C++ Stack Exercises: Implement a stack using a dynamic array with push, pop
20. Implement Stack using Dynamic Array with Push, Pop, and Top Check
Write a C++ program to implement a stack using a dynamic array with push and pop operations. Find the top element of the stack and check if the stack is empty or not.
Test Data:
Input the size of the stack: Is the stack empty? Yes
Input some elements onto the stack:
Stack elements are: 9 7 5 3 1
Is the stack full? No
Sample Solution:
C++ Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
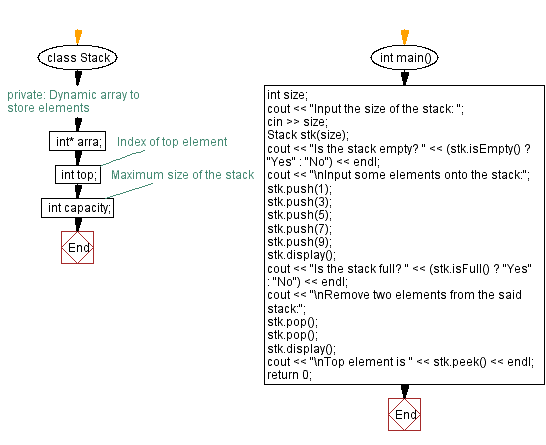
class Stack {
private:
// Dynamic array to store elements
int* arra;
int top; // Index of top element
int capacity; // Maximum size of the stack
public:
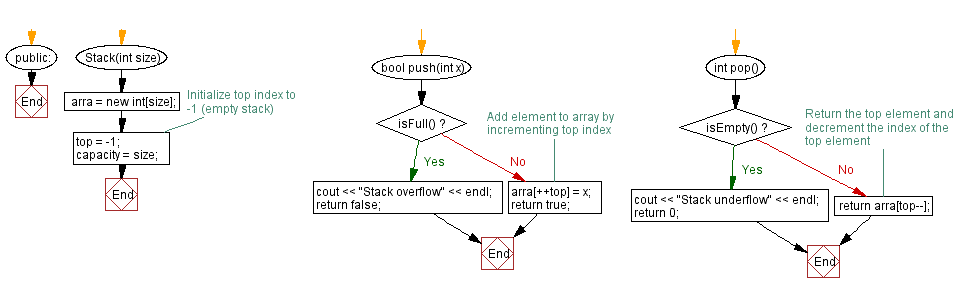
// Constructor to initialize the stack with a given size
Stack(int size) {
arra = new int[size]; // Allocate memory for the stack array
top = -1; // Initialize top index to -1 (empty stack)
capacity = size; // Set the maximum capacity of the stack
}
// Function to push an element onto the stack
bool push(int x) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Stack overflow" << endl; // Display overflow message if the stack is full
return false;
}
// Add element to array by incrementing top index
arra[++top] = x;
return true;
}
// Function to pop an element from the stack
int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Stack underflow" << endl; // Display underflow message if the stack is empty
return 0;
}
// Return the top element and decrement the index of the top element
return arra[top--];
}
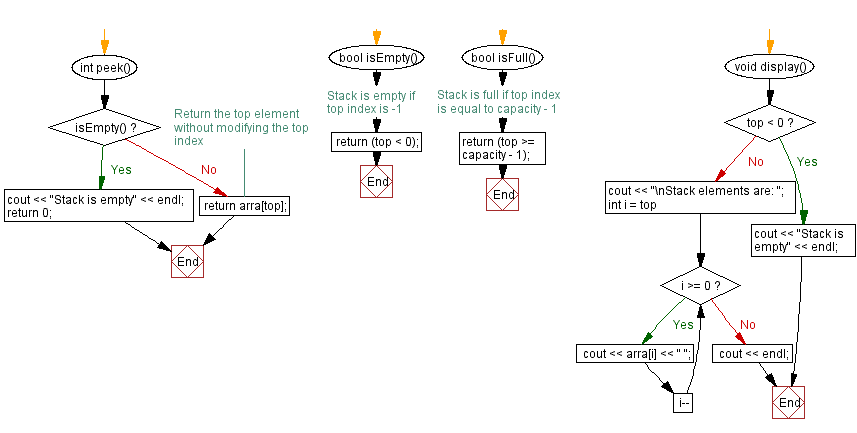
// Function to peek the top element of the stack without removing it
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Stack is empty" << endl; // Display message if the stack is empty
return 0;
}
// Return the top element without modifying the top index
return arra[top];
}
// Function to check if the stack is empty
bool isEmpty() {
// Stack is empty if top index is -1
return (top < 0);
}
// Function to check if the stack is full
bool isFull() {
// Stack is full if top index is equal to capacity - 1
return (top >= capacity - 1);
}
// Function to display the elements of the stack
void display() {
if (top < 0) {
cout << "Stack is empty" << endl; // Display message if the stack is empty
return;
}
cout << "\nStack elements are: ";
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--)
cout << arra[i] << " "; // Display the elements of the stack
cout << endl;
}
};
int main() {
int size;
cout << "Input the size of the stack: ";
cin >> size; // Take input for the size of the stack
Stack stk(size); // Create a stack of the given size
cout << "Is the stack empty? " << (stk.isEmpty() ? "Yes" : "No") << endl; // Check if the stack is empty
cout << "\nInput some elements onto the stack:";
stk.push(1);
stk.push(3);
stk.push(5);
stk.push(7);
stk.push(9);
stk.display(); // Display the elements of the stack
cout << "Is the stack full? " << (stk.isFull() ? "Yes" : "No") << endl; // Check if the stack is full
cout << "\nRemove two elements from the said stack:";
stk.pop();
stk.pop();
stk.display(); // Display the updated elements of the stack
cout << "\nTop element is " << stk.peek() << endl; // Display the top element of the stack
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Input the size of the stack: 8 Is the stack empty? Yes Input some elements onto the stack: Stack elements are: 9 7 5 3 1 Is the stack full? No Remove two elements from the said stack: Stack elements are: 5 3 1 Top element is 5
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to implement a stack using a dynamic array, checking for empty and full conditions with custom messages.
- Develop a C++ program that creates a dynamic array-based stack and efficiently handles push/pop operations with error checks.
- Design a C++ program to implement a dynamic stack using an array and display the top element after each operation.
- Implement a C++ program to manage a dynamic array-based stack with real-time updates of the top element and status messages.
Go to:
PREV : Sort the Elements of a Linked List-Based Stack.
NEXT : Sort a Dynamic Array-Based Stack.
CPP Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
