Java: Create all possible permutations of a given array of distinct integers
68. Generate all permutations of a distinct integer array
Write a Java program to create all possible permutations of a given array of distinct integers.
Example:
Input :
nums1 = {1, 2, 3, 4}
nums2 = {1, 2, 3}
Output:
Possible permutations of the said array:
[1, 2, 3, 4]
[1, 2, 4, 3]
[1, 3, 2, 4]
[1, 3, 4, 2]
....
[4, 3, 2, 1]
[4, 3, 1, 2]
[4, 1, 3, 2]
[4, 1, 2, 3]
Possible permutations of the said array:
[1, 2, 3]
[1, 3, 2]
[2, 1, 3]
[2, 3, 1]
[3, 2, 1]
[3, 1, 2]
Sample Solution:
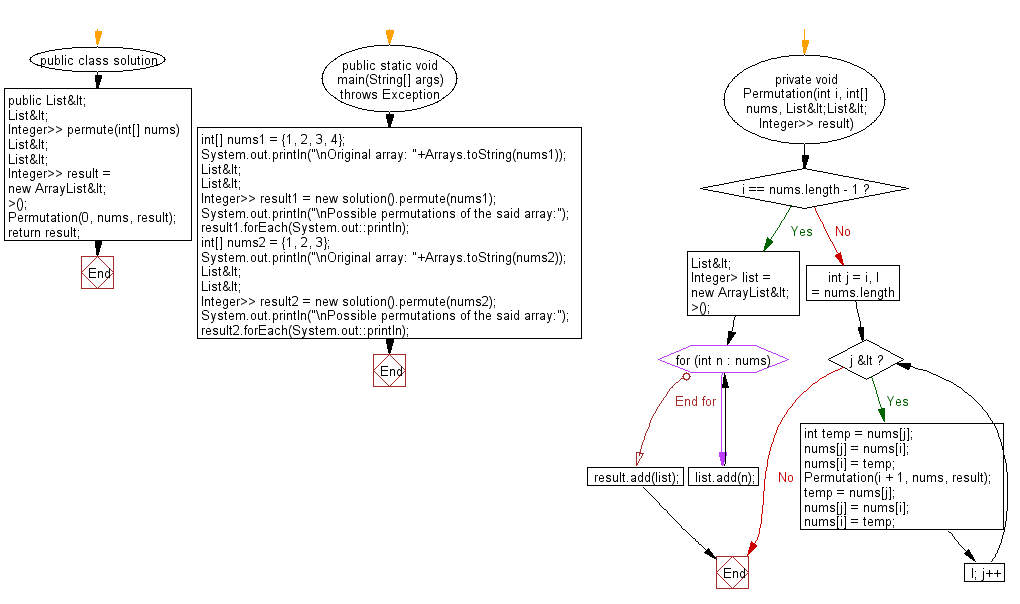
Java Code:
// Import the necessary Java classes.
import java.util.*;
import java.util.List;
// Define the 'solution' class.
public class solution {
// Main method to demonstrate permutation of arrays.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Initialize the first array.
int[] nums1 = {1, 2, 3, 4};
System.out.println("\nOriginal array 1: " + Arrays.toString(nums1));
// Calculate and display the permutations of the first array.
List<List<Integer>> result1 = new solution().permute(nums1);
System.out.println("\nPossible permutations of the first array:");
result1.forEach(System.out::println);
// Initialize the second array.
int[] nums2 = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println("\nOriginal array 2: " + Arrays.toString(nums2));
// Calculate and display the permutations of the second array.
List<List<Integer>> result2 = new solution().permute(nums2);
System.out.println("\nPossible permutations of the second array:");
result2.forEach(System.out::println);
}
// Method to calculate permutations of an array.
public List<List<Integer>>permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Permutation(0, nums, result);
return result;
}
// Recursive method to generate permutations.
private void Permutation(int i, int[] nums, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (i == nums.length - 1) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int n : nums) list.add(n);
result.add(list);
} else {
for (int j = i, l = nums.length; j < l; j++) {
int temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
Permutation(i + 1, nums, result);
temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
}
}
}
}
Sample Output:
Original array: [1, 2, 3, 4] Possible permutations of the said array: [1, 2, 3, 4] [1, 2, 4, 3] [1, 3, 2, 4] [1, 3, 4, 2] [1, 4, 3, 2] [1, 4, 2, 3] [2, 1, 3, 4] [2, 1, 4, 3] [2, 3, 1, 4] [2, 3, 4, 1] [2, 4, 3, 1] [2, 4, 1, 3] [3, 2, 1, 4] [3, 2, 4, 1] [3, 1, 2, 4] [3, 1, 4, 2] [3, 4, 1, 2] [3, 4, 2, 1] [4, 2, 3, 1] [4, 2, 1, 3] [4, 3, 2, 1] [4, 3, 1, 2] [4, 1, 3, 2] [4, 1, 2, 3] Original array: [1, 2, 3] Possible permutations of the said array: [1, 2, 3] [1, 3, 2] [2, 1, 3] [2, 3, 1] [3, 2, 1] [3, 1, 2]
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to generate all possible unique subsets of a given array.
- Write a Java program to find all unique permutations of an array that may contain duplicate elements.
- Write a Java program to generate all possible k-length permutations from a given array.
- Write a Java program to find all permutations of an array where adjacent elements must differ by at least 2.
Go to:
PREV : Find subarray with largest sum in a circular array.
NEXT : Find minimum subarray sum of specified size
Java Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
