C++ Dynamic Memory Allocation: Linked list operations with memory allocation
8. Dynamically Allocate Memory for a Linked List and Perform Basic Operations
Write a C++ program to dynamically allocate memory for a linked list and perform basic operations like insert and delete node(s).
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <iostream> // Including the Input/Output Stream Library
// Definition of a structure named Node for a linked list
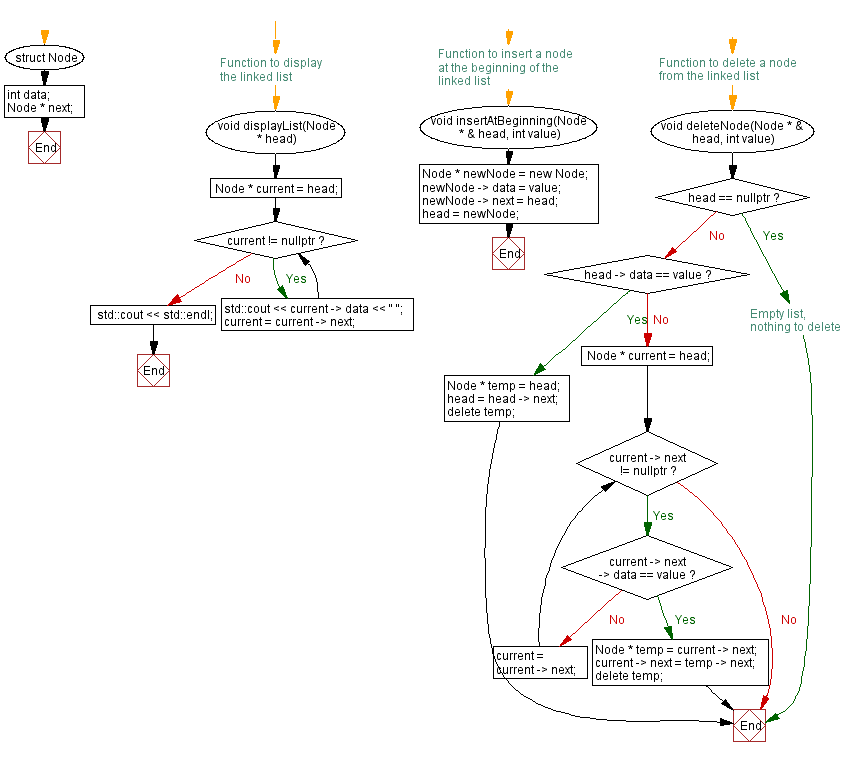
struct Node {
int data; // Data stored in the node
Node * next; // Pointer to the next node
};
// Function to display the linked list
void displayList(Node * head) {
Node * current = head; // Initialize a pointer 'current' to traverse the list
while (current != nullptr) { // Loop through the list until the end
std::cout << current->data << " "; // Output the data in the current node
current = current->next; // Move to the next node
}
std::cout << std::endl; // Output a new line after printing the list
}
// Function to insert a node at the beginning of the linked list
void insertAtBeginning(Node * & head, int value) {
Node * newNode = new Node; // Create a new node
newNode->data = value; // Set the data of the new node
newNode->next = head; // Point the new node to the current head
head = newNode; // Update the head to the new node
}
// Function to delete a node from the linked list
void deleteNode(Node * & head, int value) {
if (head == nullptr) {
return; // Empty list, nothing to delete
}
if (head->data == value) {
Node * temp = head; // Store the current head in a temporary node
head = head->next; // Move the head to the next node
delete temp; // Delete the original head node
return;
}
Node * current = head; // Initialize a pointer 'current' to traverse the list
while (current->next != nullptr) { // Traverse until the end of the list
if (current->next->data == value) { // Check if the next node has the value to be deleted
Node * temp = current->next; // Store the next node in a temporary node
current->next = temp->next; // Update the pointers to skip the node to be deleted
delete temp; // Delete the node with the value
return;
}
current = current->next; // Move to the next node
}
}
// Function to deallocate the memory of the linked list
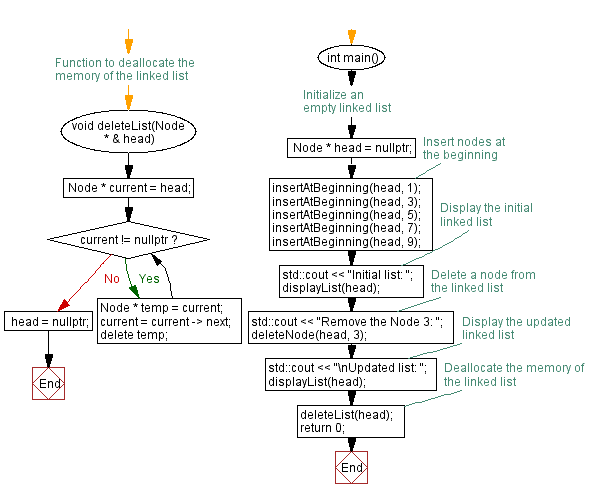
void deleteList(Node * & head) {
Node * current = head; // Initialize a pointer 'current' to traverse the list
while (current != nullptr) { // Loop until the end of the list
Node * temp = current; // Store the current node in a temporary node
current = current->next; // Move to the next node
delete temp; // Delete the stored node
}
head = nullptr; // Set the head to null after deleting all nodes
}
int main() {
Node * head = nullptr; // Initialize an empty linked list
// Insert nodes at the beginning
insertAtBeginning(head, 1);
insertAtBeginning(head, 3);
insertAtBeginning(head, 5);
insertAtBeginning(head, 7);
insertAtBeginning(head, 9);
// Display the initial linked list
std::cout << "Initial list: ";
displayList(head);
// Delete a node from the linked list
std::cout << "Remove the Node 3: ";
deleteNode(head, 3);
// Display the updated linked list
std::cout << "\nUpdated list: ";
displayList(head);
// Deallocate the memory of the linked list
deleteList(head);
return 0; // Returning 0 to indicate successful execution of the program
}
Sample Output:
Initial list: 9 7 5 3 1 Remove the Node 3: Updated list: 9 7 5 1
Explanation:
In the above exercise, we define a Node structure to represent each node of the linked list. Each node contains a data field and a pointer to the next node.
There are several functions to perform basic operations on the linked list:
- displayList() function displays the elements of the linked list.
- insertAtBeginning() function inserts a new node at the beginning of the linked list.
- deleteNode() function deletes a node with a specified value from the linked list.
- deleteList() function deallocates the memory of the entire linked list.
Inside the main() function, we first initialize an empty linked list by setting the head to nullptr.
- Next we insert nodes at the beginning of the linked list using insertAtBeginning() and delete a specific node using deleteNode() function.
- After each operation, we display the linked list using displayList().
- Finally, deallocate the linked list memory using deleteList() to free the memory occupied by the linked list.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to dynamically create a singly linked list, then implement functions to insert nodes at the beginning and end.
- Write a C++ program to build a linked list dynamically, and implement deletion of a node by its value, printing the list before and after deletion.
- Write a C++ program that uses dynamic memory allocation to create a linked list and then reverses the list using pointer manipulation.
- Write a C++ program to implement a linked list with dynamic node creation and a function to search for an element, returning its position.
Go to:
PREV : Dynamically Allocate Memory for a Structure and Input Its Members.
NEXT : Dynamically Allocate Memory for a Stack and Implement Push/Pop.
CPP Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
