C++ Dynamic Memory Allocation: Creating Objects with new Operator
5. Dynamically Create an Object of a Class Using New
Write a C++ program to dynamically create an object of a class using the new operator.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <iostream> // Including the Input/Output Stream Library
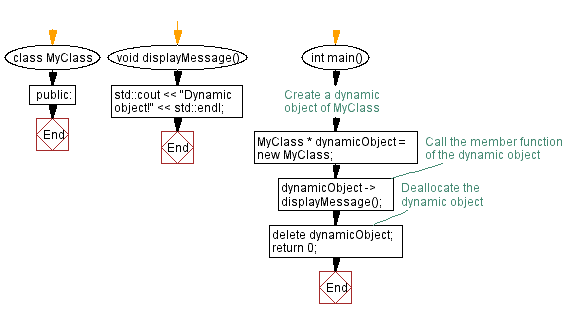
class MyClass { // Declaration of a class named MyClass
public:
void displayMessage() { // Public member function within the class MyClass
std::cout << "Dynamic object!" << std::endl; // Outputting a message
}
};
int main() {
// Create a dynamic object of MyClass
MyClass * dynamicObject = new MyClass; // Dynamically allocating memory for an object of type MyClass
// Call the member function of the dynamic object
dynamicObject -> displayMessage(); // Accessing the member function of the dynamically created object using the pointer to the object
// Deallocate the dynamic object
delete dynamicObject; // Deallocating the memory occupied by the dynamic object
return 0; // Returning 0 to indicate successful execution of the program
}
Sample Output:
Dynamic object!
Explanation:
In the above exercise,
- At first we define a class called MyClass with a member function displayMessage() that simply outputs a message.
- Inside the main() function, we use the new operator to dynamically create an object of MyClass and assign its address to a pointer called dynamicObject. This dynamically created object resides in the heap memory.
- Then use the arrow operator (->) to call the displayMessage() member function of the dynamic object.
- Finally, deallocate the dynamically created object using the delete operator to free the memory occupied by the object.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to define a simple class with member variables and methods, then dynamically create an object and call its methods.
- Write a C++ program that dynamically allocates an object of a class representing a complex number and prints its real and imaginary parts.
- Write a C++ program to create a class for a student record, dynamically allocate an object, assign values using member functions, and display the record.
- Write a C++ program that uses the new operator to dynamically allocate an object of a class with a constructor and destructor, then prints a message upon creation and deletion.
Go to:
PREV : Dynamically Allocate Memory for a Character and a String with User Input.
NEXT : Dynamically Create an Array of Objects Using New.
CPP Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
