C++ Vector Exercises: Consecutive Numbers in a vector
1. Consecutive Rearrangement in Vector
Write a C++ program to check whether numbers in a vector can be rearranged so that each number appears exactly once in a consecutive list of numbers. Return true otherwise false.
Sample Data:
{1, 2 ,5, 7, 4, 3, 6} -> true
{1, 2 ,5, 0, 3, 6, 7} ->false
Visual Presentation:
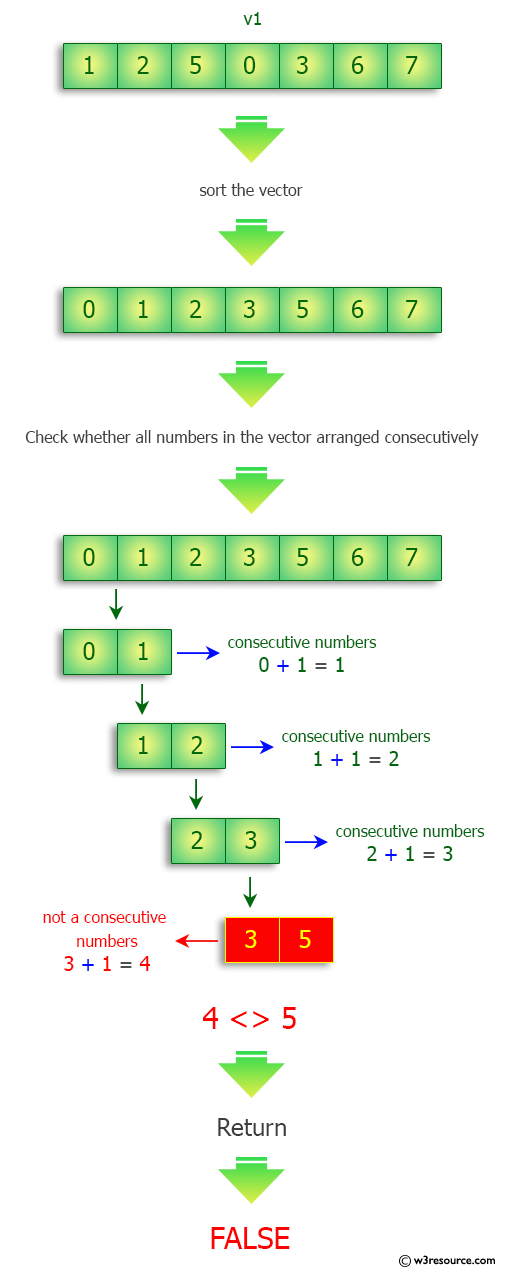
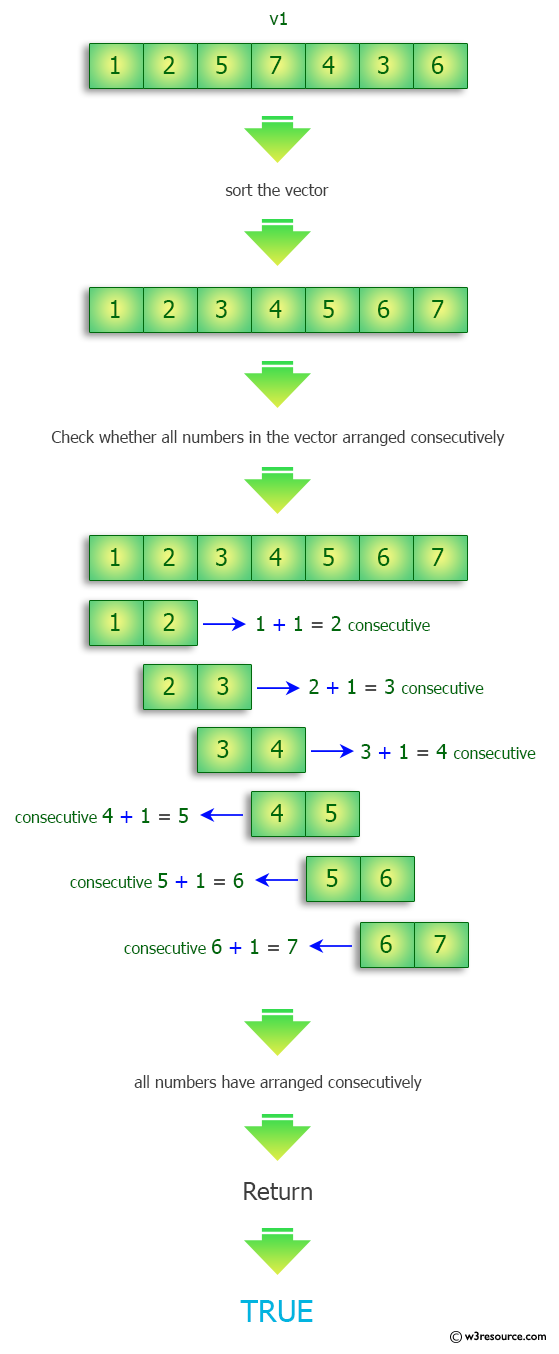
Sample Solution-1:
C++ Code:
#include <algorithm> // Including the Algorithm Library for sorting
#include <iostream> // Including the Input/Output Stream Library
#include <vector> // Including the Vector Library for using vectors
using namespace std; // Using the Standard Namespace
// Function to test if the elements in the vector are consecutive
bool test(std::vector<int> nums) {
std::sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // Sorting the elements of the vector in ascending order
// Loop through the vector to check if elements are consecutive
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size() - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i + 1] != (nums[i] + 1)) {
return false; // If the elements are not consecutive, return false
}
}
return true; // If all elements are consecutive, return true
}
// Main function
int main() {
// Declaring a vector of integers and initializing it with values
// Uncomment either of the following lines to test different sets of numbers
// vector<int> nums = {1, 2 ,5, 7, 4, 3, 6}; // Test vector with non-consecutive numbers
vector<int> nums = {1, 2 ,5, 0, 3, 6, 7}; // Test vector with consecutive numbers
// Printing the elements of the vector
for (int x : nums)
cout << x << " ";
cout << "\nCheck consecutive numbers in the said vector! " << test(nums) << endl; // Calling the test function to check if elements are consecutive and displaying the result
}
Sample Output:
1 2 5 0 3 6 7 Check consecutive numbers in the said vector! 0
Flowchart:
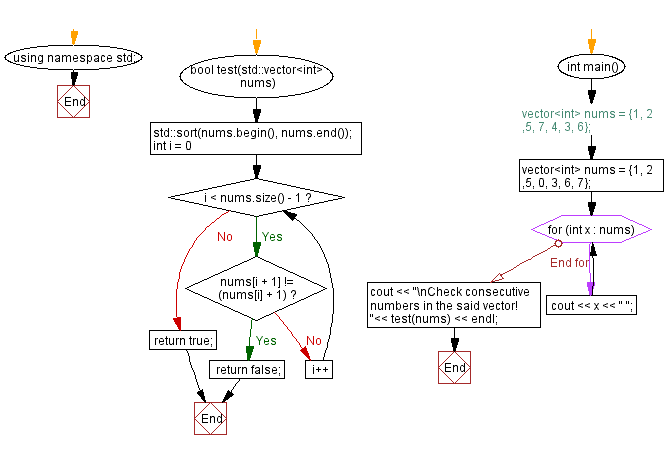
Sample Solution-2:
C++ Code:
#include <algorithm> // Include the algorithm header for the sort function
#include <iostream> // Include the iostream header for input and output operations
#include <vector> // Include the vector header for using the vector container
using namespace std; // Use the std namespace to simplify code
bool test(std::vector<int> nums)
{
std::sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // Sort the elements of the vector in ascending order
int last = nums.at(0) - 1; // Initialize a variable to store the last value, set to one less than the first element
for (int number : nums) {
if ((number - last) != 1) // Check if the current number is not one greater than the last one
return false; // If not, the numbers are not consecutive, so return false
last = number; // Update the last value to the current number for the next iteration
}
return true; // If all numbers are consecutive, return true
}
int main(){
vector<int> nums = {1, 2 ,5, 7, 4, 3, 6}; // Initialize a vector with a set of integers
//vector<int> nums = {1, 2 ,5, 0, 3, 6, 7}; // Another set of integers for testing
for (int x : nums)
cout << x << " "; // Print each element of the vector
cout << "\nCheck consecutive numbers in the said vector! "<< test(nums) << endl; // Check and display if the numbers are consecutive
}
Sample Output:
1 2 5 7 4 3 6 Check consecutive numbers in the said vector! 1
Flowchart:
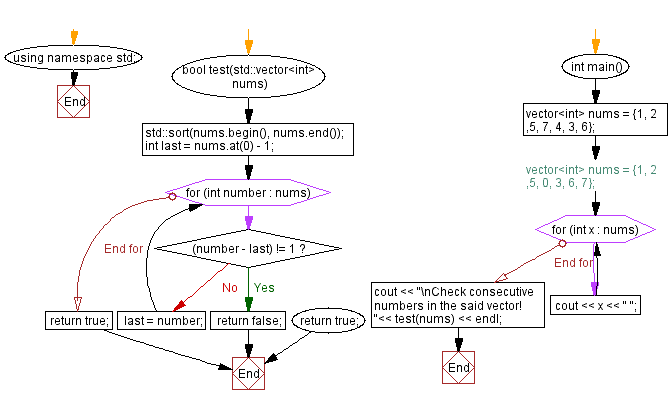
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program that checks if the numbers in a vector can be rearranged into a sequence of consecutive integers using sorting and verifying adjacent differences.
- Write a C++ program to determine whether a vector can form a consecutive sequence by counting the minimum and maximum and checking if max - min + 1 equals the vector’s size.
- Write a C++ program that uses a hash set to check if all numbers in a vector are unique and then verifies the consecutive property by comparing with an expected range.
- Write a C++ program that reads a vector of integers and returns true if it can be rearranged into a sequence with no gaps by iterating through the sorted vector.
Go to:
PREV : C++ Vector Exercises Home
NEXT : Elements Smaller Than Adjacent Neighbours.
C++ Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
