Java Encapsulation: Implementing Car Class with Getter and Setter Methods
Write a Java program to create a class called Car with private instance variables company_name, model_name, year, and mileage. Provide public getter and setter methods to access and modify the company_name, model_name, and year variables. However, only provide a getter method for the mileage variable.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Car.java
// Car Class
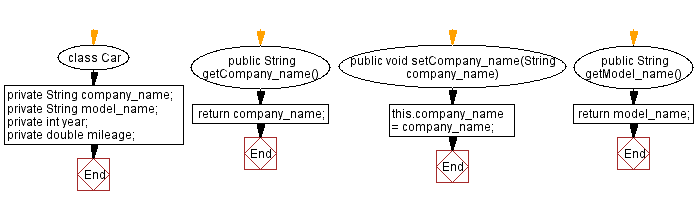
class Car {
// Declare a private String variable for the company name
private String company_name;
// Declare a private String variable for the model name
private String model_name;
private int year;
// Declare a private int variable for the year
// Declare a private double variable for the mileage
private double mileage;
// Getter method for company_name
public String getCompany_name() {
return company_name;
}
// Setter method for company_name
public void setCompany_name(String company_name) {
this.company_name = company_name;
}
// Getter method for model_name
public String getModel_name() {
return model_name;
}
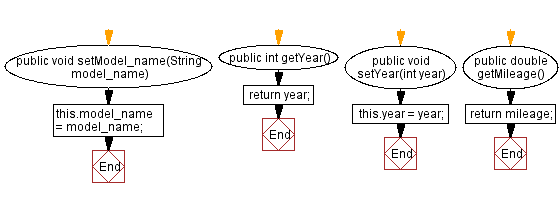
// Setter method for model_name
public void setModel_name(String model_name) {
this.model_name = model_name;
}
// Getter method for year
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
// Setter method for year
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
// Getter method for mileage
public double getMileage() {
return mileage;
}
}
// Main.java
// Main Class
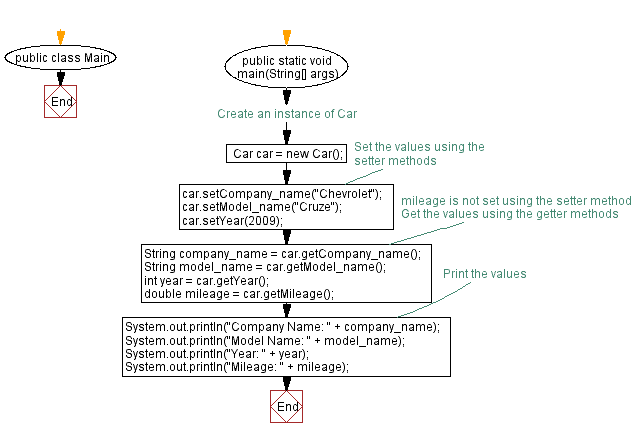
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of Car
Car car = new Car();
// Set the values using the setter methods
car.setCompany_name("Chevrolet");
car.setModel_name("Cruze");
car.setYear(2009);
// mileage is not set using the setter method
// Get the values using the getter methods
String company_name = car.getCompany_name();
String model_name = car.getModel_name();
int year = car.getYear();
double mileage = car.getMileage();
// Print the values
System.out.println("Company Name: " + company_name);
System.out.println("Model Name: " + model_name);
System.out.println("Year: " + year);
System.out.println("Mileage: " + mileage);
}
}
Output:
Company Name: Chevrolet Model Name: Cruze Year: 2009 Mileage: 0.0
Explanation:
In this code, the Car class encapsulates the private instance variables company_name, model_name, year, and mileage. The getCompany_name(), getModel_name(), and getYear() methods are public getter methods that allow other classes to access company_name, model_name, and year, respectively. The corresponding set methods are provided to modify these variables.
The getMileage() method is a public getter method that allows other classes to access mileage values. However, no setter method is provided for mileage, meaning it cannot be modified outside the Car class.
In the Main class, an object car of the Car class is created. Company_name, model_name, and year values are set using the respective setter methods, and then retrieved using the getter methods.
The mileage is then retrieved using the getMileage() method and printed using System.out.println().
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Car" class prevents setting a year before 1886 (year of the first car).
- Write a Java program where the "Car" class includes a method to calculate fuel efficiency.
- Write a Java program where the "Car" class allows updating the mileage only through a drive method.
- Write a Java program where the "Car" class supports setting a maximum speed limit.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
PREV : Implementing a circle class with getter, setter, and calculation methods.
NEXT : Implementing a Student Class with Grade Validation.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
