Java Program: Method to check and handle odd numbers
2. Throw Exception for Odd Number
Write a Java program to create a method that takes an integer as a parameter and throws an exception if the number is odd.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
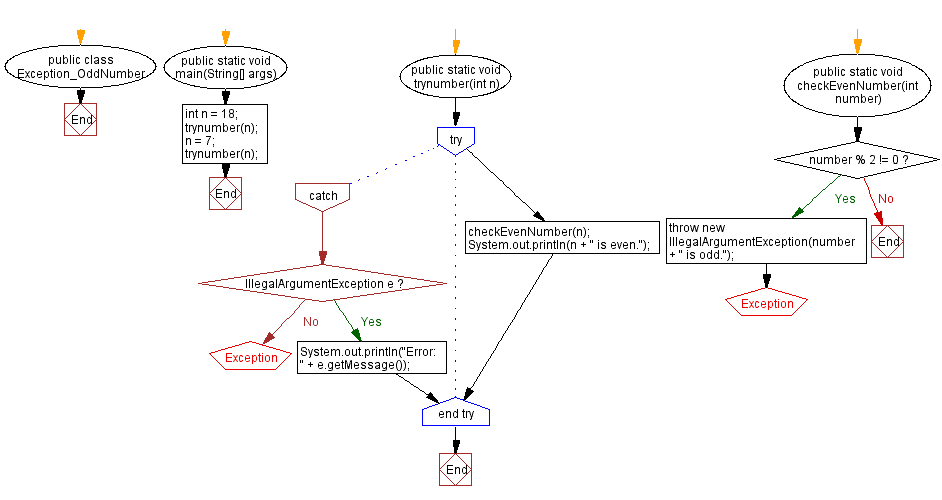
public class Exception_OddNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 18;
trynumber(n);
n = 7;
trynumber(n);
}
public static void trynumber(int n) {
try {
checkEvenNumber(n);
System.out.println(n + " is even.");
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
public static void checkEvenNumber(int number) {
if (number % 2 != 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(number + " is odd.");
}
}
}
Sample Output:
18 is even. Error: 7 is odd.
Explanation:
In the above exercise,
- The Exception_OddNumber class is the main class.
- In the main method, an integer n is declared and assigned 18. The trynumber method is then called with n as an argument.
- The trynumber method handles the exception. It contains a try-catch block. Inside the try block, the method checkEvenNumber is called, passing n as an argument. If the number is even, the message "[number] is even." is printed.
- If an exception occurs in the try block, it is caught by the catch block, which handles IllegalArgumentException. In this case, the error message "Error: [exception message]" is printed.
- After the first call to trynumber(n), the value of n is updated to 7, and the trynumber method is called again. This time, since 7 is an odd number, an exception is thrown.
- The checkEvenNumber method checks if a given number is even or odd. If the number is odd, it throws an IllegalArgumentException with the message "[number] is odd."
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to create a method that accepts an integer and throws a custom OddNumberException if the number is odd.
- Write a Java program where a method throws an exception for odd numbers and demonstrates exception propagation across multiple method calls.
- Write a Java program to create a method that takes an integer and, using a ternary operator, throws an exception if the number is odd; otherwise, returns its double.
- Write a Java program to create a method that logs an error message and throws an exception when an odd integer is passed, then catches the exception in the main method.
Go to:
PREV : Throw and Catch Exception with Try-Catch.
NEXT : Throw Exception if File Not Found.
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
