Java: Inventory Management
Write a Java program to create a class called "Inventory" with a collection of products and methods to add and remove products, and to check for low inventory.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Product.java
// Define the Product class
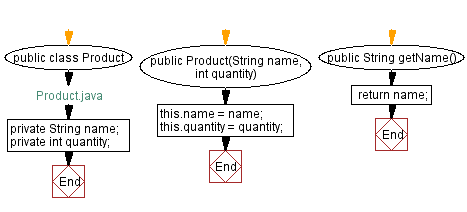
public class Product {
// Private field to store the name of the product
private String name;
// Private field to store the quantity of the product
private int quantity;
// Constructor to initialize the name and quantity of the product
public Product(String name, int quantity) {
// Assign the name parameter to the name field
this.name = name;
// Assign the quantity parameter to the quantity field
this.quantity = quantity;
}
// Getter method for the name field
public String getName() {
// Return the value of the name field
return name;
}
// Setter method for the name field
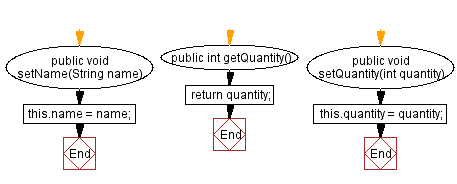
public void setName(String name) {
// Assign the name parameter to the name field
this.name = name;
}
// Getter method for the quantity field
public int getQuantity() {
// Return the value of the quantity field
return quantity;
}
// Setter method for the quantity field
public void setQuantity(int quantity) {
// Assign the quantity parameter to the quantity field
this.quantity = quantity;
}
}
In the above code, we create a class called "Product" with two private attributes, "name" and "quantity". We also create a constructor to initialize these attributes and getter and setter methods to access and modify them.
// Inventory.java
// Import the ArrayList class from the java.util package
import java.util.ArrayList;
// Define the Inventory class
public class Inventory {
// Private field to store a list of Product objects
private ArrayList<Product> products;
// Constructor to initialize the products field
public Inventory() {
// Create a new ArrayList to hold Product objects
products = new ArrayList<Product>();
}
// Method to add a Product to the products list
public void addProduct(Product product) {
// Add the specified product to the products list
products.add(product);
}
// Method to remove a Product from the products list
public void removeProduct(Product product) {
// Remove the specified product from the products list
products.remove(product);
}
// Method to check for low inventory products
public void checkLowInventory() {
// Iterate through the list of products
for (Product product : products) {
// Check if the product quantity is less than or equal to 100
if (product.getQuantity() <= 100) {
// Print a message indicating the product is running low on inventory
System.out.println(product.getName() + " is running low on inventory. Current quantity: " + product.getQuantity());
}
}
}
}
Here we create a class called "Inventory" with a private attribute "products", which is an ArrayList of Product objects. We also create a constructor to initialize this attribute as an empty list and methods to add and remove products from the list. Additionally, we create a method called "checkLowInventory()" to check for low inventory levels in the products list.
// Main.java
// Define the Main class
public class Main {
// Main method, entry point of the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new instance of the Inventory class
Inventory inventory = new Inventory();
// Create new Product objects with name and quantity
Product product1 = new Product("LED TV", 200);
Product product2 = new Product("Mobile", 80);
Product product3 = new Product("Tablet", 50);
// Print a message indicating products are being added to the inventory
System.out.println("Add three products in inventory:");
// Add the products to the inventory
inventory.addProduct(product1);
inventory.addProduct(product2);
inventory.addProduct(product3);
// Print a message indicating low inventory check
System.out.println("\nCheck low inventory:");
// Check and print products with low inventory
inventory.checkLowInventory();
// Print a message indicating a product is being removed from the inventory
System.out.println("\nRemove Tablet from the inventory!");
// Remove the Tablet product from the inventory
inventory.removeProduct(product3);
// Print a message indicating another low inventory check
System.out.println("\nAgain check low inventory:");
// Check and print products with low inventory again
inventory.checkLowInventory();
}
}
In the "Main" class, we create an instance of the Inventory class and add three Product objects to the list. We then call the "checkLowInventory()" method to check for low inventory levels. Next, we remove one of the products from the list and call the "checkLowInventory()" method again to see if there are any other low inventory levels.
Sample Output:
Add three products in inventory: Check low inventory: Mobile is running low on inventory. Current quantity: 80 Tablet is running low on inventory. Current quantity: 50 Remove Tablet from the inventory! Again check low inventory: Mobile is running low on inventory. Current quantity: 80
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Inventory" class automatically reorders products when stock is low.
- Write a Java program to implement a method in the "Inventory" class that predicts future demand for a product.
- Write a Java program where the "Inventory" class keeps track of expiration dates and removes expired products.
- Write a Java program to add a search feature in the "Inventory" class to find products by category.
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus.
Java OOP Previous: Airplane class to check flight status and delay.
Java OOP Next: School Management System.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
