Java: Create an array of its anti-diagonals from a given square matrix
37. Get anti-diagonals from square matrix
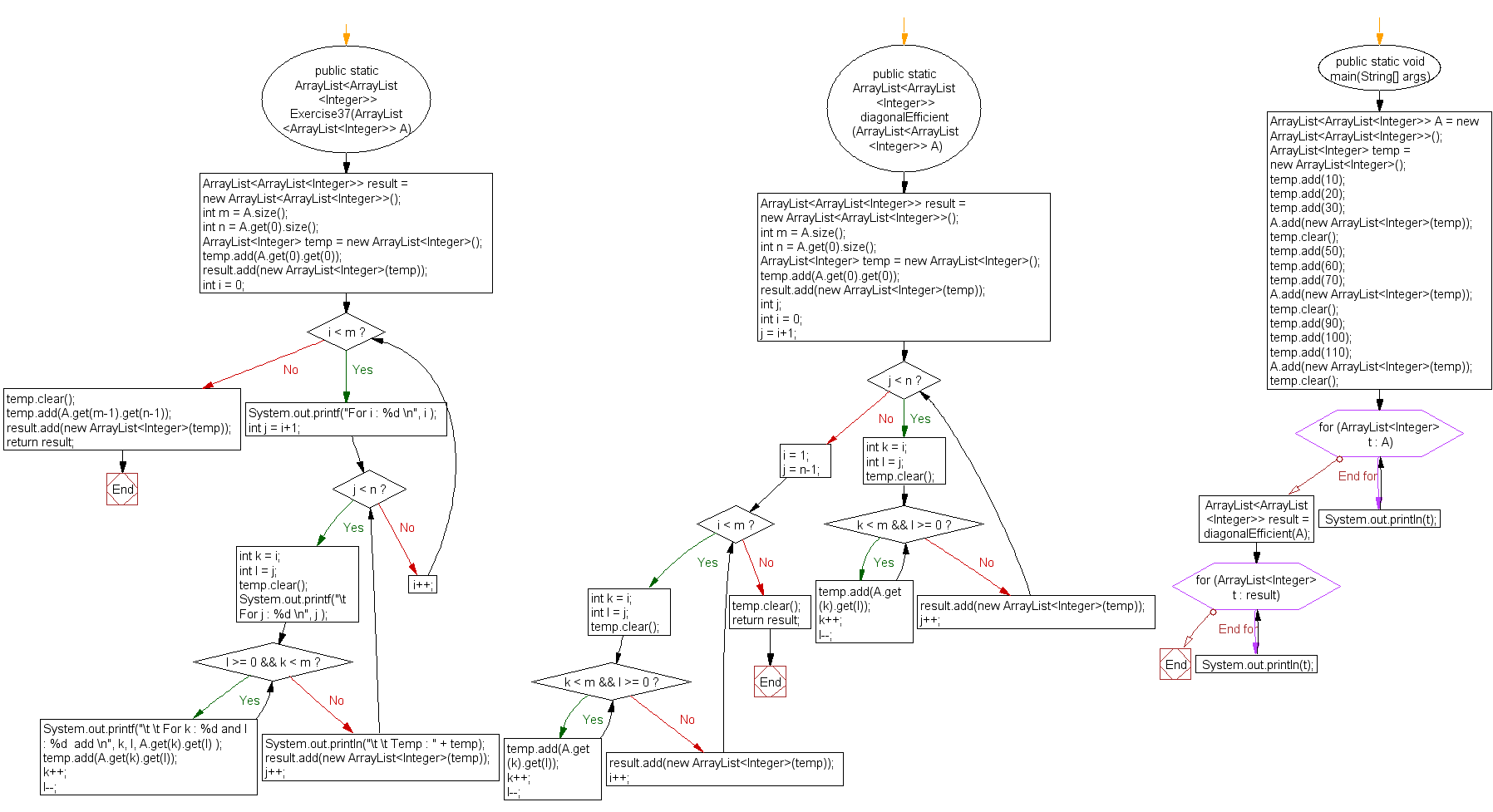
Write a Java program to create an array of its anti-diagonals from a given square matrix.
Example:
Input :
1 2
3 4
Output:
[
[1],
[2, 3],
[4]
]
Input:
[10, 20, 30]
[50, 60, 70]
[90, 100, 110]
Output:
[10]
[20, 50]
[30, 60, 90]
[70, 100]
[110]
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
//https://github.com/nagajyothi/Arrays/blob/master/Diagonal.java
// Import necessary Java libraries.
import java.util.*;
// Define a class named Exercise37.
public class Exercise37 {
// A method to compute and return diagonal elements efficiently.
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> diagonalEfficient(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> A) {
// Create a list of lists to store the diagonal elements.
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
// Get the number of rows and columns in the 2D array.
int m = A.size();
int n = A.get(0).size();
// Create a list to temporarily store diagonal elements.
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// Add the first diagonal element to the result.
temp.add(A.get(0).get(0));
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
// Iterate through the columns of the first row and add diagonal elements to the result.
int i = 0;
int j = i + 1;
while (j < n) {
int k = i;
int l = j;
temp.clear();
while (k < m && l >= 0) {
temp.add(A.get(k).get(l));
k++;
l--;
}
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
j++;
}
// Iterate through the rows of the last column and add diagonal elements to the result.
i = 1;
j = n - 1;
while (i < m) {
int k = i;
int l = j;
temp.clear();
while (k < m && l >= 0) {
temp.add(A.get(k).get(l));
k++;
l--;
}
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
i++;
}
// Clear the temporary list and return the result.
temp.clear();
return result;
}
// The main method for executing the program.
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a 2D array represented as a list of lists.
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> A = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
ArrayList<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
temp.add(10);
temp.add(20);
temp.add(30);
A.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
temp.clear();
temp.add(50);
temp.add(60);
temp.add(70);
A.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
temp.clear();
temp.add(90);
temp.add(100);
temp.add(110);
A.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp));
temp.clear();
// Print the original 2D array.
for (ArrayList<Integer> t : A) {
System.out.println(t);
}
// Call the diagonalEfficient method and print the result.
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = diagonalEfficient(A);
for (ArrayList<Integer> t : result) {
System.out.println(t);
}
}
}
Sample Output:
[10, 20, 30] [50, 60, 70] [90, 100, 110] [10] [20, 50] [30, 60, 90] [70, 100] [110]
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to compute the diagonal sum of a square matrix.
- Write a Java program to rotate a given matrix by 90 degrees.
- Write a Java program to find the determinant of a square matrix.
- Write a Java program to check if a given matrix is symmetric.
Go to:
PREV : Find triplets summing to given number.
NEXT : Find majority element in array.
Java Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.