Java Inheritance Programming - Person Class with methods called getFirstName() and getLastName()
Write a Java program to create a class known as Person with methods called getFirstName() and getLastName(). Create a subclass called Employee that adds a new method named getEmployeeId() and overrides the getLastName() method to include the employee's job title.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Person.java
// Parent class Person
// Define the Person class
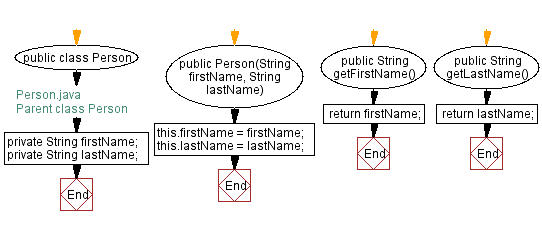
public class Person {
// Private fields for first name and last name
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
// Constructor to initialize first name and last name
public Person(String firstName, String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
// Method to get the first name
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
// Method to get the last name
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
}
// Employee.java
// Child class Employee
// Declare the Employee class which extends the Person class
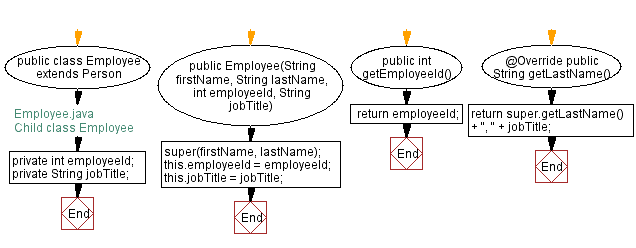
public class Employee extends Person {
// Private instance variable for employee ID
private int employeeId;
// Private instance variable for job title
private String jobTitle;
// Constructor for Employee class, taking first name, last name, employee ID, and job title as parameters
public Employee(String firstName, String lastName, int employeeId, String jobTitle) {
// Call the constructor of the superclass (Person) with first name and last name
super(firstName, lastName);
// Initialize the employeeId instance variable
this.employeeId = employeeId;
// Initialize the jobTitle instance variable
this.jobTitle = jobTitle;
}
// Public method to get the employee ID
public int getEmployeeId() {
return employeeId;
}
// Override the getLastName method from the superclass (Person)
@Override
public String getLastName() {
// Return the last name from the superclass combined with the job title
return super.getLastName() + ", " + jobTitle;
}
}
// Main.java
// Main class
// Declare the Main class
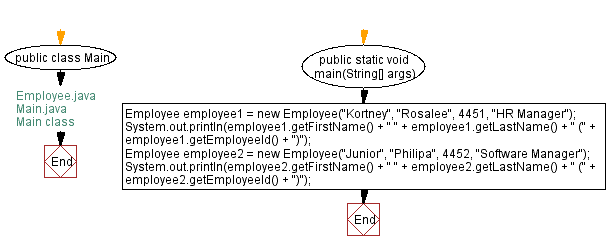
public class Main {
// Main method to execute the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an Employee object named employee1 with first name, last name, employee ID, and job title
Employee employee1 = new Employee("Kortney", "Rosalee", 4451, "HR Manager");
// Print the first name, last name with job title, and employee ID of employee1
System.out.println(employee1.getFirstName() + " " + employee1.getLastName() + " (" + employee1.getEmployeeId() + ")");
// Create an Employee object named employee2 with first name, last name, employee ID, and job title
Employee employee2 = new Employee("Junior", "Philipa", 4452, "Software Manager");
// Print the first name, last name with job title, and employee ID of employee2
System.out.println(employee2.getFirstName() + " " + employee2.getLastName() + " (" + employee2.getEmployeeId() + ")");
}
}
Output:
Kortney Rosalee, HR Manager (4451) Junior Philipa, Software Manager (4452)
Explanation:
The Person class has two private instance variables, firstName and lastName, and two public methods, getFirstName() and getLastName(), that return the values of these variables.
The Employee class is a subclass of Person, and adds two private instance variables, employeeId and jobTitle, as well as a public method called getEmployeeId(). It also overrides the getLastName() method from the Person class to include the employee's jobTitle.
In the above Main class, we create two instances of the Employee class, namely "employee1" and "employee2".
"employee1" is initialized with the values "Kortney" for the first name, "Rosalee" for the last name, 4451 for the employee ID, and "HR Manager" for the job title. Employee1's getFirstName(), getLastName(), and getEmployeeId() methods of "employee1" are called. Their return values are concatenated into a string, which is printed to the console.
Similarly, Employee2's getFirstName(), getLastName(), and getEmployeeId() methods of employee2 are called. Their return values are concatenated into a string, which is printed to the console.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Employee" subclass generates an email ID based on name and job title.
- Write a Java program where the "Person" class allows name changes under certain conditions.
- Write a Java program where the "Employee" subclass includes a method to calculate annual leave balance.
- Write a Java program where the "Person" class tracks education history, and subclasses extend it.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
PREV : Animal Class with a method move().
NEXT : Create a class called Shape with methods called getPerimeter() and getArea().
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
