Java ProPolymorphism: Shape base class with Circle, Square, and Triangle subclasses
Write a Java program to create a base class Shape with methods draw() and calculateArea(). Create three subclasses: Circle, Square, and Triangle. Override the draw() method in each subclass to draw the respective shape, and override the calculateArea() method to calculate and return the area of each shape.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Shape.java
// Define an abstract class named Shape
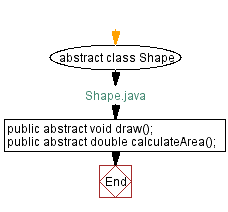
abstract class Shape {
// Declare an abstract method draw, to be implemented by subclasses
public abstract void draw();
// Declare an abstract method calculateArea, to be implemented by subclasses
public abstract double calculateArea();
}
// Circle.java
// Define a class named Circle that extends Shape
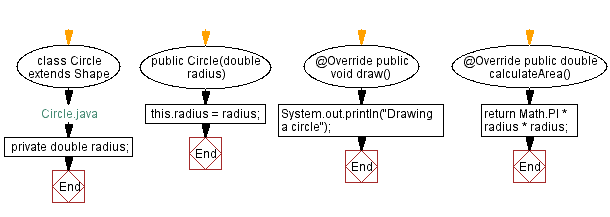
class Circle extends Shape {
// Declare a private double variable radius
private double radius;
// Define a constructor that takes a double radius as a parameter
public Circle(double radius) {
// Assign the parameter radius to the instance variable radius
this.radius = radius;
}
// Override the draw method from the Shape class
@Override
public void draw() {
// Print "Drawing a circle" to the console
System.out.println("Drawing a circle");
}
// Override the calculateArea method from the Shape class
@Override
public double calculateArea() {
// Return the area of the circle using the formula π * radius^2
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
}
// Square.java
// Define a class named Square that extends Shape
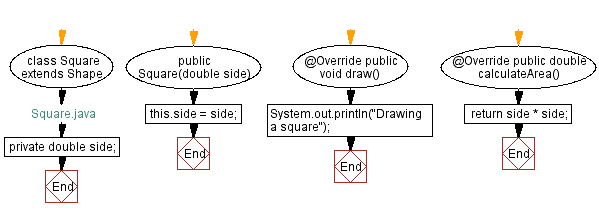
class Square extends Shape {
// Declare a private double variable side
private double side;
// Define a constructor that takes a double side as a parameter
public Square(double side) {
// Assign the parameter side to the instance variable side
this.side = side;
}
// Override the draw method from the Shape class
@Override
public void draw() {
// Print "Drawing a square" to the console
System.out.println("Drawing a square");
}
// Override the calculateArea method from the Shape class
@Override
public double calculateArea() {
// Return the area of the square using the formula side * side
return side * side;
}
}
// Triangle.java
// Define a class named Triangle that extends Shape
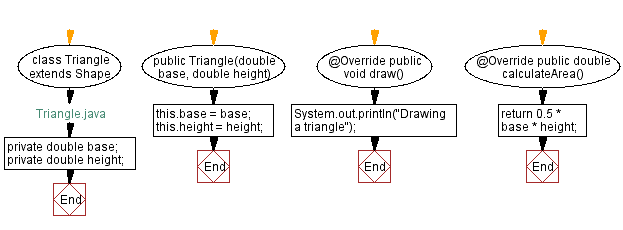
class Triangle extends Shape {
// Declare private double variables base and height
private double base;
private double height;
// Define a constructor that takes a double base and a double height as parameters
public Triangle(double base, double height) {
// Assign the parameter base to the instance variable base
this.base = base;
// Assign the parameter height to the instance variable height
this.height = height;
}
// Override the draw method from the Shape class
@Override
public void draw() {
// Print "Drawing a triangle" to the console
System.out.println("Drawing a triangle");
}
// Override the calculateArea method from the Shape class
@Override
public double calculateArea() {
// Return the area of the triangle using the formula 0.5 * base * height
return 0.5 * base * height;
}
}
// Main.java
// Define the Main class
public class Main {
// Define the main method, the entry point of the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of Circle with radius 7.0 and assign it to the variable circle of type Shape
Shape circle = new Circle(7.0);
// Create an instance of Square with side length 12.0 and assign it to the variable square of type Shape
Shape square = new Square(12.0);
// Create an instance of Triangle with base 5.0 and height 3.0 and assign it to the variable triangle of type Shape
Shape triangle = new Triangle(5.0, 3.0);
// Call the drawShapeAndCalculateArea method with circle as the argument
drawShapeAndCalculateArea(circle);
// Call the drawShapeAndCalculateArea method with square as the argument
drawShapeAndCalculateArea(square);
// Call the drawShapeAndCalculateArea method with triangle as the argument
drawShapeAndCalculateArea(triangle);
}
// Define the drawShapeAndCalculateArea method that takes a Shape object as a parameter
public static void drawShapeAndCalculateArea(Shape shape) {
// Call the draw method on the shape object
shape.draw();
// Call the calculateArea method on the shape object and store the result in a variable area
double area = shape.calculateArea();
// Print the area of the shape to the console
System.out.println("Area: " + area);
}
}
Output:
Drawing a circle Area: 153.93804002589985 Drawing a square Area: 144.0 Drawing a triangle Area: 7.5
Explanation:
In the above exercise -
- "Shape" is the base abstract class, with Circle, Square, and Triangle as its subclasses. Each subclass overrides the draw() method to provide their specific shape drawing implementation. It also overrides the calculateArea() method to calculate and return the area of each shape.
- In the "Main()" class, we have a static method drawShapeAndCalculateArea(Shape shape) that takes an object of the base class Shape as a parameter. Inside this method, we call the draw() and calculateArea() methods on the shape object. Since the drawShapeAndCalculateArea method takes a Shape type parameter, it can accept objects of all three subclasses: Circle, Square, and Triangle, thanks to polymorphism.
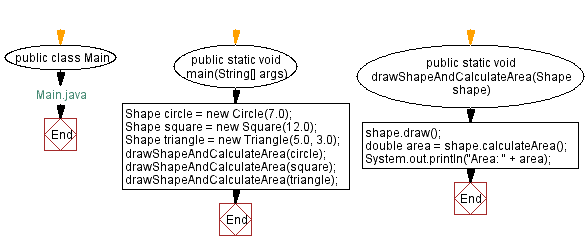
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Shape" class supports filling the shape with a specific pattern.
- Write a Java program where the "Shape" class calculates the aspect ratio of each shape.
- Write a Java program where the "Shape" class determines the shape with the largest area among a list of shapes.
- Write a Java program where the "Shape" class includes a method to check if two shapes are congruent.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
PREV : Animal Base Class with Bird and Panthera Subclasses.
NEXT : BankAccount base class with Savings, Checking Account subclasses.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
