Java Inheritance Programming - Vehicle class hierarchy
Write a Java program to create a vehicle class hierarchy. The base class should be Vehicle, with subclasses Truck, Car and Motorcycle. Each subclass should have properties such as make, model, year, and fuel type. Implement methods for calculating fuel efficiency, distance traveled, and maximum speed.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Vehicle.java
// Parent class Vehicle
// Declare the abstract class Vehicle
public abstract class Vehicle {
// Private instance variable for the make of the vehicle
private String make;
// Private instance variable for the model of the vehicle
private String model;
// Private instance variable for the year of the vehicle
private int year;
// Private instance variable for the fuel type of the vehicle
private String fuelType;
// Private instance variable for the fuel efficiency of the vehicle
private double fuelEfficiency;
// Constructor for the Vehicle class, taking make, model, year, fuel type, and fuel efficiency as parameters
public Vehicle(String make, String model, int year, String fuelType, double fuelEfficiency) {
// Initialize the make instance variable
this.make = make;
// Initialize the model instance variable
this.model = model;
// Initialize the year instance variable
this.year = year;
// Initialize the fuelType instance variable
this.fuelType = fuelType;
// Initialize the fuelEfficiency instance variable
this.fuelEfficiency = fuelEfficiency;
}
// Public method to get the make of the vehicle
public String getMake() {
return make;
}
// Public method to get the model of the vehicle
public String getModel() {
return model;
}
// Public method to get the year of the vehicle
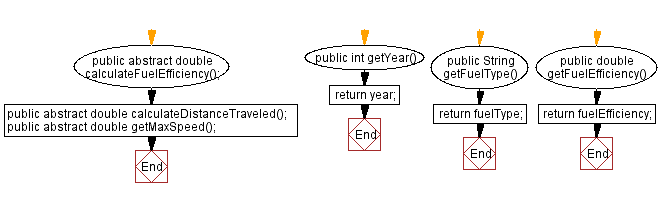
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
// Public method to get the fuel type of the vehicle
public String getFuelType() {
return fuelType;
}
// Public method to get the fuel efficiency of the vehicle
public double getFuelEfficiency() {
return fuelEfficiency;
}
// Abstract method to calculate the fuel efficiency, to be implemented by subclasses
public abstract double calculateFuelEfficiency();
// Abstract method to calculate the distance traveled, to be implemented by subclasses
public abstract double calculateDistanceTraveled();
// Abstract method to get the maximum speed, to be implemented by subclasses
public abstract double getMaxSpeed();
}
Explanation:
This is an abstract class that serves as the parent class for the other vehicle classes. It contains five private instance variables (make, model, year, fuelType, and fuelEfficiency) and six public methods (a constructor, five getters for the instance variables, and three abstract methods). The abstract methods are meant to be overridden by child classes with specific implementations.
// Truck.java
// Child class Truck
// Declare the Truck class which extends the Vehicle class
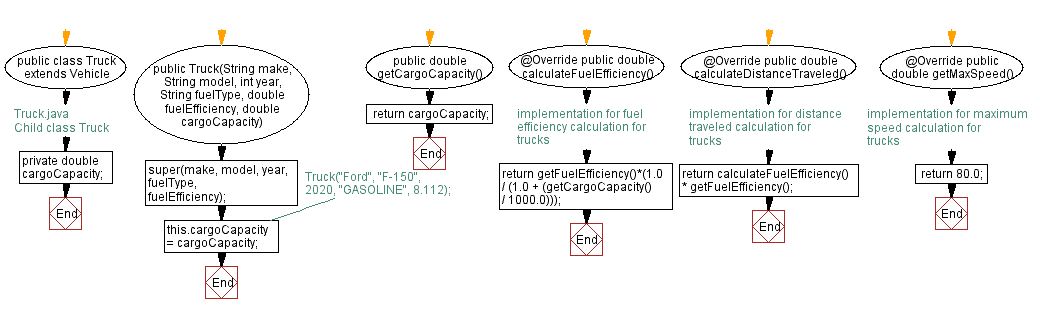
public class Truck extends Vehicle {
// Private instance variable for the cargo capacity of the truck
private double cargoCapacity;
// Constructor for the Truck class, taking make, model, year, fuel type, fuel efficiency, and cargo capacity as parameters
public Truck(String make, String model, int year, String fuelType, double fuelEfficiency, double cargoCapacity) {
// Call the constructor of the superclass (Vehicle) with make, model, year, fuel type, and fuel efficiency
super(make, model, year, fuelType, fuelEfficiency);
// Initialize the cargoCapacity instance variable
this.cargoCapacity = cargoCapacity;
}
// Public method to get the cargo capacity of the truck
public double getCargoCapacity() {
return cargoCapacity;
}
// Override the calculateFuelEfficiency method from the superclass (Vehicle)
@Override
public double calculateFuelEfficiency() {
// Implementation for fuel efficiency calculation for trucks
return getFuelEfficiency() * (1.0 / (1.0 + (getCargoCapacity() / 1000.0)));
}
// Override the calculateDistanceTraveled method from the superclass (Vehicle)
@Override
public double calculateDistanceTraveled() {
// Implementation for distance traveled calculation for trucks
return calculateFuelEfficiency() * getFuelEfficiency();
}
// Override the getMaxSpeed method from the superclass (Vehicle)
@Override
public double getMaxSpeed() {
// Implementation for maximum speed calculation for trucks
return 80.0;
}
}
Explanation:
The above class is a child class of Vehicle and extends the Vehicle class. It has an additional instance variable, cargoCapacity. The class has a constructor that accepts all the necessary parameters including cargo capacity. The class overrides the three abstract methods of the parent class and provides specific implementations of the methods.
// Car.java
// Child class Car
// Declare the Car class which extends the Vehicle class
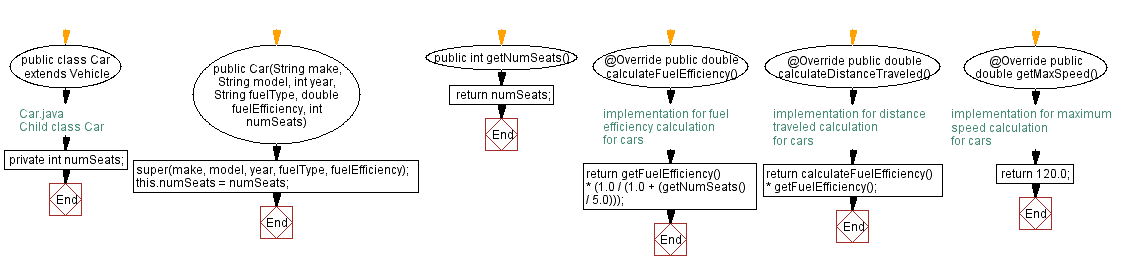
public class Car extends Vehicle {
// Private instance variable for the number of seats in the car
private int numSeats;
// Constructor for the Car class, taking make, model, year, fuel type, fuel efficiency, and number of seats as parameters
public Car(String make, String model, int year, String fuelType, double fuelEfficiency, int numSeats) {
// Call the constructor of the superclass (Vehicle) with make, model, year, fuel type, and fuel efficiency
super(make, model, year, fuelType, fuelEfficiency);
// Initialize the numSeats instance variable
this.numSeats = numSeats;
}
// Public method to get the number of seats in the car
public int getNumSeats() {
return numSeats;
}
// Override the calculateFuelEfficiency method from the superclass (Vehicle)
@Override
public double calculateFuelEfficiency() {
// Implementation for fuel efficiency calculation for cars
return getFuelEfficiency() * (1.0 / (1.0 + (getNumSeats() / 5.0)));
}
// Override the calculateDistanceTraveled method from the superclass (Vehicle)
@Override
public double calculateDistanceTraveled() {
// Implementation for distance traveled calculation for cars
return calculateFuelEfficiency() * getFuelEfficiency();
}
// Override the getMaxSpeed method from the superclass (Vehicle)
@Override
public double getMaxSpeed() {
// Implementation for maximum speed calculation for cars
return 120.0;
}
}
Explanation:
The above class is another child class of Vehicle and extends the Vehicle class. It has an additional instance variable, numSeats. The class has a constructor that accepts all the necessary parameters including the number of seats. The class overrides the three abstract methods of the parent class and provides specific implementations of the methods.
// Motorcycle.java
// Child class Motorcycle
// Declare the Motorcycle class which extends the Vehicle class
public class Motorcycle extends Vehicle {
// Private instance variable for the engine displacement of the motorcycle
private double engineDisplacement;
// Constructor for the Motorcycle class, taking make, model, year, fuel type, and fuel efficiency as parameters
public Motorcycle(String make, String model, int year, String fuelType, double fuelEfficiency) {
// Call the constructor of the superclass (Vehicle) with make, model, year, fuel type, and fuel efficiency
super(make, model, year, fuelType, fuelEfficiency);
// Initialize the engineDisplacement instance variable (currently commented out)
// this.engineDisplacement = engineDisplacement;
}
// Public method to get the engine displacement of the motorcycle
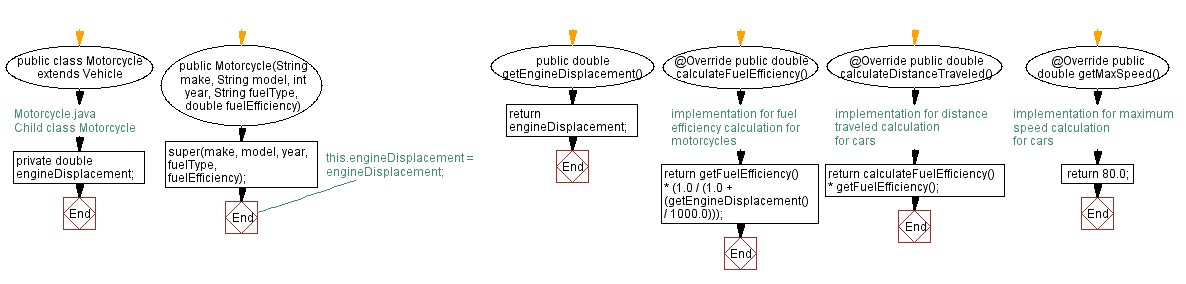
public double getEngineDisplacement() {
return engineDisplacement;
}
// Override the calculateFuelEfficiency method from the superclass (Vehicle)
@Override
public double calculateFuelEfficiency() {
// Implementation for fuel efficiency calculation for motorcycles
return getFuelEfficiency() * (1.0 / (1.0 + (getEngineDisplacement() / 1000.0)));
}
// Override the calculateDistanceTraveled method from the superclass (Vehicle)
@Override
public double calculateDistanceTraveled() {
// Implementation for distance traveled calculation for motorcycles
return calculateFuelEfficiency() * getFuelEfficiency();
}
// Override the getMaxSpeed method from the superclass (Vehicle)
@Override
public double getMaxSpeed() {
// Implementation for maximum speed calculation for motorcycles
return 80.0;
}
}
Explanation:
This is also a child class of Vehicle and extends the Vehicle class. It has an additional instance variable, engineDisplacement. The class has a constructor that accepts all the necessary parameters. The class overrides the three abstract methods of the parent class and provides specific implementations of the methods.
// Main.java
// Main class
// Declare the Main class
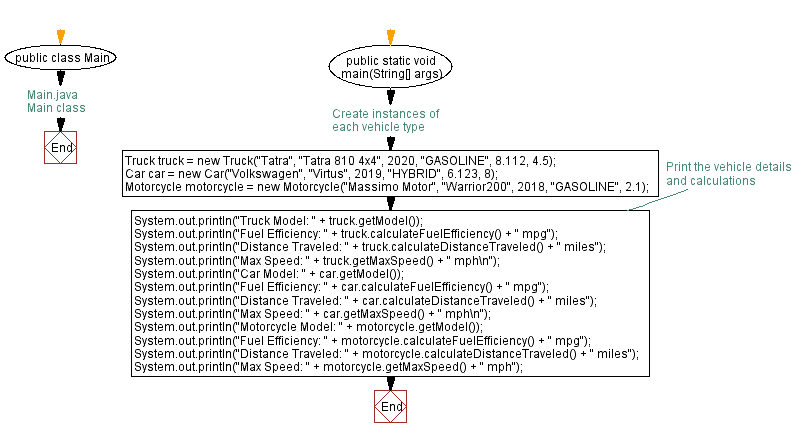
public class Main {
// Main method to execute the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of the Truck class with make, model, year, fuel type, fuel efficiency, and cargo capacity
Truck truck = new Truck("Tatra", "Tatra 810 4x4", 2020, "GASOLINE", 8.112, 4.5);
// Create an instance of the Car class with make, model, year, fuel type, fuel efficiency, and number of seats
Car car = new Car("Volkswagen", "Virtus", 2019, "HYBRID", 6.123, 8);
// Create an instance of the Motorcycle class with make, model, year, fuel type, and fuel efficiency
Motorcycle motorcycle = new Motorcycle("Massimo Motor", "Warrior200", 2018, "GASOLINE", 2.1);
// Print the truck's model
System.out.println("Truck Model: " + truck.getModel());
// Print the truck's calculated fuel efficiency
System.out.println("Fuel Efficiency: " + truck.calculateFuelEfficiency() + " mpg");
// Print the truck's calculated distance traveled
System.out.println("Distance Traveled: " + truck.calculateDistanceTraveled() + " miles");
// Print the truck's maximum speed
System.out.println("Max Speed: " + truck.getMaxSpeed() + " mph\n");
// Print the car's model
System.out.println("Car Model: " + car.getModel());
// Print the car's calculated fuel efficiency
System.out.println("Fuel Efficiency: " + car.calculateFuelEfficiency() + " mpg");
// Print the car's calculated distance traveled
System.out.println("Distance Traveled: " + car.calculateDistanceTraveled() + " miles");
// Print the car's maximum speed
System.out.println("Max Speed: " + car.getMaxSpeed() + " mph\n");
// Print the motorcycle's model
System.out.println("Motorcycle Model: " + motorcycle.getModel());
// Print the motorcycle's calculated fuel efficiency
System.out.println("Fuel Efficiency: " + motorcycle.calculateFuelEfficiency() + " mpg");
// Print the motorcycle's calculated distance traveled
System.out.println("Distance Traveled: " + motorcycle.calculateDistanceTraveled() + " miles");
// Print the motorcycle's maximum speed
System.out.println("Max Speed: " + motorcycle.getMaxSpeed() + " mph");
}
}
Explanation:
The above class is the main class that contains the main method. It creates instances of each vehicle type, sets their values, and then prints their respective details and calculations such as fuel efficiency, distance traveled, and max speed.
Output:
Truck Model: Tatra 810 4x4 Fuel Efficiency: 8.075659532105526 mpg Distance Traveled: 65.50975012444003 miles Max Speed: 80.0 mph Car Model: Virtus Fuel Efficiency: 2.355 mpg Distance Traveled: 14.419665 miles Max Speed: 120.0 mph Motorcycle Model: Warrior200 Fuel Efficiency: 2.1 mpg Distance Traveled: 4.41 miles Max Speed: 80.0 mph
Flowchart of Vehicle class:
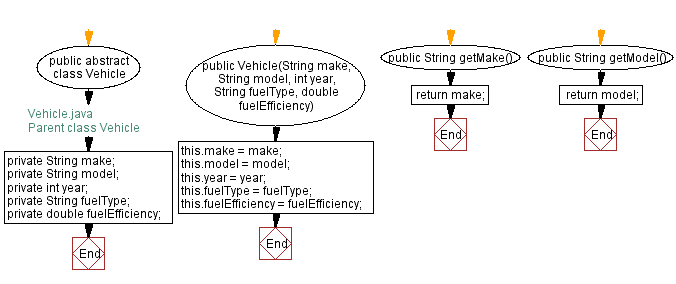
Flowchart of Child class Truck:
Flowchart of Child class Car:
Flowchart of Child class Motorcycle:
Flowchart of Vehicle class Main:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Truck" subclass calculates load capacity based on cargo weight.
- Write a Java program where the "Car" subclass implements a method to estimate travel time for long trips.
- Write a Java program where the "Motorcycle" subclass includes a method to check tire pressure before a ride.
- Write a Java program where the "Vehicle" class introduces a method for maintenance scheduling.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
PREV : Create a class called Shape with methods called getPerimeter() and getArea().
NEXT : Employee Class Hierarchy.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
