C++ Dynamic Memory Allocation: Initializing 2D arrays of floats and strings
3. Dynamically Allocate Two Two-Dimensional Arrays of Floating Values and Strings
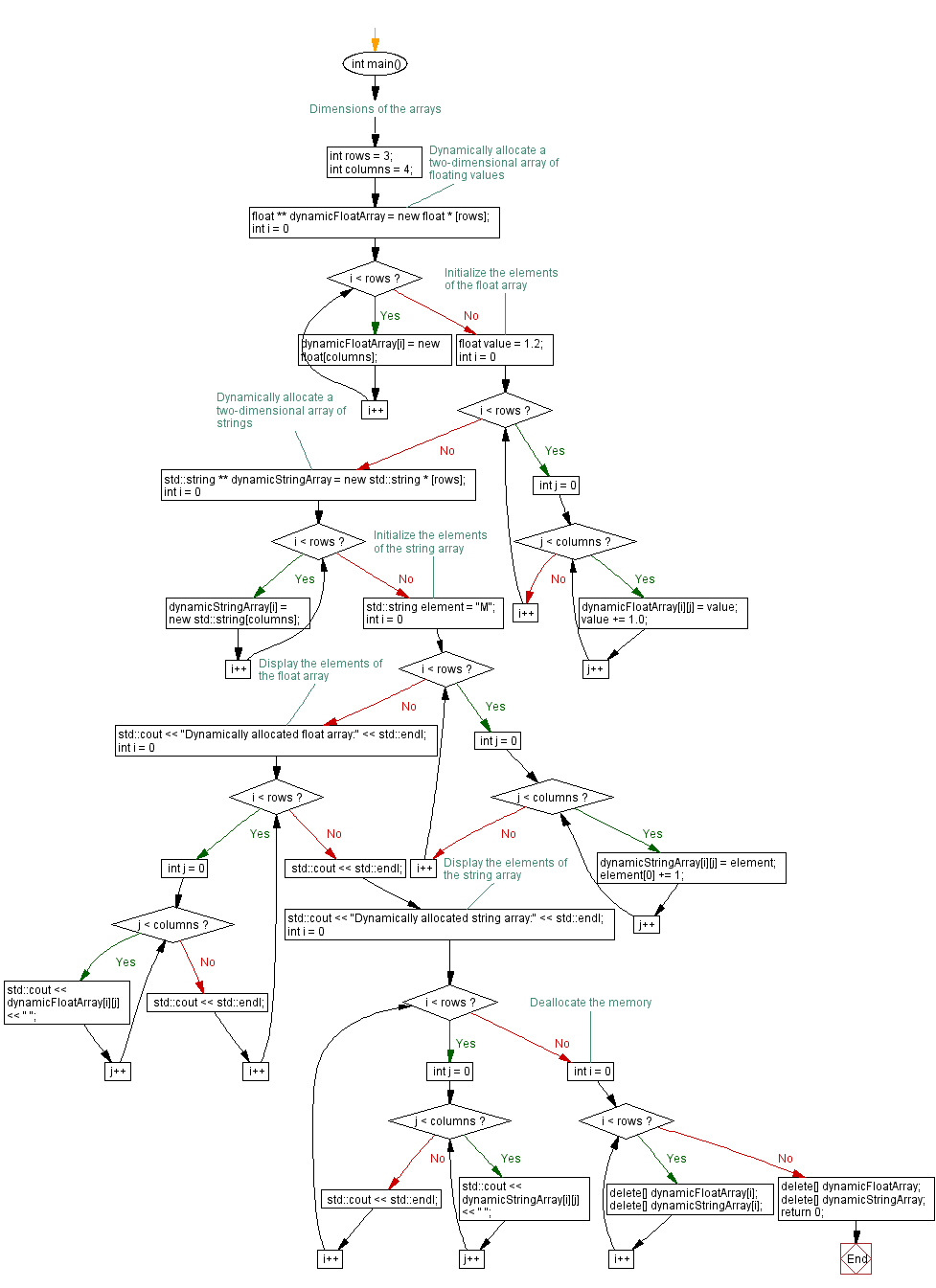
Write a C++ program to dynamically allocate two two-dimensional arrays of floating values and strings. Initialize its elements.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <iostream> // Including the Input/Output Stream Library
#include <string> // Including the String Library
int main() {
// Dimensions of the arrays
int rows = 3; // Number of rows in the arrays
int columns = 4; // Number of columns in the arrays
// Dynamically allocate a two-dimensional array of floating values
float ** dynamicFloatArray = new float * [rows]; // Allocating memory for the array of float pointers (rows)
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
dynamicFloatArray[i] = new float[columns]; // Allocating memory for each row (array of floats)
}
// Initialize the elements of the float array
float value = 1.2; // Initial value for the array
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
dynamicFloatArray[i][j] = value; // Assigning values to each element of the float array
value += 1.0; // Incrementing the value for the next element
}
}
// Dynamically allocate a two-dimensional array of strings
std::string ** dynamicStringArray = new std::string * [rows]; // Allocating memory for the array of string pointers (rows)
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
dynamicStringArray[i] = new std::string[columns]; // Allocating memory for each row (array of strings)
}
// Initialize the elements of the string array
std::string element = "M"; // Initial string element
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
dynamicStringArray[i][j] = element; // Assigning values to each element of the string array
element[0] += 1; // Modifying the string element for the next element
}
}
// Display the elements of the float array
std::cout << "Dynamically allocated float array:" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
std::cout << dynamicFloatArray[i][j] << " "; // Outputting each element of the dynamically allocated float array
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// Display the elements of the string array
std::cout << "Dynamically allocated string array:" << std::endl;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
std::cout << dynamicStringArray[i][j] << " "; // Outputting each element of the dynamically allocated string array
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// Deallocate the memory allocated for both arrays
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
delete[] dynamicFloatArray[i];
delete[] dynamicStringArray[i];
}
delete[] dynamicFloatArray;
delete[] dynamicStringArray;
return 0; // Returning 0 to indicate successful execution of the program
}
Sample Output:
Dynamically allocated float array: 1.2 2.2 3.2 4.2 5.2 6.2 7.2 8.2 9.2 10.2 11.2 12.2 Dynamically allocated string array: M N O P Q R S T U V W X
Explanation:
In the above exercise,
- First declare the two-dimensional array dimensions: rows and columns.
- Dynamically allocate memory for the float array using a nested loop.
- Create an array of pointers, dynamicFloatArray, where each pointer points to an array of floats. Each float element is initialized with a value incremented by 1.0 in each iteration.
- Similarly, dynamically allocate memory for the string array using another nested loop.
- Create an array of pointers, dynamicStringArray, where each pointer points to an array of strings.
- Each string element is initialized with a character and incremented by one letter in each iteration.
- Finally display the elements of both arrays using nested loops and std::cout. The float array elements are displayed in a matrix format, while the string array elements are shown as strings separated by spaces.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to dynamically allocate a 2D array of floats with dimensions m x n (user input) and initialize it with random float numbers, then print the matrix.
- Write a C++ program to dynamically create two 2D arrays: one for floating-point numbers and one for strings, then fill them with sample data and display both matrices.
- Write a C++ program to allocate two 2D arrays of floats and strings of size m x n, where the string array is initialized with formatted representations of the corresponding float values.
- Write a C++ program that reads dimensions m and n, dynamically allocates two 2D arrays (one float, one string), assigns values from user input to both, and then prints the arrays side by side.
Go to:
PREV : Dynamically Allocate an Array of Integers and Strings.
NEXT : Dynamically Allocate Memory for a Character and a String with User Input.
CPP Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
