C++ Object-Oriented Programming: Shape class and derived shapes
10. Shape Class with Virtual Functions and Derived Classes
Write a C++ program to implement a class called Shape with virtual member functions for calculating area and perimeter. Derive classes such as Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle from the Shape class and override virtual functions accordingly.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <iostream> // Include necessary header for input/output stream
#include <cmath> // Include necessary header for mathematical functions
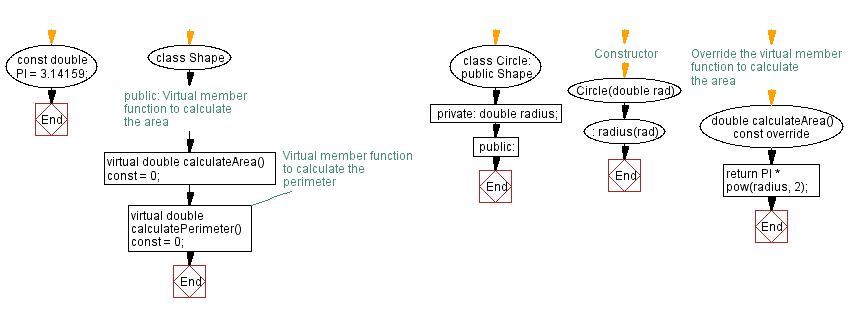
const double PI = 3.14159; // Define constant value for PI
class Shape { // Define a base class named Shape
public:
// Virtual member function to calculate the area (pure virtual function)
virtual double calculateArea() const = 0;
// Virtual member function to calculate the perimeter (pure virtual function)
virtual double calculatePerimeter() const = 0;
};
class Circle: public Shape { // Define a derived class named Circle inheriting from Shape
private:
double radius; // Private member variable to store the radius of the circle
public:
// Constructor for Circle class
Circle(double rad): radius(rad) {}
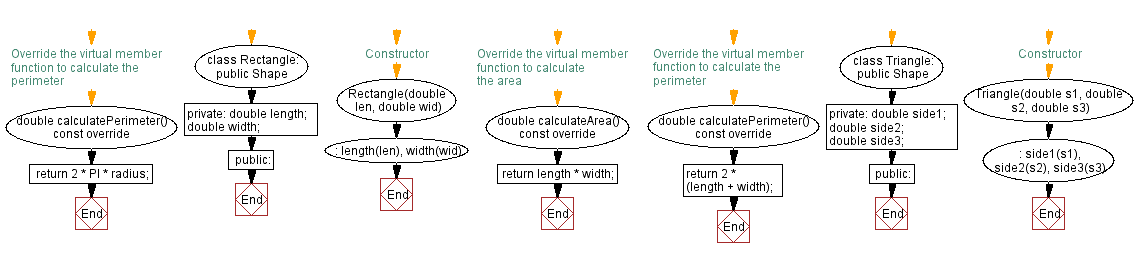
// Override the virtual member function to calculate the area
double calculateArea() const override {
return PI * pow(radius, 2); // Calculate the area of the circle using the radius
}
// Override the virtual member function to calculate the perimeter
double calculatePerimeter() const override {
return 2 * PI * radius; // Calculate the perimeter of the circle using the radius
}
};
class Rectangle: public Shape { // Define a derived class named Rectangle inheriting from Shape
private:
double length; // Private member variable to store the length of the rectangle
double width; // Private member variable to store the width of the rectangle
public:
// Constructor for Rectangle class
Rectangle(double len, double wid): length(len), width(wid) {}
// Override the virtual member function to calculate the area
double calculateArea() const override {
return length * width; // Calculate the area of the rectangle using its length and width
}
// Override the virtual member function to calculate the perimeter
double calculatePerimeter() const override {
return 2 * (length + width); // Calculate the perimeter of the rectangle using its length and width
}
};
class Triangle: public Shape { // Define a derived class named Triangle inheriting from Shape
private:
double side1; // Private member variable to store the first side of the triangle
double side2; // Private member variable to store the second side of the triangle
double side3; // Private member variable to store the third side of the triangle
public:
// Constructor for Triangle class
Triangle(double s1, double s2, double s3): side1(s1), side2(s2), side3(s3) {}
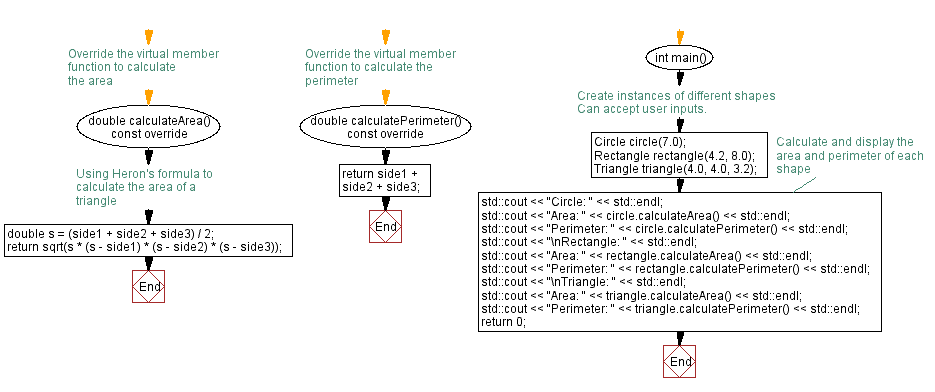
// Override the virtual member function to calculate the area
double calculateArea() const override {
// Using Heron's formula to calculate the area of a triangle
double s = (side1 + side2 + side3) / 2; // Calculate the semi-perimeter of the triangle
return sqrt(s * (s - side1) * (s - side2) * (s - side3)); // Calculate the area using Heron's formula
}
// Override the virtual member function to calculate the perimeter
double calculatePerimeter() const override {
return side1 + side2 + side3; // Calculate the perimeter of the triangle using its sides
}
};
int main() {
// Create instances of different shapes: Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle
Circle circle(7.0); // Create a Circle object with radius 7.0
Rectangle rectangle(4.2, 8.0); // Create a Rectangle object with length 4.2 and width 8.0
Triangle triangle(4.0, 4.0, 3.2); // Create a Triangle object with sides 4.0, 4.0, and 3.2
// Calculate and display the area and perimeter of each shape
std::cout << "Circle: " << std::endl;
std::cout << "Area: " << circle.calculateArea() << std::endl; // Calculate and output the area of the circle
std::cout << "Perimeter: " << circle.calculatePerimeter() << std::endl; // Calculate and output the perimeter of the circle
std::cout << "\nRectangle: " << std::endl;
std::cout << "Area: " << rectangle.calculateArea() << std::endl; // Calculate and output the area of the rectangle
std::cout << "Perimeter: " << rectangle.calculatePerimeter() << std::endl; // Calculate and output the perimeter of the rectangle
std::cout << "\nTriangle: " << std::endl;
std::cout << "Area: " << triangle.calculateArea() << std::endl; // Calculate and output the area of the triangle
std::cout << "Perimeter: " << triangle.calculatePerimeter() << std::endl; // Calculate and output the perimeter of the triangle
return 0; // Return 0 to indicate successful completion
}
Sample Output:
Circle: Area: 153.938 Perimeter: 43.9823 Rectangle: Area: 33.6 Perimeter: 24.4 Triangle: Area: 5.8657 Perimeter: 11.2
Explanation:
In the above exercise,
- The Shape class is defined by two pure virtual member functions: calculateArea() and calculatePerimeter(). These functions are meant to be overridden by derived classes.
- The Circle class is derived from Shape and overrides the virtual functions to calculate the area and perimeter of a circle. This is based on the given radius.
- The Rectangle class is derived from Shape and overrides the virtual functions to calculate the area and perimeter of a rectangle. This is based on the given length and width.
- The Triangle class is derived from Shape and overrides the virtual functions to calculate the area and perimeter of a triangle. This is based on the given side lengths.
- In the main function, instances of Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle are created.
- The calculateArea() and calculatePerimeter() member functions are called on each shape object to calculate and display the respective area and perimeter.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to implement an abstract Shape class with virtual functions for area and perimeter, and derive Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle classes that override these functions.
- Write a C++ program to create a Shape class with pure virtual methods, then implement derived classes for Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle, and display their computed properties.
- Write a C++ program that demonstrates polymorphism by storing pointers to different Shape-derived objects in a vector and iterating to call area and perimeter functions.
- Write a C++ program to design a Shape class with virtual functions and derive several shapes, then overload
Go to:
PREV : Student Class with Grade Calculation.
NEXT : C++ File Handling Exercises Home.
CPP Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
