Java Inheritance Programming - Create a class called Shape with methods called getPerimeter() and getArea()
Write a Java program to create a class called Shape with methods called getPerimeter() and getArea(). Create a subclass called Circle that overrides the getPerimeter() and getArea() methods to calculate the area and perimeter of a circle.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Shape.java
// Parent class Shape
// Declare the Shape class
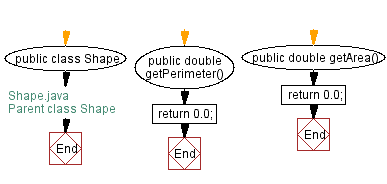
public class Shape {
// Public method to get the perimeter of the shape, returning a default value of 0.0
public double getPerimeter() {
return 0.0;
}
// Public method to get the area of the shape, returning a default value of 0.0
public double getArea() {
return 0.0;
}
}
// Circle.java
// Child class Circle
// Declare the Circle class which extends the Shape class
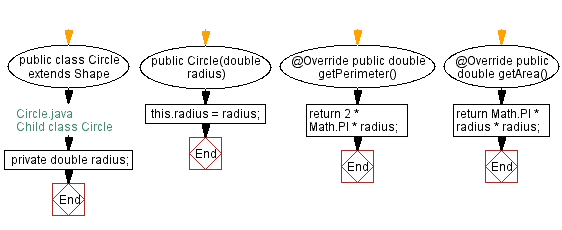
public class Circle extends Shape {
// Private instance variable for the radius of the circle
private double radius;
// Constructor for the Circle class, taking the radius as a parameter
public Circle(double radius) {
// Initialize the radius instance variable
this.radius = radius;
}
// Override the getPerimeter method from the superclass (Shape)
@Override
public double getPerimeter() {
// Return the perimeter of the circle calculated as 2 * π * radius
return 2 * Math.PI * radius;
}
// Override the getArea method from the superclass (Shape)
@Override
public double getArea() {
// Return the area of the circle calculated as π * radius^2
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
}
// Main.java
// Main class
// Declare the Main class
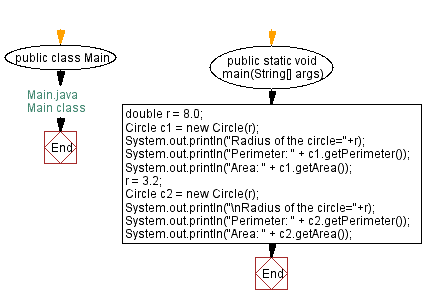
public class Main {
// Main method to execute the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare a double variable r and initialize it to 8.0
double r = 8.0;
// Create a Circle object named c1 with radius r
Circle c1 = new Circle(r);
// Print the radius of the circle c1
System.out.println("Radius of the circle=" + r);
// Print the perimeter of the circle c1
System.out.println("Perimeter: " + c1.getPerimeter());
// Print the area of the circle c1
System.out.println("Area: " + c1.getArea());
// Update the value of r to 3.2
r = 3.2;
// Create a Circle object named c2 with radius r
Circle c2 = new Circle(r);
// Print the radius of the circle c2
System.out.println("\nRadius of the circle=" + r);
// Print the perimeter of the circle c2
System.out.println("Perimeter: " + c2.getPerimeter());
// Print the area of the circle c2
System.out.println("Area: " + c2.getArea());
}
}
Output:
Radius of the circle=8.0 Perimeter: 50.26548245743669 Area: 201.06192982974676 Radius of the circle=3.2 Perimeter: 20.106192982974676 Area: 32.169908772759484
Explanation:
In the above exercise, the Shape class is a base class that provides generic methods for calculating the perimeter and area of a shape. The Circle class is a subclass that extends Shape and overrides the getPerimeter() and getArea() methods to implement circle formulas.
The Circle class has a private radius field that takes a radius argument to initialize the field. The getPerimeter() method uses the formula 2πr to calculate the circumference of the circle. The getArea() method uses the formula πr^2 to calculate the circle area.
In the Main class -
The given code creates two Circle objects, c1 and c2, and calculates their perimeter and area using the getPerimeter() and getArea() methods. The radius of each circle is first set using a double variable r. The output displays the radius, perimeter, and area of each circle.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Circle" subclass checks if a point lies inside the circle.
- Write a Java program where the "Shape" class introduces a method to rotate shapes, and subclasses implement it.
- Write a Java program where the "Circle" subclass adds a method to determine if two circles overlap.
- Write a Java program where the "Shape" class allows dynamic scaling, and subclasses override it based on dimensions.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
PREV : BankAccount class with methods called deposit() and withdraw().
NEXT : Vehicle class hierarchy .
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
