C++ Queue Exercises: Union of two queues
27. Find the Union of Two Queues
Write a C++ program to find the union of two queues.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <iostream> // Including necessary library for input and output operations
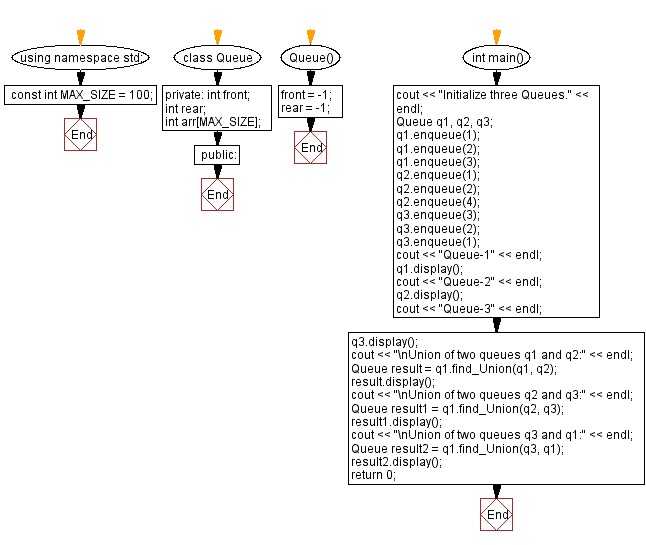
using namespace std;
const int MAX_SIZE = 100; // Maximum size for the queue
class Queue {
private:
int front; // Front of the queue
int rear; // Rear of the queue
int arr[MAX_SIZE]; // Array to store queue elements
public:
Queue() {
front = -1; // Initializing front index to -1
rear = -1; // Initializing rear index to -1
}
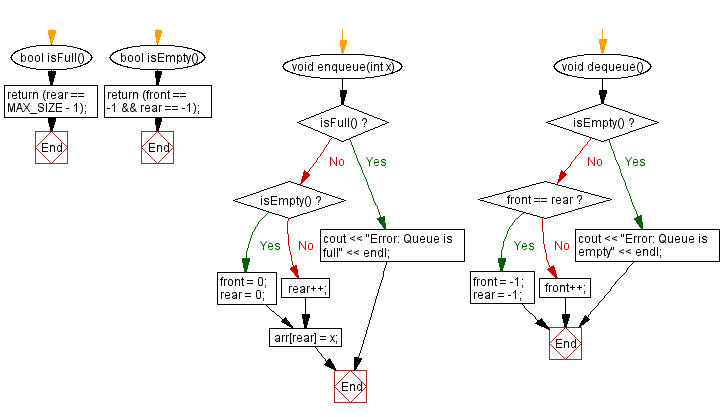
bool isFull() {
return (rear == MAX_SIZE - 1); // Check if the queue is full
}
bool isEmpty() {
return (front == -1 && rear == -1); // Check if the queue is empty
}
void enqueue(int x) {
if (isFull()) {
cout << "Error: Queue is full" << endl; // Display error if the queue is full
return;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
front = 0;
rear = 0;
} else {
rear++;
}
arr[rear] = x; // Add an element to the rear of the queue
}
void dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Error: Queue is empty" << endl; // Display error if the queue is empty
return;
}
if (front == rear) {
front = -1;
rear = -1;
} else {
front++;
}
}
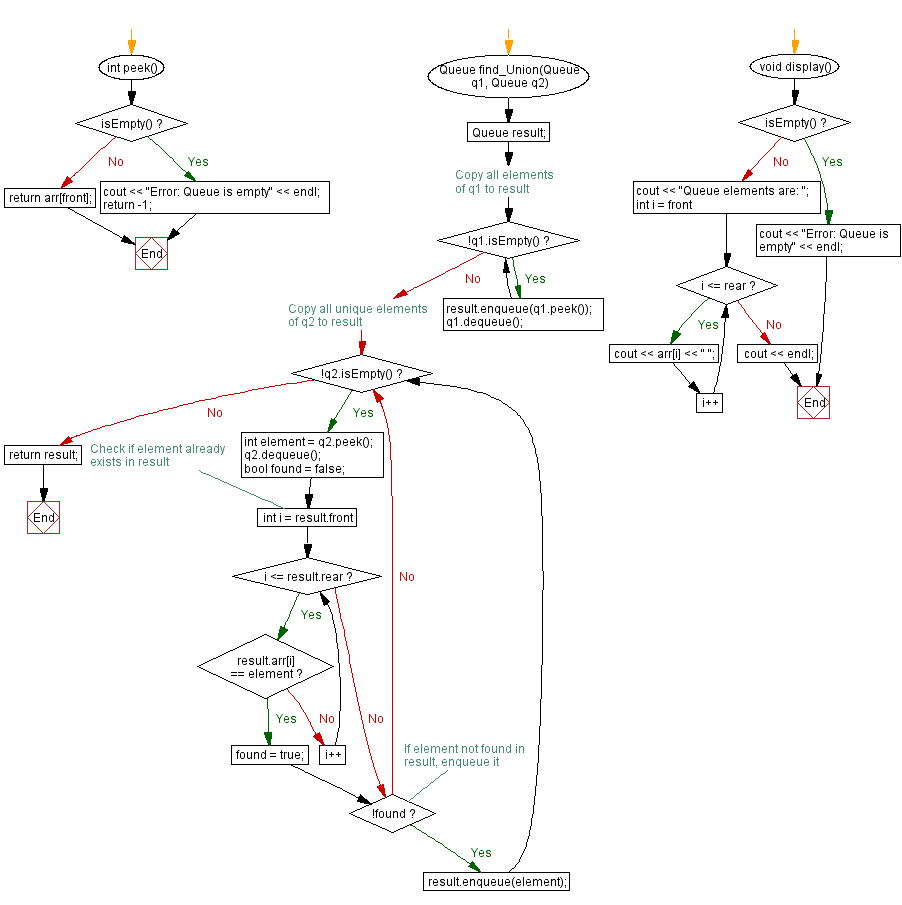
int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Error: Queue is empty" << endl; // Display error if the queue is empty
return -1;
}
return arr[front]; // Return the element at the front of the queue
}
Queue find_Union(Queue q1, Queue q2) {
Queue result; // Initialize a new queue to store the union
// Copy all elements of q1 to result
while (!q1.isEmpty()) {
result.enqueue(q1.peek());
q1.dequeue();
}
// Copy all unique elements of q2 to result
while (!q2.isEmpty()) {
int element = q2.peek();
q2.dequeue();
bool found = false;
// Check if element already exists in result
for (int i = result.front; i <= result.rear; i++) {
if (result.arr[i] == element) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
// If element not found in result, enqueue it
if (!found) {
result.enqueue(element);
}
}
return result; // Return the resulting queue containing the union
}
void display() {
if (isEmpty()) {
cout << "Error: Queue is empty" << endl; // Display error if the queue is empty
return;
}
cout << "Queue elements are: ";
for (int i = front; i <= rear; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " "; // Display all elements in the queue
}
cout << endl;
}
};
int main() {
cout << "Initialize three Queues." << endl;
Queue q1, q2, q3; // Creating instances of Queue
q1.enqueue(1);
q1.enqueue(2);
q1.enqueue(3);
q2.enqueue(1);
q2.enqueue(2);
q2.enqueue(4);
q3.enqueue(3);
q3.enqueue(2);
q3.enqueue(1);
cout << "Queue-1" << endl;
q1.display(); // Display elements of Queue-1
cout << "Queue-2" << endl;
q2.display(); // Display elements of Queue-2
cout << "Queue-3" << endl;
q3.display(); // Display elements of Queue-3
cout << "\nUnion of two queues q1 and q2:" << endl;
Queue result = q1.find_Union(q1, q2); // Get union of q1 and q2
result.display(); // Display the union
cout << "\nUnion of two queues q2 and q3:" << endl;
Queue result1 = q1.find_Union(q2, q3); // Get union of q2 and q3
result1.display(); // Display the union
cout << "\nUnion of two queues q3 and q1:" << endl;
Queue result2 = q1.find_Union(q3, q1); // Get union of q3 and q1
result2.display(); // Display the union
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Initialize three Queues. Queue-1 Queue elements are: 1 2 3 Queue-2 Queue elements are: 1 2 4 Queue-3 Queue elements are: 3 2 1 Union of two queues q1 and q2: Queue elements are: 1 2 3 4 Union of two queues q2 and q3: Queue elements are: 1 2 4 3 Union of two queues q3 and q1: Queue elements are: 3 2 1
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to merge two queues into one by taking the union of their elements and removing duplicates.
- Write a C++ program to combine two queues and output a new queue that contains every distinct element from both.
- Write a C++ program to compute the union of two queues and display the resulting queue in sorted order.
- Write a C++ program to join two queues into a single container by merging elements and ensuring no repetition.
Go to:
PREV : Find the Intersection of Two Queues.
NEXT : C++ Numbers Exercises Home.
CPP Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
