C#: Sum of all prime numbers in an array
Write a C# Sharp program that calculates the sum of all prime numbers in an array of numbers.
Sample Data:
({ 7, 5, 85, 9, 11, 23, 18 }) -> 46
({ 200, 300, 250, 151, 162 }) -> 151
Sample Solution-1:
C# Sharp Code:
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace exercises
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Initializing an array of integers
int[] nums = { 7, 5, 85, 9, 11, 23, 18 };
// Displaying original array elements using string.Join method
Console.WriteLine("Original array elements:");
Console.WriteLine($"{string.Join(", ", nums)}");
// Finding and displaying the sum of all prime numbers in the array
Console.WriteLine("Sum of all prime numbers in the said array: " + test(nums));
// Creating another array of integers
int[] nums1 = { 200, 300, 250, 151, 162 };
Console.WriteLine("\nOriginal array elements:");
Console.WriteLine($"{string.Join(", ", nums1)}");
// Finding and displaying the sum of all prime numbers in the second array
Console.WriteLine("Sum of all prime numbers in the said array: " + test(nums1));
}
// Method to check if a number is prime and calculate the sum of all prime numbers in the array
public static int test(int[] arr)
{
int result = 0;
// Loop through each number in the array
foreach (int number in arr)
{
// Check if the number is prime by calling the IsPrime method
if (IsPrime(number, number / 2))
{
// If the number is prime, add it to the result
result += number;
}
}
return result;
}
// Method to check if a number is prime using recursion
static bool IsPrime(int n1, int i)
{
if (i == 1)
{
// Base case: If i becomes 1, the number is prime, so return true
return true;
}
else
{
// If the number is divisible by i, it's not prime; otherwise, recursively call IsPrime with i decremented by 1
if (n1 % i == 0)
return false;
else
return IsPrime(n1, i - 1); // Recursively call IsPrime itself with i decremented by 1
}
}
}
}
Sample Output:
Original array elements: 7, 5, 85, 9, 11, 23, 18 Sum of all prime numbers in the said array: 46 Original array elements: 200, 300, 250, 151, 162 Sum of all prime numbers in the said array: 151
Flowchart:
![]()
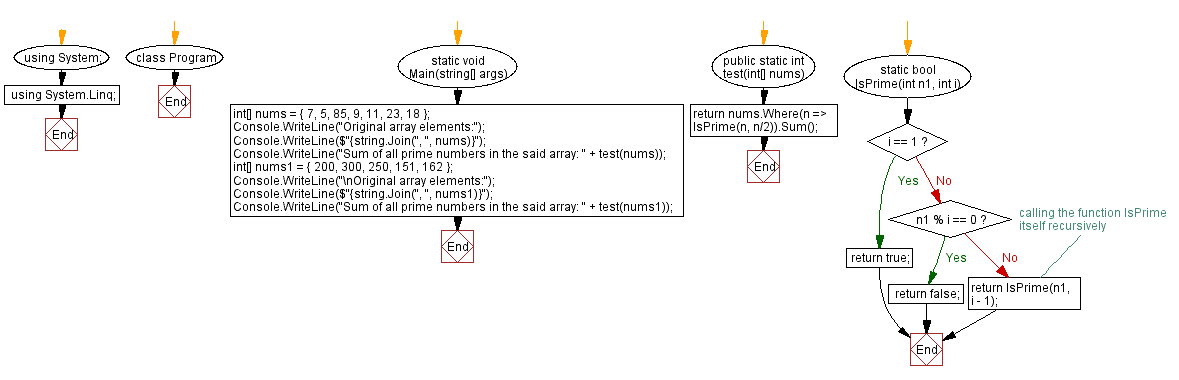
Sample Solution-2:
C# Sharp Code:
using System;
using System.Linq;
namespace exercises
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Initializing an array of integers
int[] nums = { 7, 5, 85, 9, 11, 23, 18 };
// Displaying original array elements using string.Join method
Console.WriteLine("Original array elements:");
Console.WriteLine($"{string.Join(", ", nums)}");
// Finding and displaying the sum of all prime numbers in the array
Console.WriteLine("Sum of all prime numbers in the said array: " + test(nums));
// Creating another array of integers
int[] nums1 = { 200, 300, 250, 151, 162 };
Console.WriteLine("\nOriginal array elements:");
Console.WriteLine($"{string.Join(", ", nums1)}");
// Finding and displaying the sum of all prime numbers in the second array
Console.WriteLine("Sum of all prime numbers in the said array: " + test(nums1));
}
// Method to calculate the sum of all prime numbers in the array using LINQ
public static int test(int[] nums)
{
// Using LINQ to filter prime numbers and calculate their sum
return nums.Where(n => IsPrime(n, n / 2)).Sum();
}
// Method to check if a number is prime using recursion
static bool IsPrime(int n1, int i)
{
if (i == 1)
{
// Base case: If i becomes 1, the number is prime, so return true
return true;
}
else
{
// If the number is divisible by i, it's not prime; otherwise, recursively call IsPrime with i decremented by 1
if (n1 % i == 0)
return false;
else
return IsPrime(n1, i - 1); // Recursively call IsPrime itself with i decremented by 1
}
}
}
}
Sample Output:
Original array elements: 7, 5, 85, 9, 11, 23, 18 Sum of all prime numbers in the said array: 46 Original array elements: 200, 300, 250, 151, 162 Sum of all prime numbers in the said array: 151
Flowchart:
Go to:
PREV : Check specific digit in an array of numbers.
NEXT : Smallest positive which is not present in an array.
C# Sharp Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
