C++ Stack Exercises: Sort the stack (using a vector) elements
25. Sort the Elements of a Vector-Based Stack
Write a C++ program that sorts the stack (using a vector) elements.
Test Data:
Create a stack object:
Input and store (using vector) some elements onto the stack:
Stack elements are: 1 3 2 6 5 -1 0
Sort the stack items in ascending order:
Stack elements are: -1 0 1 2 3 5 6
Sample Solution:
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> // Required for using sort() function
using namespace std;
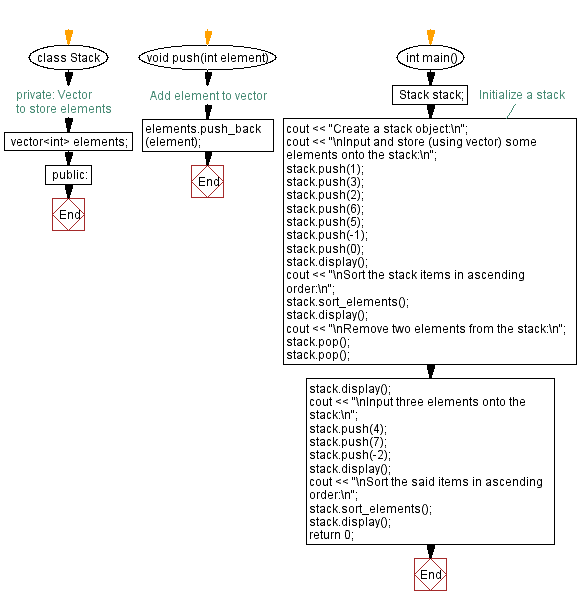
class Stack {
private:
vector<int> elements; // Vector to store elements
public:
// Function to push an element onto the stack
void push(int element) {
elements.push_back(element); // Add element to the end of the vector
}
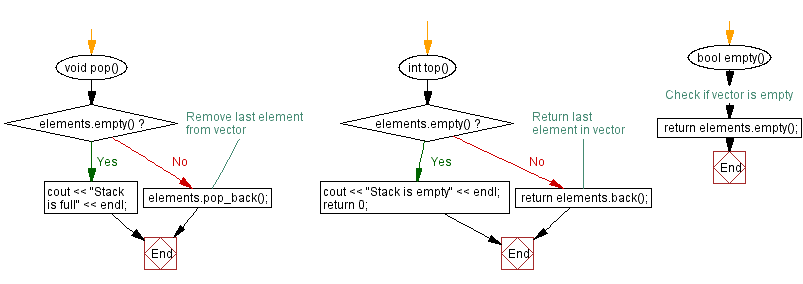
// Function to pop an element from the stack
void pop() {
if (elements.empty()) {
cout << "Stack is full" << endl; // Display full message if the stack is empty
} else {
elements.pop_back(); // Remove the last element from the vector
}
}
// Function to get the top element of the stack
int top() {
if (elements.empty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty" << endl; // Display empty message if the stack is empty
return 0;
} else {
return elements.back(); // Return the last element in the vector
}
}
// Function to check if the stack is empty
bool empty() {
return elements.empty(); // Check if the vector is empty
}
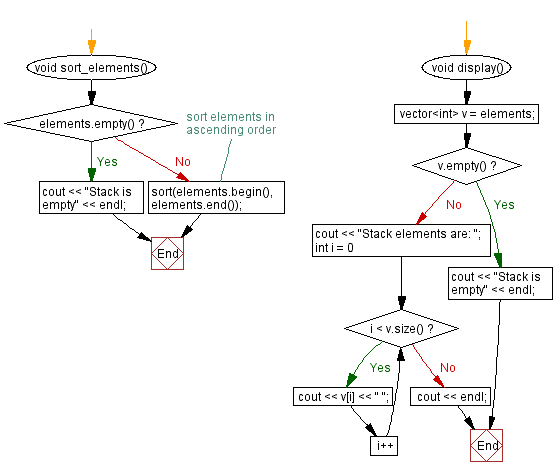
// Function to sort elements of the stack in ascending order
void sort_elements() {
if (elements.empty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty" << endl; // Display empty message if the stack is empty
return;
}
sort(elements.begin(), elements.end()); // Sort elements in ascending order
}
// Function to display the elements of the stack
void display() {
vector<int> v = elements;
if (v.empty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty" << endl; // Display empty message if the stack is empty
return;
}
cout << "Stack elements are: ";
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
cout << v[i] << " "; // Display the elements of the stack
}
cout << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Stack stack;
cout << "Create a stack object:\n"; // Initialize a stack
cout << "\nInput and store (using vector) some elements onto the stack:\n";
stack.push(1);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(6);
stack.push(5);
stack.push(-1);
stack.push(0);
stack.display();
cout << "\nSort the stack items in ascending order:\n";
stack.sort_elements();
stack.display();
cout << "\nRemove two elements from the stack:\n";
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
stack.display();
cout << "\nInput three elements onto the stack:\n";
stack.push(4);
stack.push(7);
stack.push(-2);
stack.display();
cout << "\nSort the said items in ascending order:\n";
stack.sort_elements();
stack.display();
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Create a stack object: Input and store (using vector) some elements onto the stack: Stack elements are: 1 3 2 6 5 -1 0 Sort the stack items in ascending order: Stack elements are: -1 0 1 2 3 5 6 Remove two elements from the stack: Stack elements are: -1 0 1 2 3 Input three elements onto the stack: Stack elements are: -1 0 1 2 3 4 7 -2 Sort the said items in ascending order: Stack elements are: -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 7
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to sort a vector-based stack in ascending order using the STL sort algorithm.
- Develop a C++ program that implements a vector-based stack and rearranges its elements in sorted order.
- Design a C++ program to create a stack using vectors and sort its elements while preserving the original order.
- Implement a C++ program to manage a stack using vectors and apply a custom sorting algorithm to its elements.
Go to:
PREV : Implement Stack using Vector with Push, Pop, and Top Check.
NEXT : Reverse the Elements of a Vector-Based Stack.
CPP Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
