Asynchronous Task Execution in Java with Callable and Future
12. Use Callable and Future for async execution
Write a Java program to demonstrate the usage of the Callable and Future interfaces for executing tasks asynchronously and obtaining their results.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
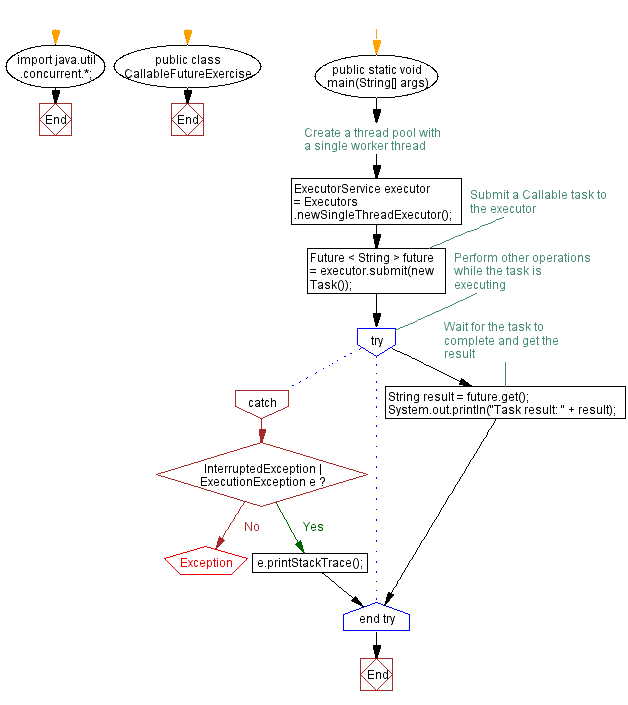
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CallableFutureExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a thread pool with a single worker thread
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// Submit a Callable task to the executor
Future < String > future = executor.submit(new Task());
// Perform other operations while the task is executing
try {
// Wait for the task to complete and get the result
String result = future.get();
System.out.println("Task result: " + result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
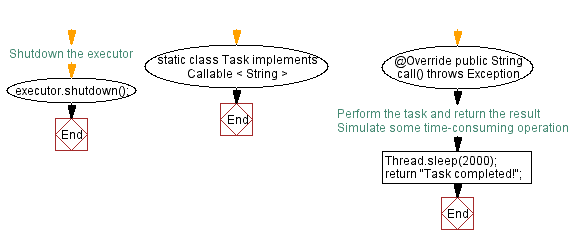
// Shutdown the executor
executor.shutdown();
}
static class Task implements Callable < String > {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
// Perform the task and return the result
Thread.sleep(2000); // Simulate some time-consuming operation
return "Task completed!";
}
}
}
Sample Output:
Task result: Task completed!
Explanation:
In the above exercise -
- First we create a Callable task called "Task" that performs a time-consuming operation and returns a String result. We then create an ExecutorService with a single worker thread using the Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() method.
- We submit the Task to the executor using the submit() method, which returns a Future object representing the task result. We can continue performing other operations while the task executes.
- To obtain the result of the task, we call the get() method on the Future object. This method blocks until the task is complete and returns the result. We handle possible exceptions like InterruptedException and ExecutionException that may occur during the execution or retrieval of the result.
- Finally, we shutdown the executor using the shutdown() method to release its resources.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to submit multiple Callable tasks to an ExecutorService and retrieve their results using Future.get().
- Write a Java program to implement a timeout mechanism for asynchronous tasks using Future.get() with a timeout parameter.
- Write a Java program to chain multiple Callable tasks and combine their results using Future and CompletableFuture.
- Write a Java program to handle exceptions in asynchronous tasks by wrapping Callable tasks and processing Future exceptions.
Go to:
PREV : Exchange data between threads using Exchanger.
NEXT : Schedule tasks using ScheduledExecutorService.
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
