Java: Consecutive Numbers in an array
76. Check if numbers in array can form a consecutive list
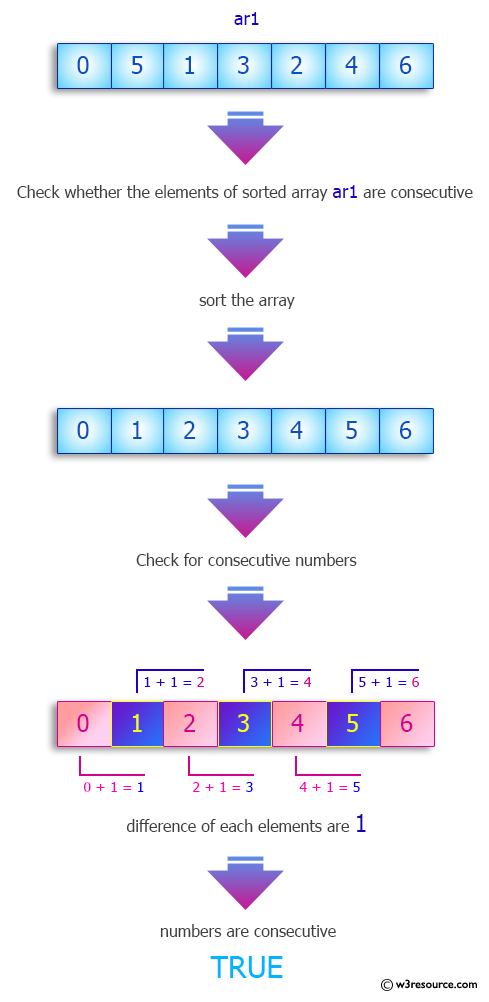
Write a Java program to determine whether numbers in an array can be rearranged so that each number appears exactly once in a consecutive list of numbers. Return true otherwise false.
Sample Data:
{1, 2 ,5, 0, 4, 3, 6} -> true
{1, 2 ,5, 0, 3, 6, 7} ->false
Pictorial Presentation:
Sample Solution-1:
Java Code:
// Import necessary Java classes.
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
// Define the 'Main' class.
public class Main {
// Define the main method for running the program.
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize an array of numbers.
int[] nums = {1, 2 ,5, 0, 4, 3, 6};
// int[] nums = {1, 2 ,5, 0, 3, 6, 7};
System.out.printf("\nOriginal array: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
// Call the 'test' method to check for consecutive numbers in the array.
boolean result = test(nums);
System.out.printf("\nCheck consecutive numbers in the said array! " + result);
}
// Define the 'test' method to check for consecutive numbers in the array.
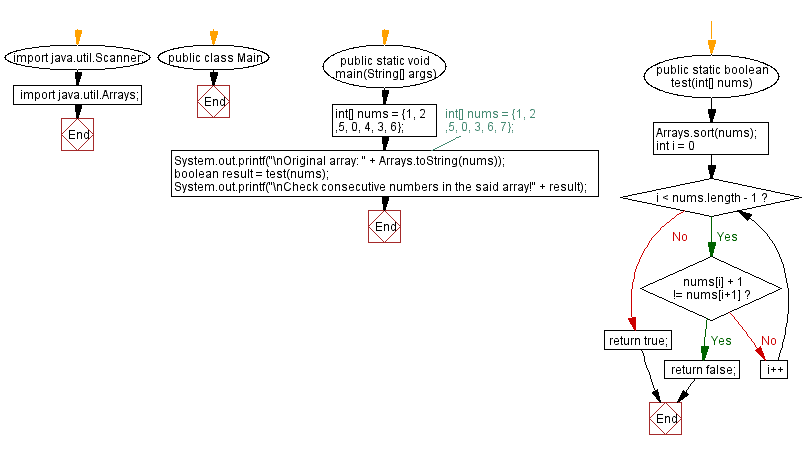
public static boolean test(int[] nums) {
// Sort the 'nums' array in ascending order.
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
// Check if the current number and the next number are consecutive.
if (nums[i] + 1 != nums[i + 1])
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
Sample Output:
Original array: [1, 2, 5, 0, 4, 3, 6] Check consecutive numbers in the said array!true
Flowchart:
Sample Solution-2:
Java Code:
// Import necessary Java classes.
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
// Define the 'Main' class.
public class Main {
// Define the main method for running the program.
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Initialize an array of numbers.
int[] nums = {1, 2 ,5, 0, 3, 6, 7};
// int[] nums = {1, 2 ,5, 0, 4, 3, 6};
System.out.printf("\nOriginal array: " + Arrays.toString(nums));
// Call the 'test' method to check for consecutive numbers in the array.
boolean result = test(nums);
System.out.printf("\nCheck consecutive numbers in the said array! " + result);
}
// Define the 'test' method to check for consecutive numbers in the array.
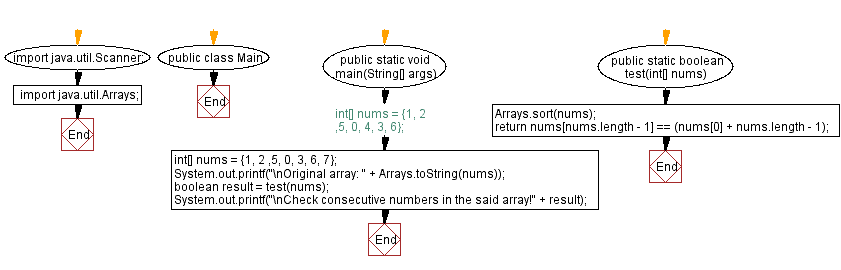
public static boolean test(int[] nums) {
// Sort the 'nums' array in ascending order.
Arrays.sort(nums);
// Check if the last number in the sorted array is equal to the first number plus the array length minus 1.
return nums[nums.length - 1] == (nums[0] + nums.length - 1);
}
}
Sample Output:
Original array: [1, 2, 5, 0, 3, 6, 7] Check consecutive numbers in the said array!false
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to check if an array can be rearranged into an arithmetic sequence.
- Write a Java program to determine if an array contains all numbers in a given range.
- Write a Java program to find the missing numbers in a sequence from a given array.
- Write a Java program to check if an array can be rearranged to form a sequence with a constant difference.
Go to:
PREV : Calculate the largest gap between sorted elements in array.
NEXT : Check if array alternates between positive and negative.
Java Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
