of the teacher
public Teacher(String name, String subject) {
// Assign the name parameter to the name field
this.name = name;
// Assign the subject parameter to the subject field
this.subject = subject;
}
// Getter method for the name field
public String getName() {
// Return the value of the name field
return name;
}
// Setter method for the name field
public void setName(String name) {
// Assign the name parameter to the name field
this.name = name;
}
// Getter method for the subject field
public String getSubject() {
// Return the value of the subject field
return subject;
}
// Setter method for the subject field
public void setSubject(String subject) {
// Assign the subject parameter to the subject field
this.subject = subject;
}
}
The Teacher class represents a teacher in a school. It has two private attributes: name (teacher's name) and subject (Subject the teacher teaches). The class has a constructor that takes two arguments, the teacher's name and subject, and initializes the corresponding attributes. It also has getter and setter methods to access and modify the name and subject attributes.
// SchoolClass.java
// Import the ArrayList class from the java.util package
import java.util.ArrayList;
// Define the SchoolClass class
public class SchoolClass {
// Private field to store the name of the class
private String className;
// Private field to store the teacher of the class
private Teacher teacher;
// Private field to store a list of Student objects
private ArrayList<Student> students;
// Constructor to initialize the className, teacher, and students fields
public SchoolClass(String className, Teacher teacher) {
// Assign the className parameter to the className field
this.className = className;
// Assign the teacher parameter to the teacher field
this.teacher = teacher;
// Create a new ArrayList to hold Student objects
this.students = new ArrayList<Student>();
}
// Getter method for the className field
public String getClassName() {
// Return the value of the className field
return className;
}
// Setter method for the className field
public void setClassName(String className) {
// Assign the className parameter to the className field
this.className = className;
}
// Getter method for the teacher field
public Teacher getTeacher() {
// Return the value of the teacher field
return teacher;
}
// Setter method for the teacher field
public void setTeacher(Teacher teacher) {
// Assign the teacher parameter to the teacher field
this.teacher = teacher;
}
// Getter method for the students field
public ArrayList<Student> getStudents() {
// Return the list of students
return students;
}
// Method to add a Student to the students list
public void addStudent(Student student) {
// Add the specified student to the students list
students.add(student);
}
// Method to remove a Student from the students list
public void removeStudent(Student student) {
// Remove the specified student from the students list
students.remove(student);
}
}
The SchoolClass class represents a class in a school. It has a private attribute className to store the name of the class and another private attribute teacher of type Teacher to store the teacher of the class. It also has a private attribute students of type ArrayList
The class has getter and setter methods for className and teacher. It also has methods addStudent and removeStudent to add and remove a student from the students list. The getStudents method returns the list of students in the class.
//Main.java
// Import the ArrayList class from the java.util package
import java.util.ArrayList;
// Define the Main class
public class Main {
// Main method, entry point of the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new instance of the School class
School school = new School();
// Create new Student objects with name and age
Student student1 = new Student("Mats Yatzil", 15);
Student student2 = new Student("Karolina Ralf", 16);
Student student3 = new Student("Felicie Anuschka", 16);
Student student4 = new Student("Norbert Micha", 15);
// Add the students to the school
school.addStudent(student1);
school.addStudent(student2);
school.addStudent(student3);
school.addStudent(student4);
// Create new Teacher objects with name and subject
Teacher teacher1 = new Teacher("Jens Amalia", "Math");
Teacher teacher2 = new Teacher("Elise Giiwedin", "English");
Teacher teacher3 = new Teacher("Angelika Lotta", "Science");
// Add the teachers to the school
school.addTeacher(teacher1);
school.addTeacher(teacher2);
school.addTeacher(teacher3);
// Create new SchoolClass objects with class name and teacher
SchoolClass mathClass = new SchoolClass("Mathematics", teacher1);
// Add students to the math class
mathClass.addStudent(student1);
mathClass.addStudent(student2);
mathClass.addStudent(student3);
mathClass.addStudent(student4);
SchoolClass englishClass = new SchoolClass("English", teacher2);
// Add students to the English class
englishClass.addStudent(student1);
englishClass.addStudent(student2);
englishClass.addStudent(student3);
SchoolClass scienceClass = new SchoolClass("Science", teacher3);
// Add students to the Science class
scienceClass.addStudent(student1);
scienceClass.addStudent(student2);
scienceClass.addStudent(student3);
scienceClass.addStudent(student4);
// Add the classes to the school
school.addClass(mathClass);
school.addClass(englishClass);
school.addClass(scienceClass);
// Print general school information
System.out.println("School information:");
System.out.println("Number of students: " + school.getStudents().size());
System.out.println("Number of teachers: " + school.getTeachers().size());
System.out.println("Number of classes: " + school.getClasses().size());
System.out.println();
// Print math class information
System.out.println("Math class information:");
System.out.println("Class name: " + mathClass.getClassName());
System.out.println("Teacher: " + mathClass.getTeacher().getName());
System.out.println("Number of students: " + mathClass.getStudents().size());
System.out.println();
// Print English class information
System.out.println("English class information:");
System.out.println("Class name: " + englishClass.getClassName());
System.out.println("Teacher: " + englishClass.getTeacher().getName());
System.out.println("Number of students: " + englishClass.getStudents().size());
System.out.println();
// Print Science class information
System.out.println("Science class information:");
System.out.println("Class name: " + scienceClass.getClassName());
System.out.println("Teacher: " + scienceClass.getTeacher().getName());
System.out.println("Number of students: " + scienceClass.getStudents().size());
System.out.println();
// Remove a student, a teacher, and a class from the school
school.removeStudent(student1);
school.removeTeacher(teacher2);
school.removeClass(mathClass);
// Print updated school information after removal
System.out.println("School information after removing one student, teacher and class:");
System.out.println("Number of students: " + school.getStudents().size());
System.out.println("Number of teachers: " + school.getTeachers().size());
System.out.println("Number of classes: " + school.getClasses().size());
}
}
The "Main" class is the program entry point. It creates objects of the "School", "Student", "Teacher", and "SchoolClass" classes to demonstrate the school system's functionality. It adds students, teachers, and classes to the school object using its respective methods. It then retrieves and prints information about the number of students, teachers, and classes in the school. It also prints the details of each class, including the name of the class, the teacher's name, and the number of students in each class. Finally, it removes one student, one teacher, and one class from the school and prints updated information about the school.
Sample Output:
School information: Number of students: 4 Number of teachers: 3 Number of classes: 3 Math class information: Class name: Mathematics Teacher: Jens Amalia Number of students: 4 English class information: Class name: English Teacher: Elise Giiwedin Number of students: 3 Science class information: Class name: Science Teacher: Angelika Lotta Number of students: 4 School information after removing one student, teacher and Class: Number of students: 3 Number of teachers: 2 Number of classes: 2
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "School" class tracks teacher performance based on student feedback.
- Write a Java program to modify the "School" class so that it assigns students to classes dynamically based on subject preferences.
- Write a Java program where the "School" class schedules parent-teacher meetings based on student performance.
- Write a Java program to implement a method in the "School" class that predicts enrollment numbers for the next year.
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus.
Java OOP Previous: Inventory Management.
Java OOP Next: Manage a music library of songs.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
