Java: Manage student courses using the Student class
Write a Java program to create a class called "Student" with a name, grade, and courses attributes, and methods to add and remove courses.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
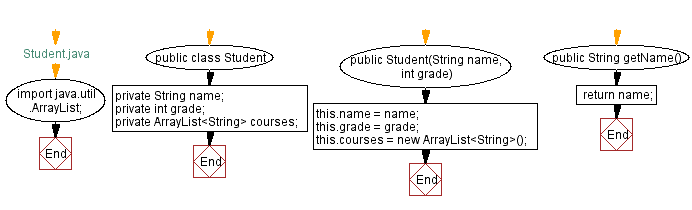
// Student.java
// Import the ArrayList class from the Java Collections Framework
import java.util.ArrayList;
// Define the Student class
public class Student {
// Declare a private variable to store the name of the student
private String name;
// Declare a private variable to store the grade of the student
private int grade;
// Declare a private ArrayList to store the courses of the student
private ArrayList courses;
// Constructor for the Student class
public Student(String name, int grade) {
// Initialize the name of the student
this.name = name;
// Initialize the grade of the student
this.grade = grade;
// Initialize the courses ArrayList
this.courses = new ArrayList();
}
// Method to get the name of the student
public String getName() {
// Return the name of the student
return name;
}
// Method to get the grade of the student
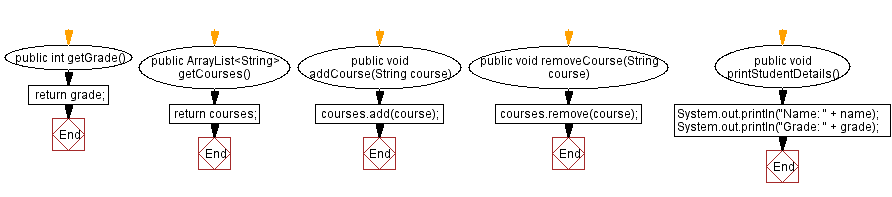
public int getGrade() {
// Return the grade of the student
return grade;
}
// Method to get the courses of the student
public ArrayList getCourses() {
// Return the courses ArrayList
return courses;
}
// Method to add a course to the student's course list
public void addCourse(String course) {
// Add the given course to the courses ArrayList
courses.add(course);
}
// Method to remove a course from the student's course list
public void removeCourse(String course) {
// Remove the given course from the courses ArrayList
courses.remove(course);
}
// Method to print the details of the student
public void printStudentDetails() {
// Print the name of the student
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
// Print the grade of the student
System.out.println("Grade: " + grade);
}
}
The above "Student" class has three private attributes: 'name', 'grade', and 'courses'. The 'name' and 'grade' attributes are initialized in the constructor with the values passed as arguments. The 'courses' attribute is initialized as an empty array list. There are getter methods for the 'name', 'grade', and 'courses' attributes. There are also methods to add and remove courses from the 'courses' attribute.
// Main.java
// Define the Main class
public class Main {
// Main method, the entry point of the Java application
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new Student object named student1 with name "Carolus Vitali" and grade 11
Student student1 = new Student("Carolus Vitali", 11);
// Create a new Student object named student2 with name "Nakeisha Uhuru" and grade 10
Student student2 = new Student("Nakeisha Uhuru", 10);
// Create a new Student object named student3 with name "Gabriella Cherice" and grade 10
Student student3 = new Student("Gabriella Cherice", 10);
// Print a header for student details
System.out.println("Student Details:");
// Print the details of student1
student1.printStudentDetails();
// Print the details of student2
student2.printStudentDetails();
// Print the details of student3
student3.printStudentDetails();
// Print a message indicating courses are being added for student1
System.out.println("Adding courses for " + student1.getName());
// Add the course "Math" to student1's courses
student1.addCourse("Math");
// Add the course "Science" to student1's courses
student1.addCourse("Science");
// Add the course "English" to student1's courses
student1.addCourse("English");
// Print student1's name and their list of courses
System.out.println(student1.getName() + "'s courses: " + student1.getCourses());
// Print a message indicating courses are being added for student2
System.out.println("\nAdding courses for " + student2.getName());
// Add the course "History" to student2's courses
student2.addCourse("History");
// Add the course "Geography" to student2's courses
student2.addCourse("Geography");
// Add the course "English" to student2's courses
student2.addCourse("English");
// Print student2's name and their list of courses
System.out.println(student2.getName() + "'s courses: " + student2.getCourses());
// Print a message indicating the course "Science" is being removed for student1
System.out.println("\nRemoving 'Science' course for " + student1.getName());
// Remove the course "Science" from student1's courses
student1.removeCourse("Science");
// Print student1's name and their updated list of courses
System.out.println(student1.getName() + "'s courses: " + student1.getCourses());
}
}
The above Main class creates three instances of the Student class, adds courses to their courses list using the “addCourse()” method, and prints out the list of courses for each student using the “getCourses()” method. It then removes a course for student1 using the ‘removeCourse()’ method, and prints out the updated list of courses for student1.
Sample Output:
Student Details: Name: Carolus Vitali Grade: 11 Name: Nakeisha Uhuru Grade: 10 Name: Gabriella Cherice Grade: 10 Adding courses for Carolus Vitali Carolus Vitali's courses: [Math, Science, English] Adding courses for Nakeisha Uhuru Nakeisha Uhuru's courses: [History, Geography, English] Removing 'Science' course for Carolus Vitali Carolus Vitali's courses: [Math, English]
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to modify the "Student" class to calculate the average grade of all enrolled courses.
- Write a Java program where the "Student" class keeps a record of attendance and warns if attendance is too low.
- Write a Java program to implement a method in the "Student" class that checks if a student is eligible for a scholarship.
- Write a Java program where the "Student" class tracks a student's progress and predicts graduation date.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus.
PREV : Employee class with years of service calculation.
NEXT : Library class with add and remove books methods.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
