Java: Find and print one continuous subarray to sort an entire array
72. Find continuous subarray to sort for array to be sorted
Write a Java program to find and print one continuous subarray (from a given array of integers) that if you only sort the said subarray in ascending order then the entire array will be sorted in ascending order.
Example:
Input :
nums1 = {1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 6}
nums2 = { 1, 3, 2, 7, 5, 6, 4, 8}
Output:
Continuous subarray:
1 2 3 0
Continuous subarray:
3 2 7 5 6 4
Sample Solution:
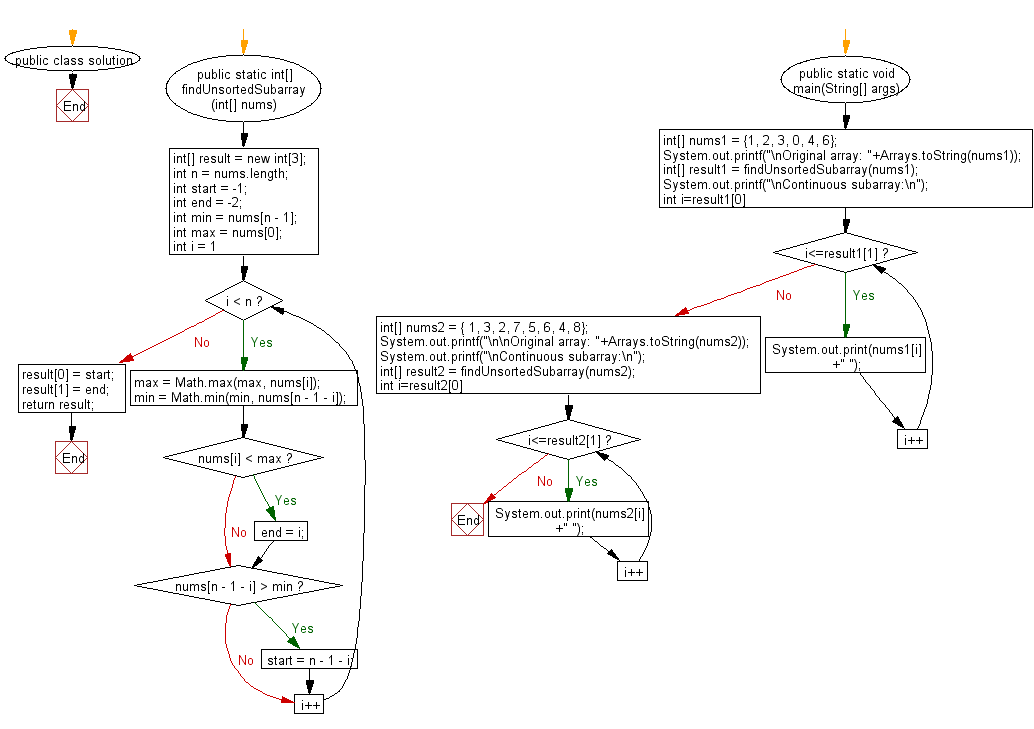
Java Code:
// Import the necessary Java classes.
import java.util.Arrays;
// Define the 'solution' class.
public class solution {
// Define a method to find the minimum continuous subarray for sorting.
public static int[] findUnsortedSubarray(int[] nums) {
// Initialize an array to store the result, where result[0] represents the start index and result[1] represents the end index.
int[] result = new int[2];
// Get the length of the input array.
int n = nums.length;
// Initialize variables for the start and end indices and for finding the minimum and maximum values.
int start = -1;
int end = -2;
int min = nums[n - 1];
int max = nums[0];
// Traverse the array to find the subarray that needs sorting.
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// Update the maximum and minimum values.
max = Math.max(max, nums[i]);
min = Math.min(min, nums[n - 1 - i]);
// Check if the current element is less than the maximum value.
if (nums[i] < max) {
end = i;
}
// Check if the current element is greater than the minimum value.
if (nums[n - 1 - i] > min) {
start = n - 1 - i;
}
}
// Update the result array with the start and end indices of the subarray to be sorted.
result[0] = start;
result[1] = end;
// Return the result.
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initialize the first array.
int[] nums1 = {1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 6};
System.out.printf("\nOriginal array: "+Arrays.toString(nums1));
// Find and print the continuous subarray that needs sorting.
int[] result1 = findUnsortedSubarray(nums1);
System.out.printf("\nContinuous subarray:\n");
for (int i = result1[0]; i <= result1[1]; i++) {
System.out.print(nums1[i] + " ");
}
// Initialize the second array.
int[] nums2 = { 1, 3, 2, 7, 5, 6, 4, 8};
System.out.printf("\n\nOriginal array: "+Arrays.toString(nums2));
System.out.printf("\nContinuous subarray:\n");
// Find and print the continuous subarray that needs sorting.
int[] result2 = findUnsortedSubarray(nums2);
for (int i = result2[0]; i <= result2[1]; i++) {
System.out.print(nums2[i] + " ");
}
}
}
Sample Output:
Original array: [1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 6] Continuous subarray: 1 2 3 0 Original array: [1, 3, 2, 7, 5, 6, 4, 8] Continuous subarray: 3 2 7 5 6 4
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to find the longest contiguous subarray that is already sorted.
- Write a Java program to find the number of elements that need to be sorted to make the whole array sorted.
- Write a Java program to find the smallest contiguous subarray that, when reversed, will make the entire array sorted.
- Write a Java program to check if an array can be sorted by swapping at most two elements.
Go to:
PREV : Find largest number from a list of non-negative integers.
NEXT : Sort array where only two elements are out of place.
Java Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
