Java Program: File reading and empty file exception handling
5. Throw Exception if File is Empty
Write a Java program that reads a file and throws an exception if the file is empty.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
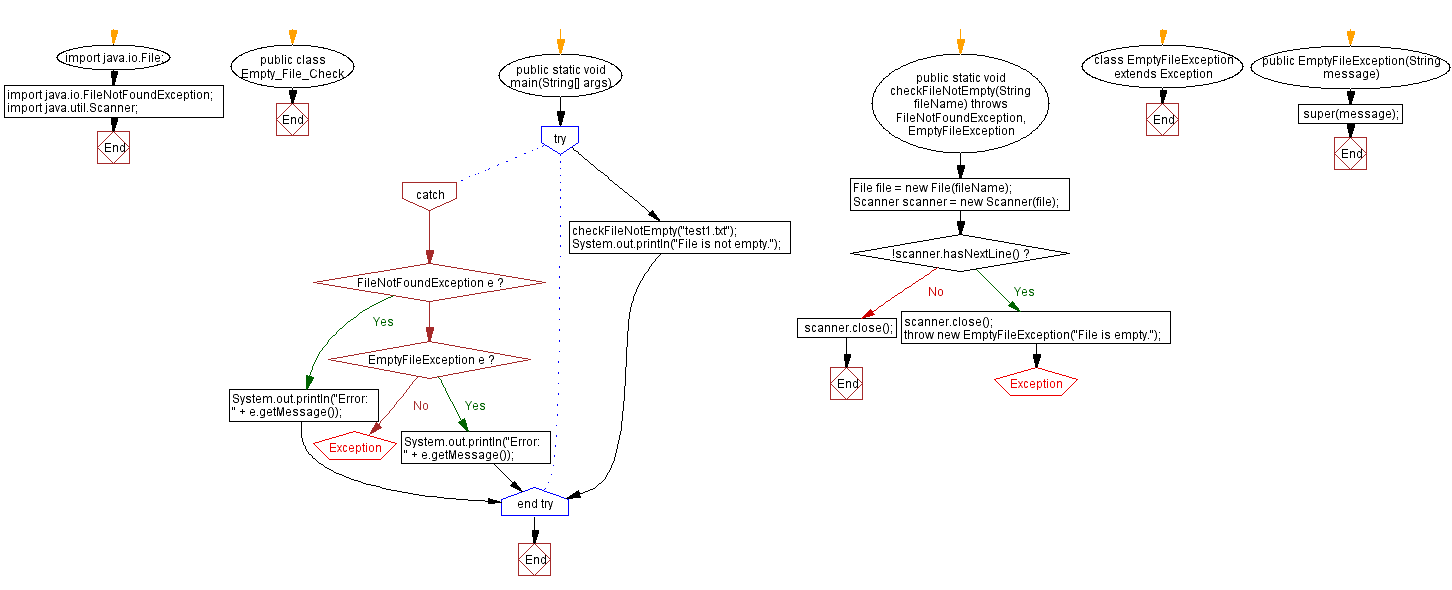
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Empty_File_Check {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
checkFileNotEmpty("test1.txt");
System.out.println("File is not empty.");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (EmptyFileException e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void checkFileNotEmpty(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException, EmptyFileException {
File file = new File(fileName);
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file);
if (!scanner.hasNextLine()) {
scanner.close();
throw new EmptyFileException("File is empty.");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
class EmptyFileException extends Exception {
public EmptyFileException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
Sample Output:
Content of the file (test1.txt): 0 0 0 File is not empty.
Content of the file (test1.txt): Error: File is empty.
Explanation:
In the above exercise,
- The program includes two classes: Empty_File_Check and EmptyFileException.
- The Empty_File_Check class contains the main method, which serves as the program's entry point.
- In the main method, we call the checkFileNotEmpty method, passing the file name "test1.txt" as an argument. We handle two types of exceptions: FileNotFoundException and EmptyFileException.
- The checkFileNotEmpty method checks if a file is empty. It takes the file name as a parameter and can potentially throw two types of exceptions: FileNotFoundException and EmptyFileException.
- Inside the checkFileNotEmpty method, we create a File object using the provided file name. We also create a Scanner object to read the file's contents.
- We use an if statement to check if the scanner does not have a next line, indicating that the file is blank. If the file is empty, we throw an EmptyFileException with the message "File is empty."
- After checking the file, we close the Scanner object.
- The EmptyFileException class is a custom exception class that extends the base Exception class. It provides a constructor that takes a message parameter and passes it to the superclass constructor using the super keyword.
- If a FileNotFoundException occurs in the main method, it is caught, and an appropriate error message is printed.
- If an EmptyFileException occurs in the checkFileNotEmpty method, it is caught in the main method. The error message indicating an empty file is printed.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to read a file and throw a custom EmptyFileException if its content is empty.
- Write a Java program to check the file size using NIO and throw an exception if the file is zero bytes.
- Write a Java program to read a file and throw an exception if it contains only whitespace characters.
- Write a Java program to validate a file's content before processing and throw an exception if no valid data is found.
Go to:
PREV : Throw Exception for Positive Numbers in File.
NEXT : Throw Exception for Duplicate Integers.
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
