Java Program: Thread Synchronization with Semaphores
From Wikipedia -
In computer science, a semaphore is a variable or abstract data type used to control access to a common resource by multiple threads and avoid critical section problems in a concurrent system such as a multitasking operating system. Semaphores are a type of synchronization primitive.
4. Use Semaphore for thread synchronization
Write a Java program to demonstrate Semaphore usage for thread synchronization.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
//SemaphoreExercise.java
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
public class SemaphoreExercise {
private static final int NUM_THREADS = 5;
private static final int NUM_PERMITS = 2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(NUM_PERMITS);
Thread[] threads = new Thread[NUM_THREADS];
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(new Worker(semaphore));
threads[i].start();
}
try {
for (Thread thread: threads) {
thread.join();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static class Worker implements Runnable {
private Semaphore semaphore;
public Worker(Semaphore semaphore) {
this.semaphore = semaphore;
}
public void run() {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
// Perform work that requires the semaphore
System.out.println("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " acquired the semaphore.");
Thread.sleep(2000); // Simulating work
System.out.println("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " released the semaphore.");
semaphore.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Sample Output:
Thread Thread-0 acquired the semaphore. Thread Thread-1 acquired the semaphore. Thread Thread-0 released the semaphore. Thread Thread-1 released the semaphore. Thread Thread-2 acquired the semaphore. Thread Thread-3 acquired the semaphore. Thread Thread-3 released the semaphore. Thread Thread-2 released the semaphore. Thread Thread-4 acquired the semaphore. Thread Thread-4 released the semaphore.
Explanation:
In the above exercise -
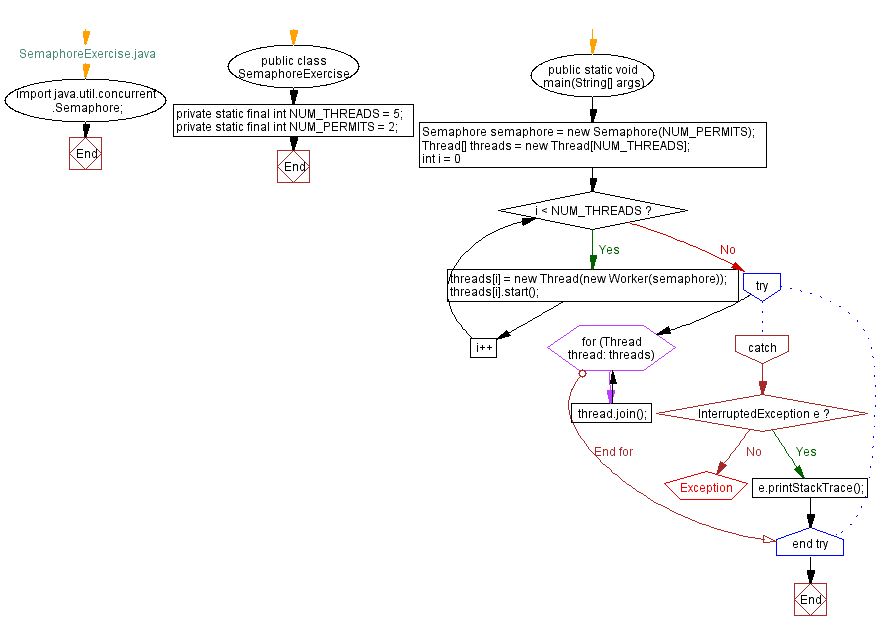
- The "SemaphoreExercise" class represents the main program. It creates an instance of "Semaphore" with a specified number of permits (NUM_PERMITS).
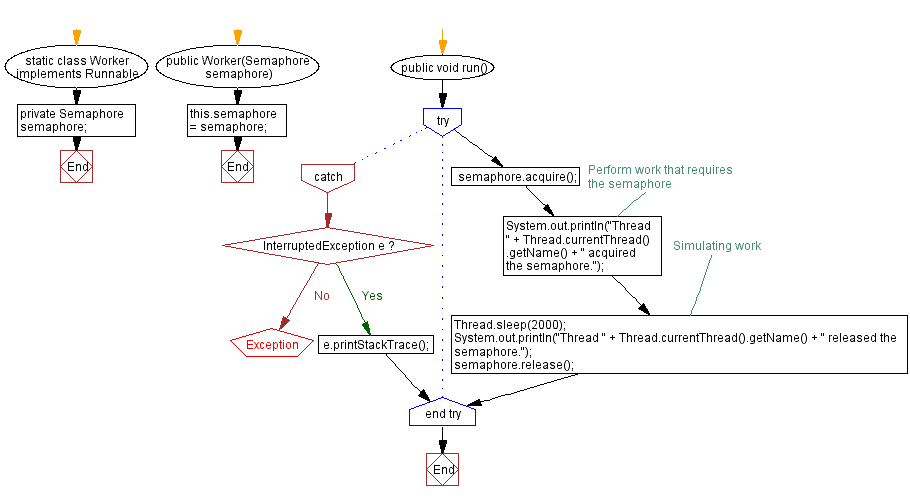
- The "Worker" class implements the Runnable interface and represents a worker thread. Each worker thread acquires a permit from the semaphore using the acquire() method. It performs some work that requires the semaphore, and then releases the permit using the release() method.
- In the main() method, we create an array of worker threads, start them concurrently, and wait for them to finish using the join() method.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to implement a semaphore that limits concurrent access to a resource among multiple threads.
- Write a Java program to simulate a fixed-size thread pool using semaphores to control the number of active threads.
- Write a Java program to create a resource pool where a semaphore manages the available resource count concurrently.
- Write a Java program to test semaphore fairness by simulating high contention among threads and logging their access order.
Go to:
PREV : Synchronize threads using ReentrantLock.
NEXT : Synchronize threads using CyclicBarrier.
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
