Java Inheritance Programming - Employee class with methods called work, getSalary
Write a Java program to create a class called Employee with methods called work() and getSalary(). Create a subclass called HRManager that overrides the work() method and adds a new method called addEmployee().
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
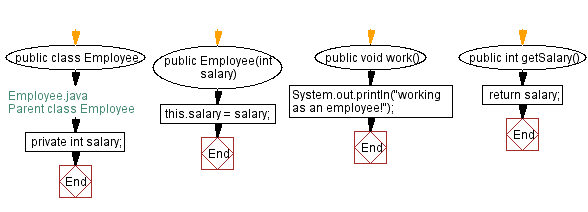
// Employee.java
// Parent class Employee
public class Employee {
// Private field to store the salary of the employee
private int salary;
// Constructor to initialize the salary of the employee
public Employee(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
// Method to simulate the employee working
public void work() {
// Print a message indicating the employee is working
System.out.println("working as an employee!");
}
// Getter method to retrieve the salary of the employee
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
}
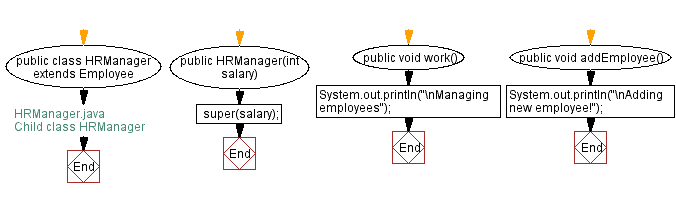
// HRManager.java
// Child class HRManager
public class HRManager extends Employee {
// Constructor to initialize the salary of the HRManager
public HRManager(int salary) {
// Call the parent class constructor with the salary
super(salary);
}
// Overridden method to simulate the HRManager working
public void work() {
// Print a message indicating the HRManager is managing employees
System.out.println("\nManaging employees");
}
// Method to simulate adding a new employee
public void addEmployee() {
// Print a message indicating a new employee is being added
System.out.println("\nAdding new employee!");
}
}
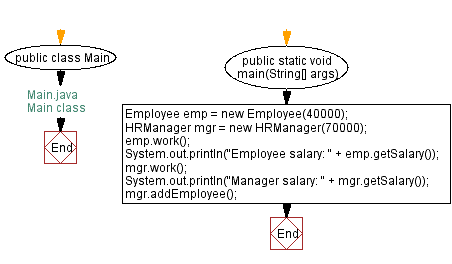
// Main.java
// Main class
public class Main {
// Main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an Employee object with a salary of 40000
Employee emp = new Employee(40000);
// Create an HRManager object with a salary of 70000
HRManager mgr = new HRManager(70000);
// Call the work method on the Employee object
emp.work();
// Print the salary of the Employee object
System.out.println("Employee salary: " + emp.getSalary());
// Call the work method on the HRManager object
mgr.work();
// Print the salary of the HRManager object
System.out.println("Manager salary: " + mgr.getSalary());
// Call the addEmployee method on the HRManager object
mgr.addEmployee();
}
}
Output:
working as an employee! Employee salary: 40000 Managing employees Manager salary: 70000 Adding new employee!
Explanation:
In the above exercise, the Employee class has a work() method that prints a message and a getSalary() method that returns the employee's salary. The HRManager subclass extends the Employee class and overrides the work() method to display a different message. It adds a method addEmployee() that prints a message indicating that a new employee is being added. The Main class creates an instance of Employee and HRManager, calls the work() and getSalary() methods, and also calls the addEmployee() method on the HRManager object.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "HRManager" subclass includes a method to schedule interviews for candidates.
- Write a Java program where the "Employee" class tracks overtime hours and subclasses calculate additional pay.
- Write a Java program where the "HRManager" subclass allows employees to request salary increments.
- Write a Java program where the "Employee" class includes a method to display employee hierarchy within the company.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
PREV : Create a class called Shape with a method called getArea and a subclass called Rectangle.
NEXT : BankAccount class with methods called deposit() and withdraw().
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
