Java Polymorphism: Animal Base Class with Bird and Panthera Subclasses
Write a Java program to create a base class Animal with methods move() and makeSound(). Create two subclasses Bird and Panthera. Override the move() method in each subclass to describe how each animal moves. Also, override the makeSound() method in each subclass to make a specific sound for each animal.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
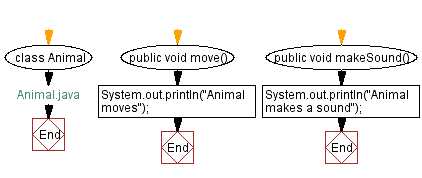
// Animal.java
class Animal { // Declare the Animal class
public void move() { // Define the move method
System.out.println("Animal moves"); // Print "Animal moves" to the console
}
public void makeSound() { // Define the makeSound method
System.out.println("Animal makes a sound"); // Print "Animal makes a sound" to the console
}
}
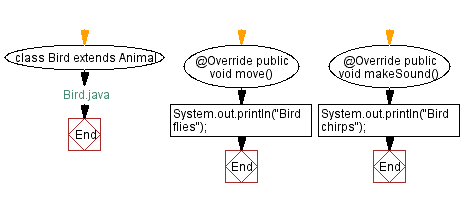
// Bird.java
class Bird extends Animal { // Declare the Bird class that extends the Animal class
@Override // Override the move method from the Animal class
public void move() { // Define the move method
System.out.println("Bird flies"); // Print "Bird flies" to the console
}
@Override // Override the makeSound method from the Animal class
public void makeSound() { // Define the makeSound method
System.out.println("Bird chirps"); // Print "Bird chirps" to the console
}
}
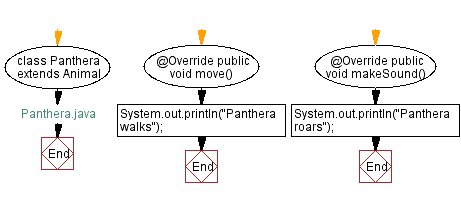
// Panthera.java
// Define a class named Panthera that extends Animal
class Panthera extends Animal {
// Override the move method from the Animal class
@Override
public void move() {
// Print "Panthera walks" to the console
System.out.println("Panthera walks");
}
// Override the makeSound method from the Animal class
@Override
public void makeSound() {
// Print "Panthera roars" to the console
System.out.println("Panthera roars");
}
}
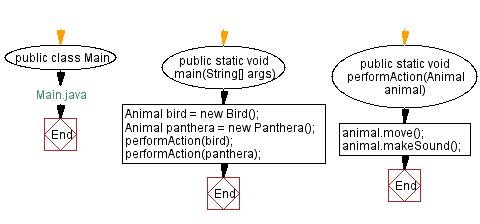
// Main.java
// Define the Main class
public class Main {
// Define the main method, the entry point of the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of Bird and assign it to the variable bird of type Animal
Animal bird = new Bird();
// Create an instance of Panthera and assign it to the variable panthera of type Animal
Animal panthera = new Panthera();
// Call the performAction method with bird as the argument
performAction(bird);
// Call the performAction method with panthera as the argument
performAction(panthera);
}
// Define the performAction method that takes an Animal object as a parameter
public static void performAction(Animal animal) {
// Call the move method on the animal object
animal.move();
// Call the makeSound method on the animal object
animal.makeSound();
}
}
Output:
Bird flies Bird chirps Panthera walks Panthera roars
Explanation:
We have the "Animal" class as the base class, and "Bird" and "Panthera" are its subclasses. Each subclass overrides the move() and makeSound() methods to provide their specific implementations.
In the "Main" class, we have a static method performAction(Animal animal) that takes an object of the base class Animal as a parameter. Inside this method, we call the move() and makeSound() methods on the animal object. Since the performAction method takes an Animal type parameter, it can accept Bird and Panthera objects.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Animal" class includes a method to determine if the animal is nocturnal.
- Write a Java program where the "Animal" class tracks the animal's habitat (land, water, or air).
- Write a Java program where the "Animal" class allows checking if two animals are from the same species.
- Write a Java program where the "Animal" class calculates the average lifespan of each subclass.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
PREV : Shape Class with Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle Subclasses for Area and Perimeter Calculation.
NEXT : Shape base class with Circle, Square, and Triangle subclasses.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
